
Import Declarations � 39 Import declarations help the compiler locate a class that’s used in the program � � import java.util.Scanner; // program uses class Scanner � Import all missing classes in Eclipse � Windows — Ctrl Shift o � Mac — Command Shift o
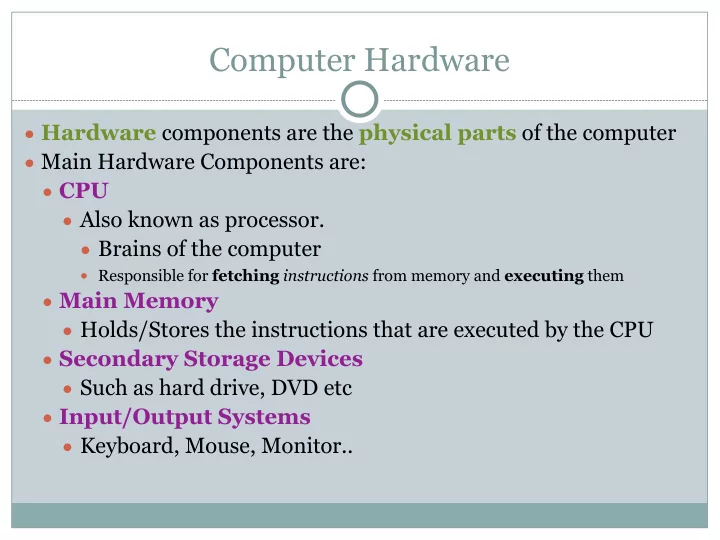
Primitive Data Types ● byte ● number 1 byte ● short Note: ● number 2 bytes Range of variables is machine dependant ● int and depends on the machine on which the ○ Decimal number 1, 10, etc program is running. ● long ○ Double precision int ● float ○ Floating point number e.g. 0.3434343 ● double ○ Double precision floats ● char ○ Single char ‘a’, ‘Z’, ‘3’, etc ● boolean ○ true ○ false
Variable ● Each variable has a memory address ● A variable has a name ● A value can be assigned to it ● Naming convention: myVariable ● Variable names cannot start with a number
Type Cast Operator ● Converts one type of data to another ● For decimal numbers, the default is double � Casting is required with floats ○ float f = (float)87.54; ○ float f = 87.54f;
Scanner : Reading input from console � 43 import java.util.Scanner; public class MainClass { public static void main(String[] args) { // create a Scanner to obtain input from the command window Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in ); int num1; int num2; int sum; System.out.print( "Enter first integer: " ); // prompt num1 = input.nextInt(); // read first number from user System.out.print( "Enter second integer: " ); // prompt num2 = input.nextInt(); // read second number from user sum = num1 + num2; // System.out.printf( "Sum is %d\n", sum ); // display sum } }
Scanner : Reading input from console � 44 import java.util.Scanner; public class MainClass { public static void main(String[] args) { // create a Scanner to obtain input from the command window Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in ); float num1; float num2; float sum; System.out.print( "Enter first integer: " ); // prompt num1 = input.nextFloat(); // read first number from user System.out.print( "Enter second integer: " ); // prompt num2 = input.nextFloat(); // read second number from user sum = num1 + num2; // System.out.printf( "Sum is %f \n", sum ); // display sum } }
Scanner : Reading input from console � 45 1. Create a Scanner object Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 2. Use the methods to obtain values: ● nextByte() ● nextShort() ● nextInt() ● nextLong() ● nextFloat() ● nextDouble() ● nextBoolean()
boolean � 46 boolean hungry = true; if(hungry) { System.out.println("Let's have some food!"); } ● Note � if(hungry) ○ is equivalent to • if(hungry == true)
String � 47 ● The String class represents a sequence of characters ● Can include letters, number and special characters ● Stored in double “ quotes ● Example ● String s = “Mike”; ● String s2 = new String(“Hello! How are you?”); ● String s3 = “Mike is 16 years old.”; ● String Methods ● http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/String.html
String � 48 ● Can concat strings and primitives: int age = 10; String s = "I am " + age + " years old" ; System.out.println(s);
Strings � 49 ● Declare and initialise your string ● Print your string ● Print first character of your string ● Print the first 3 characters of your string ● Add another string to your string (concatenation) ● Replace word in your string ● Compare strings ● Get string length ● Convert case
Declaring Variables of same type � 50 ● Variables of the same type can be declared on the same line: ● int x,y,z ● String firstname, lastname; ● int myAge, mysize, numshoes= 28; ● String firstName= “Laura”, lastName = “Thorpe”;
Operators � 51 ● Arithmetic ● Assignment ● Comparison ● Logical
Arithmetic Operators ● Addition ○ b + c ● Subtraction ○ b – c ● Multiplication ○ b * c ● Division ○ b / c ● Modulus ○ b % c ○ Returns the remainder of a divided by b
Arithmetic Operators � 53
Arithmetic Operators: Order of Evaluation � 54 ● Order of evaluation: ● * ● / ● % ● + ● - ● =
Increment and Decrement Operators ● a = a + 1 ○ is equivalent to � a++ � is equivalent to a+=1; ● a = a -1 ○ is equivalent to � a— � is equivalent to a-=1; ● What is the difference between the following two? ○ a++ ○ ++a
Basic Assignment Operator ● Examples ○ c = a + b ○ d = a - b ○ e = a * b ○ f = a / b ○ g = f
The Comparison Operators ● Returns a Boolean True = 1 ○ False = 0 ○ ● if (a == b) if a is equal to b ○ ● if (a != b) if a is not equal to b ○ ● if (a < b) if a is less than b ○ ● if (a > b) if a is greater than b ○ ● if (a <= b) if a is less than or equal to b ○ ● if (a >= b) if a is greater than or equal to b ○
The Comparison Operators
The Compound Assignment Operators ● a += b ○ a = a + b ● a -= b ○ a = a -b ● a *= b ○ a = a * b ● a /= b ○ a = a / b ● a %= b ○ a = a % b
The Boolean Logical Operators ● Take Boolean values as operands ● Boolean values are 0 or 1 ○ 0 = false ○ 1 = true ● Logical Negation (NOT) ○ ! ● Logical (AND) ○ && ● Logical (OR) ○ ||
Precedence � 61
The Ternary Operator ● [condition] ? [true expression] : [false expression] ● Condition must return true or false ● If condition returns true ○ result of the first expression is returned ● If condition returns false ○ result of the second expression is returned
Programming Decision: if if (expression1 is true) { Execute statement1 }
if (Single-Selection Statement) � 64
if (Double-Selection Statement) � 65 ● Can also have ● if - else if - else
if - else if - else if (expression 1 is true) { Execute statement 1 } else if (expression2 is true) { Execute statement 2 } else { Execute statement 3 } ● Exercise: set a variable to 100 ● Prompt user to guess number ● if user enters 100 print “correct” ● if between 90 and 110 print “in range” and higher or lower depending on guess ● if out of range print higher or lower
Tip ● x if (number % 2 == 0) Equivalent boolean even even = true; = number % 2 == 0; else even = false; (b) (a) if (even == true) Equivalent if (even) System.out.println( System.out.println( "It is even."); "It is even."); (b) (a)
the ternary operator ● [condition] ? [true expression] : [false expression] ● Condition must return true or false ● If condition returns true ○ result of the first expression is returned ● If condition returns false ○ result of the second expression is returned
switch switch (expression) { case 1: Statement 1 break; case 2: Statement 2 break; case n: Statement n break; default: Default Statement } ● A switch works with byte , short , char , and int primitive data types. ● It also works with String
Switch Example � 70 String sName = "Nina"; String favouriteColour; switch (sName.toLowerCase()) { case "rose": favouriteColour = "Yellow"; break; case "jack": favouriteColour = "Green"; break; case "sebastien": favouriteColour = "Blue"; break; case "nina": favouriteColour = "Orange"; break; default: favouriteColour = "Unknown"; break; } System.out.println(favouriteColour);
Several case labels � 71 char c = 'N'; switch(c) { case 'n': case 'N': System.out.println("NO"); break; case 'y': case 'Y': System.out.println("YES"); break; }
Looping
for statement ● for statement ○ for (initialisation; condition; expression) { Statement(s) } for(int i=0; i<5; i++) { System.out.println(i); }
Guess Age int myAge = 15; Scanner input = new Scanner( System.in ); int guess; do { System.out.print( "Guess my age: " ); guess = input.nextInt(); if(guess < 10) { System.out.println("Out of range - try higher"); } if(guess > 20) { System.out.println("Out of range - try lower"); } if(guess < 20 && guess > 10) { if(guess == 15) { System.out.println("Well done! 15 is correct."); } if(guess < 15) { System.out.println("Close - try higher"); } if(guess > 15) { System.out.println("Close - try lower"); } } }while(guess != myAge);
Times Table Method � 75 public static void times(int n) { for(int i=0; i<11; i++) { System.out.printf("%d times %d is %d \n", i, n, n*i ); } }
Loop ● Repeating a loop n times Exercise: Modify the previous example to repeat 10 times
infinite loop ● infinite loop for ( ; ; ) { Statement(s) }
while statement ● while statement white (expression) { Statement(s) } int a = 1; while(a<10) { System.out.println(a); a+=3; }
do while statement ● do while statement do { Statement(s) } while (expression); ● do while loops are used when the statement has to be executed ● At least once int a = 100; do{ System.out.println(a); a-=10; }while(a>20);
break statement ● break statement ○ Exit from the loop entirely ● Syntax ○ break; ● Output ○ a + b = 4 ○ a + b = 5 ○ a + b = 6 ○ a + b = 7 ○ a + b = 8 ○ a + b = 9
continue statement ● continue statement ○ Exit current loop � Do not execute the code after the continue statement ○ for current loop ○ Do not exit the loop entirely ○ Continue execution of loop ● Syntax ○ continue; ● Output ○ a + b = 4 ○ a + b = 5
break and continue example � 82 for(int i=0; i<20; i++) { if(i == 15) break; // break out of for loop if(i % 2 != 0) continue; // go to next iteration System.out.println(i); }
Methods
Defining and Invoking Methods Define a method Invoke a method ● return value method formal type modifier name parameters int z = max(x, y); method public static int max( int num1, int num2) { header actual parameters int result; (arguments) method parameter list body if (num1 > num2) result = num1; else method result = num2; signature return result; return value }
The Anatomy of a Method � 85 ● modifier ● It defines the access type of the method and it is optional to use. ● returnType ● Method may return a value. ● methodName ● This is the method name. ● Parameter List ● The list of parameters, it is the type, order, and number of parameters of a method. ● These are optional, method may contain zero parameters. ● method body ● The method body defines what the method does with statements.
Method Visibility � 86 ● Public ● In all classes and packages ● Private ● Only in current class ● Protected ● In current package ● In subclasses
Access Modifiers at a glance � 87
private � 88 ● Methods, variables, and constructors that are declared private can only be accessed within the declared class itself. ● Private access modifier is the most restrictive access level. Class and interfaces cannot be private. ● Variables that are declared private can be accessed outside the class, if public getter methods are present in the class. ● Using the private modifier is the main way that an object encapsulates itself and hides data from the outside world.
public � 89 ● A class, method, constructor, interface, etc. declared public can be accessed from any other class. ● Therefore, fields, methods, blocks declared inside a public class can be accessed from any class belonging to the Java Universe. ● However, if the public class we are trying to access is in a different package, then the public class still needs to be imported. Because of class inheritance, all public methods and variables of a class are inherited by its subclasses.
protected � 90 ● Variables, methods, and constructors, which are declared protected in a superclass can be accessed only by the subclasses in other package or any class within the package of the protected members' class. ● The protected access modifier cannot be applied to class and interfaces. Methods, fields can be declared protected, however methods and fields in a interface cannot be declared protected. ● Protected access gives the subclass a chance to use the helper method or variable, while preventing a non-related class from trying to use it.
Method Implementation & Call � 91 Method Implementation public static int funcName(int a, int b) { // body } Method Call funcName(a, b); int min= funcName(a, b);
Minimum Number � 92 ● Method to find minimum number public static int minFunction(int n1, int n2) { int min; if (n1 > n2) min = n2; else min = n1; return min; }
Benefits of Methods � 93 • Write a method once and reuse it anywhere • Information hiding • Hide the implementation from the user • Reduce complexity
Built-in versus User-defined Methods ● We have built-in methods and user defined methods ● Built-in Methods � Come with Java and are ready to be used ● User defined Methods � Defined by the programmer
Example: Built-in method call � 95 int a = 10; int b = 11; int min; min = Math.min(a,b); System.out.println(min);
Built-in Method Examples ● print(); ● println(); ● Exercise 1: ● List all the built-in Math methods ● Exercise 2: ● Write a method that finds the distance between 2 points
More on Methods � 97 ● Method Definition/Implementation ● Method Call ● Can store the result of the method call in a variable
Method Example � 98 //Within main method MainClass mc = new MainClass(); mc.showWelcomeMessage("narges", 80); //Method Implementation public void showWelcomeMessage(String welcomeName, int grade) { System.out.printf( "Welcome %s your grade is %d ",welcomeName, grade ); }
User Defined Methods Exercise � 99 ● Exercise: ● Write a method to convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius ●
Class & Method Declarations � 100 public class MainClass { public static void main(String[] args) { One one = new One(); one.showMessage(); } } public class One { public void showMessage() { System.out.println("Welcome to ClassOne"); } }
Recommend
More recommend