Cohesive Constraints in a Beam Search Phrase-based Decoder Nguyen - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Cohesive Constraints in a Beam Search Phrase-based Decoder Nguyen Bach, Stephan Vogel Colin Cherry Carnegie Mellon University Microsoft Research 1 Overview Apply cohesive constraints during decoding process to consider the source
Cohesive Constraints in a Beam Search Phrase-based Decoder Nguyen Bach, Stephan Vogel Colin Cherry Carnegie Mellon University Microsoft Research 1
Overview • Apply cohesive constraints during decoding process to consider the source dependency structures • Introduce extensions of the cohesive constraints. • Analyze the impact of cohesive constraints across language pairs with different reordering models • Applied to English-Spanish , English-Iraqi and Chinese- English translation tasks – Significant improvements on English-Spanish – Stable improvements on other pairs 2
Outline • Cohesive Decoding Approach • Experiments • Conclusions & Future Work 3
What is a cohesive decoding? Source 2 begins dependency tree election tomorrow 1 the presidential states 3 of the united English->French Source: the presidential election of the united states begins tomorrow la élection présidentielle commence demain des États Unis 4
What is a cohesive decoding? Source begins dependency 3 tree election tomorrow 1 the presidential states 2 of the united English->French Source: the presidential election of the united states begins tomorrow la élection présidentielle des États Unis commence demain 5
begins 2 election tomorrow 1 the presidential states 3 Phrase-based of the united decoder the presidential election of the united states begins tomorrow la élection présidentielle commence demain des États Unis begins 3 election tomorrow 1 the presidential states 2 Cohesive of the united decoding the presidential election of the united states begins tomorrow la élection présidentielle des États Unis commence demain 6
Interruption Checks (Cherry, 2008) begins election tomorrow presidential the states of the united 1 3 2 4 la élection présidentielle commence demain des États Unis 7
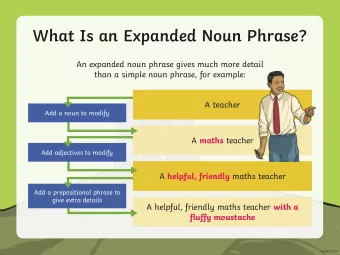
Two Questions • How to determine the largest subtree that needs to be completed before the translation process can move elsewhere in the tree? – Interruption Check: use left and right most tokens of the previous translated source phrase and climb up the tree • If a violation happens, how to constrain the decoder to penalize cohesion violated translation hypothesis? – Interruption Check : Binary event 8
Exhaustive Interruption Check • Interruption Check only penalizes the cohesion violation 1 time • Should penalties persist as long as violations remain unresolved? • Exhaustive Interruption Check keeps punishing a cohesion violation until it is fixed. 9
Exhaustive Interruption Check Exhaustive Interruption Interruption Check: NO Check: YES begins election tomorrow 5 presidential the states of the united 1 3 2 4 la élection présidentielle commence demain des États Unis 10
Cohesion Violation Penalties • Interruption Check and Exhaustive Interruption Check: binary event • Are some violations worse than others? • Penalize a cohesion violation by the number of untranslated words under the largest subtree – Interruption Check -> Interruption Count – Exhaustive Interruption Check -> Exhaustive Interruption Count 11
Rich Interruption Constraints begins /VBZ begins OBJ SBJ election /NN tomorrow /NN election tomorrow NMOD NMOD NMOD presidential /JJ the /DT states /NNS presidential the states PMOD NMOD NMOD the /DT of /IN united /VBN of the united • Penalize a cohesion violation by 4 constraints – Binary event: violation/not violate – Interruption Count: untranslated word count – Verb Count: untranslated verb count – Noun Count: untranslated noun count 12
Comparison How to penalize a cohesion violation? Number of Linguistics Binary untranslated features words Rich The previous Interruption Interruption How to Interruption phrase Check Count detect the Constraints largest Exhaustive Exhaustive subtree T(n) ? All previous Interruption Interruption N/A phrases Check Count 13
Outline • Cohesion Decoding Approach • Experiments • Conclusions & Future Work 14
English-Spanish; English-Iraqi English-Iraqi English-Spanish 33.4 25 33.2 24.8 33 24.6 32.8 24.4 32.6 24.2 BLEU BLEU 32.4 24 32.2 23.8 32 23.6 31.8 23.4 31.6 23.2 31.4 23 Europarl nctest2007 TransTac June08 Cohesive constraints obtained improvements over the standard phrase-based decoder. 15
How does the performance of the dependency parser affect cohesive constraints? 16
The Role of Dependency Parser on English-Spanish • Train 2 MALT dependency 33.2 parser models: M1 with 10% 33 M1 32.8 M2 of treebank and M2 with all 32.6 32.4 treebank. BLEU 32.2 • Performance on CoNLL-07 32 31.8 dependency test set 31.6 31.4 – M1 : 19.41% 31.2 – M2 : 86.21% • Apply to MT – M2 is better than M1 17
• Are the improvements subsumed by a strong reordering model and system scale? • What if we translate from X->English? 18
GALE Chinese-English GALE Dev07-NW GALE Dev07-WB 27.2 25.5 25.4 27 25.3 26.8 25.2 26.6 BLEU BLEU 25.1 26.4 25 26.2 24.9 26 24.8 25.8 24.7 25.6 24.6 Cohesive constraints obtained improvements even with large scale system and strong reordering models 19
Outline • Cohesion Decoding Approach • Experiments • Conclusions & Future Work 20
Conclusions & Future Work • Conclusions – Cohesive constraints are helpful – The effectiveness was shown when using with a strong reordering model – Obtained improvements with 3 language pairs and also covered a wide range of training corpus sizes, ranging from 500K up to 11M sentence pairs • Future work – A source side dependency reordering model: Learning reordering events of the phrases based on source subtree movements – A hierarchical source side dependency reordering model: extend Galley&Manning (2008). 21
Questions 22
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.