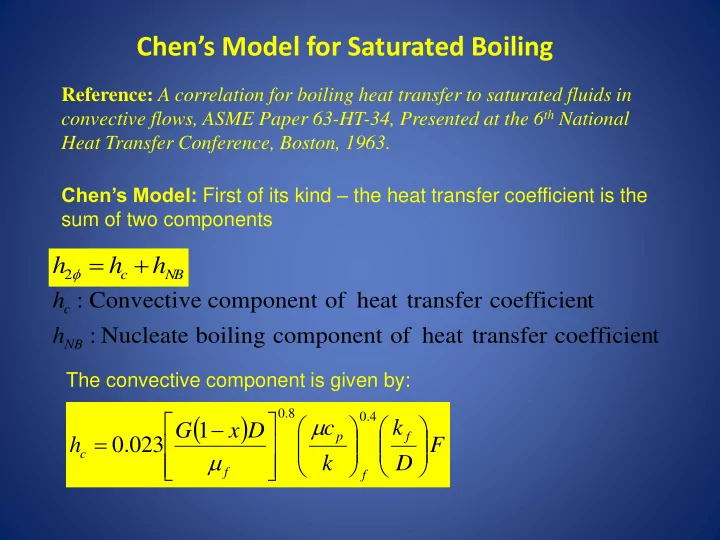

Chen’s Model for Saturated Boiling Reference: A correlation for boiling heat transfer to saturated fluids in convective flows, ASME Paper 63-HT-34, Presented at the 6 th National Heat Transfer Conference, Boston, 1963 . Chen’s Model: First of its kind – the heat transfer coefficient is the sum of two components h h h 2 c NB h : Convective component of heat transfer coefficien t c h : Nucleate boiling component of heat transfer coefficien t NB The convective component is given by: 0 . 8 0 . 4 c k G 1 x D p f h 0 . 023 F c k D f f
• Modified form of the Dittus-Boelter Equation, • The enhancement factor F accounts for the enhanced flow and turbulence effects due to the presence of vapor. 0 . 8 0 . 8 Re Re 2 2 F 0 . 8 Re G 1 x D f f Using the above in the expression for the convective heat transfer coefficient, gives: k 0 . 8 0 . 4 f 0 . 023 Re Pr h c 2 f D Pr ~ Pr and k f ~ k Chen argued that f 2 2
k 0 . 8 0 . 4 2 Hence , h c 0 . 023 Re Pr 2 2 D Since F is a flow parameter, it can be uniquely expressed as the function of the Martinelli parameter, thus: 1 F 1 for 0 . 1 X tt 0 . 736 1 1 F 2 . 35 0 . 213 for 0 . 1 X X tt tt 0 . 5 0 . 1 0 . 9 1 x g f X tt x f g • As quality increases, X decreases, therefore F increases, implying that the contribution due to evaporation increases.
The Forster - Zuber Correlation forms the basis of the heat transfer coefficient for nucleate boiling 0 . 79 0 . 49 0 . 45 k c 0 . 24 0 . 75 f f p , f h 0 . 00122 T p NB e e 0 . 5 0 . 29 0 . 24 0 . 24 h f fg g where: T T T , p p T p T e e sat e e sat : the mean superheat of the fluid in which the bubble T T T e e sat T T T grows, lower than the wall superheat, w w sat Suppression factor, S , is defined as the ratio of the mean superheat to the wall superheat. 0 . 99 T e S T sat
Using Clausius-Clapeyron Equation 0 . 24 0 . 75 T p e e S T p sat sat Therefore, using S in the expression for h NB , we get 0 . 79 0 . 49 0 . 45 k c 0 . 24 0 . 75 f f p , f h 0 . 00122 ( S ) T p NB sat sat 0 . 5 0 . 29 0 . 24 0 . 24 h f fg g • S decreases from 1 to 0 as the quality increases, approaches unity at low flows and zero at high flows. • Thus, contribution of nucleate boiling goes down as the quality increases, since evaporation takes over. Plot of S as a function of Two-Phase Reynolds number
S f Local Two Phase Reynolds Number 1 S 6 1 . 17 1 2 . 53 10 Re 2 1 . 25 Re Re F 2 f Steps involved in calculation of the heat transfer coefficient for known values of heat flux, mass velocity and quality. a. Calculate (1/X tt ). b. Calculate F , the enhancement factor from the graph or given equation. c. Calculate the convective component of the heat transfer coefficient. d. Calculate two-phase Reynolds number based on single-phase Reynolds number and value of F . e. Evaluate the suppression factor, S from the graph or equation. f. Calculate the nucleate boiling component of the heat transfer coefficient. g. Calculate as the sum of the convective component and the nucleate h 2 boiling components.
Chen Correlation - Example Chen's Correlation 5000 4500 Heat Transfer Coeff. (W/m 2 -K) 4000 3500 3000 Convective HTC 2500 Nucleate Boiling HTC 2000 Two Phase HTC 1500 1000 500 0 0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 Quality (x) G L D DeltaT Delta P m m deg C Pa kg/m2-s 400 3 0.0254 10 1.985E+5
Recommend
More recommend