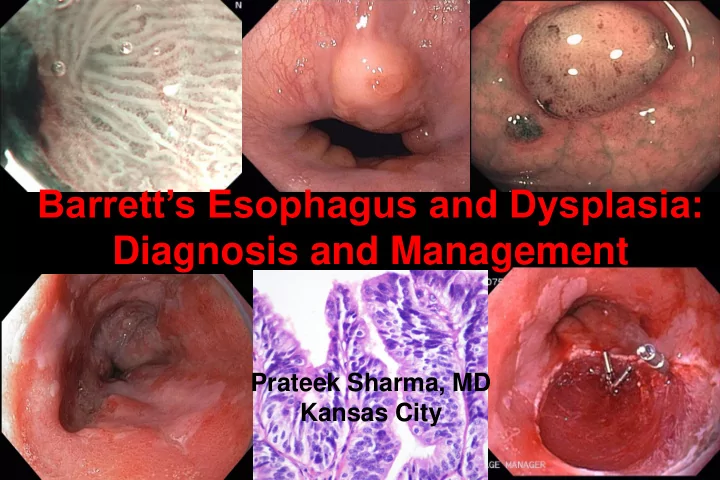

Barrett’s Esophagus and Dysplasia: Diagnosis and Management Prateek Sharma, MD Kansas City
Barrett’s associated adenocarcinoma squamous Barrett’s
Rising Incidence of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma 35 30 25 Adenocarcinoma Rate per 20 Squamous Cell 1,000,000 Carcinoma 15 Not otherwise 10 specified 5 0 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 Pohl H et al, J Natl Cancer Inst 2005
Barrett’s Esophagus Columnar lined esophagus Intestinal Metaplasia
Endoscopic recognition of the columnar lined esophagus
Terminology Issues Long Barrett’s Short Barrett’s Ultra short Barrett’s Microscopic Barrett’s Invisible Barrett’s
Prague C & M Criteria • Based on – C ircumference and M aximum extent • Patient with 5 cm long C2 Barrett’s, distal 2 cm circumferential and proximal 3 cm in form of a tongue M5 Barrett’s: C2M5 Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D et al, Gastroenterology 2006
Progression of Barrett’s Esophagus
Dysplasia and cancer in BE patients: absolute risk % 8 7.3 Cancers 6.7 7 HGD LGD 6 5 4.3 4 3 3 2 0.9 1 0.5 0 Prevalence Incidence (n=1376) (n=618) Sharma et al, Clin Gastro Hepatol 2006
Endoscopic Therapy for Esophageal Neoplasia Early Detection Accurate Staging Effective Treatment
Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) NBI Conventional imaging
Technique of Endomicroscopy Field of view: 500x500µm Range: 0-250µm Lateral resolution: <1µm
Endoscopic Therapy for Esophageal Neoplasia Early Detection Accurate Staging Effective Treatment
EMR versus EUS • 48 patients underwent EUS • Invasion confirmed in 8 (7 at surgery) Baseline Diagnosis EMR Diagnosis HGD (n=25) 24% invasive cancer EUS: no cancer Cancers (n=15) 40% invasive cancer EUS: intra mucosal Overall accuracy of EUS for staging 85% 1 over-staged, 6 under-staged Larghi A et al, Gastrointest Endosc 2005
Endoscopic Therapy for Esophageal Neoplasia Early Detection Accurate Staging Effective Treatment
PDT: 5 Year Follow Up • 208 HGD patients • PDT (138), observation (70) Progression to cancer 35 29% 28% 30 25 Patients 20 2 years (%) 15%* 5 years 15 13%* 10 5 0 PDT Observation *p = 0.02 Overholt B et al, Gastrointest Endosc 2007
EMR for BE Cancer • 100 patients with cancer • Low risk • 1.47 resection/patient – types I, IIa, IIb, IIc • Follow up: 3 years – lesion < 2 cm; mucosal – grades: G1, G2 99% 98% 100 80 60 Patient All treated % Minor bleeding, 40 endoscopically no perforation 11% 11% 20 0 Complete local Complications Recurrent 5 yr survival remission lesions Ell C et al, Gastrointest Endosc 2007
A Randomized, Multicenter, Sham Controlled Trial of RF Ablation • 128 patients with BE and dysplasia (LGD/HGD) • Mean BE length 5 cm; 12 month follow up 100 90%* 90 81%* 77%* 80 70 60 SHAM Patients 50 RFA % 40 30 23% 19% 20 10 2% 0 LGD Eradication HGD Eradication IM Eradication (n=64) (n=63) (n=127) p<0.001 Shaheen N et al. DDW 2008
Endoscopic therapy • HGD: uni/multi-focal; flat/nodular • Intra-mucosal adenocarcinoma • Careful endoscopic grading and staging of the BE segment • Diagnostic EMR a must
Continued Challenges with Endoscopic Therapy • All intestinal metaplasia cannot be eliminated (70-80%) • Strictures, bleeding, perforation • Non uniform ablation • Persistence of sub-squamous intestinal metaplasia • Persistence of genetic abnormalities
Conclusions • Clear identification of endoscopic landmarks is the basis for an endoscopic diagnosis of BE • The reliability of using the Prague C&M criteria for the endoscopy grading of BE is excellent • Dysplasia remains the best marker for risk stratification of BE patients; higher the grade of dysplasia greater the risk • Endoscopic therapies should be limited to patients with HGD and intra-mucosal adenocarcinoma; should be performed in expert centres for optimal results
Management of Barrett’s Neoplasia Enhanced endoscopic imaging Diagnosis of dysplasia LGD HGD/early cancer Diagnostic/staging EMR • Consider enrollment in trials - Chemoprevention HGD/ early cancer LGD Invasive - Ablation cancer • Continued surveillance Therapeutic EMR Combination Surgery (If length: Prague therapy: C0, M<3) EMR + ablation (RFA, PDT, Cryo)
Recommend
More recommend