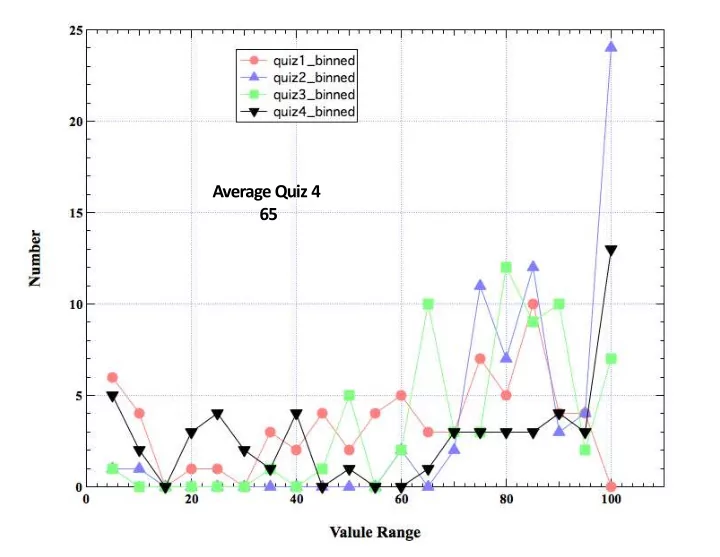

Average Quiz 4 65 1
2
3
For a single state ln(1) = 0. At absolute 0, in a perfect crystal with no defects etc. Entropy of different aspects of a system, conformational entropy, translational entropy A contribution to energy that is linear in temperature 4
5
6
Statistical Thermodynamics (Mechanics) 7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Defines “reversible” as D S = 0 Defines “impossible” as self-organizing; D S < 0 with no energy input Allows Calculation of Effeciency S=0 process has no waste energy (heat) Actually process has waste energy Ratio of Wwith waste/S=0 work = effeciency 14
15
16
17
Water 18
Water 19
Water 20
21
Rules for Carnot Cycle Isothermal (vary P) Q = - W EC = - nRT ln( V 2 / V 1 ) Isothermal Q = D U - W EC = D U + P D V = D H Isobaric W EC = - P D V Adiabatic D S = 0 Reversible Q = 0 W EC = D U = R C V ( T 2 – T 1 ) For Turbine The work done by the gas is work done by the turbine (blades moved around by the gas) plus the work done by pressures (flow work). U 2 – U 1 = -W shaft + P 1 V 1 – P 2 V 2 (adiabatic turbine) -W shaft = H 2 – H 1 Difference between shaft work and expansion/contraction work 22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
Summary of Process and General Rules D S = 0 Nozzle ( D S ) T = R ln[ V 2 / V 1 ] i.g. Isothermal D H = D ( 1/2 mv 2 ) = -R ln[ P 2 / P 1 ] ( D H ) T =0 Throttle D S = - R ln( P 2 / P 1 ) (i.g.) D S mix = -R S x i ln x i Ideal Mixing D H =1/2 mv 2 Generally D H =0 Adiabatic, Reversible D S = 0 for adiabatic reversible D S = 0 Pump D H = W S = D H ’/ h eff Isobaric (d S ) P = C p (d T ) P / T (d S /d T ) P = C p / T Turbine D S = 0 for adiabatic reversible D H = W S = D H ’ h eff Constant V olume (d S ) V = C V (d T ) V / T Carnot (Use °K) (d S /d T ) V = C V / T h eff = ( T H - T C )/ T H Engine Refrigerator COP = T C /( T H - T C ) Phase Change D S trans = D H trans / T trans Heat Pump COP = T H /( T H - T C ) 46
47
48
49
50
Water 51
Water 52
Water 53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
Recommend
More recommend