Algebra, geometry, and Pythagorean triples Kaloyan Slavov - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Algebra, geometry, and Pythagorean triples Kaloyan Slavov Department of Mathematics ETH Z urich kaloyan.slavov@math.ethz.ch February 9, 2017 1 / 8 Basics 2 , 1 , 5 , 7 2 / 8 Basics 1 2 , 1 , 5 , 7 2 7 5 2 / 8
Algebra, geometry, and Pythagorean triples Kaloyan Slavov Department of Mathematics ETH Z¨ urich kaloyan.slavov@math.ethz.ch February 9, 2017 1 / 8
Basics √ − 2 , 1 , 5 , 7 2 / 8
Basics √ 1 √ − 2 , 1 , 5 , 7 − 2 7 5 2 / 8
Basics geometry algebra √ 1 √ − 2 , 1 , 5 , 7 − 2 7 5 2 / 8
Basics geometry algebra √ 1 √ − 2 , 1 , 5 , 7 − 2 7 5 (2 , 1) 2 / 8
Basics geometry algebra √ 1 √ − 2 , 1 , 5 , 7 − 2 7 5 y (2 , 1) (2 , 1) x 2 / 8
Lines geometry algebra 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y (2 , 1) ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y (2 , 1) ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y y = � x + � (2 , 1) ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y y = � x + � (2 , 1) slope ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y 1 − 0 x + � y = (2 , 1) 2 − ( − 1) slope ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y 1 x + � y = (2 , 1) 3 slope ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y 1 x + 1 y = (2 , 1) 3 3 slope ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Lines geometry algebra y y = 1 3 x + 1 1 x + 1 3 y = (2 , 1) 3 3 slope ( − 1 , 0) x 3 / 8
Circles geometry algebra 4 / 8
Circles geometry algebra y x 1 4 / 8
Circles geometry algebra y x 2 + y 2 = 1 x 1 4 / 8
Circles geometry algebra y x 2 + y 2 = 1 ( x, y ) 1 y x x 1 4 / 8
Circles geometry algebra y x 2 + y 2 = 1 ( x, y ) √ � � 1 y − 1 3 , 2 2 Is on this circle? 3 x x 1 4 / 8
Circles geometry algebra y x 2 + y 2 = 1 ( x, y ) √ � � 1 y − 1 3 , 2 2 Is on this circle? 3 x x 1 1 9 + 8 9 = 1 = ⇒ yes. 4 / 8
Circles geometry algebra y x 2 + y 2 = 1 ( x, y ) √ � � 1 y − 1 3 , 2 2 Is on this circle? 3 x x 1 1 9 + 8 9 = 1 = ⇒ yes. 4 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers 5 / 8
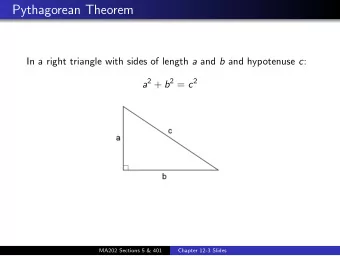
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers c b a 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 9 2 + 12 2 = 15 2 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 9 2 + 12 2 = 15 2 . . . 300 2 + 400 2 = 500 2 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 , 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 9 2 + 12 2 = 15 2 . . . 300 2 + 400 2 = 500 2 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 , 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 , 8 2 + 15 2 = 17 2 , 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 9 2 + 12 2 = 15 2 . . . 300 2 + 400 2 = 500 2 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 , 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 , 8 2 + 15 2 = 17 2 , • • • 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 9 2 + 12 2 = 15 2 . . . 300 2 + 400 2 = 500 2 5 / 8
Pythagorean triples N = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , ... } positive integers Problem Find examples of a, b, c ∈ N such that c b a 2 + b 2 = c 2 . a 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 , 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 , 8 2 + 15 2 = 17 2 , • • • 6 2 + 8 2 = 10 2 9 2 + 12 2 = 15 2 . . . 300 2 + 400 2 = 500 2 √ Non-example: 1 2 + 1 2 = ( 2) 2 5 / 8
Geometric interpretation a 2 + b 2 = c 2 a, b, c ∈ N 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇐ ⇒ a, b, c ∈ N 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 c c a, b, c ∈ N 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 c c a, b, c ∈ N ���� ���� x y 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ ⇒ c c a, b, c ∈ N ���� ���� x y 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 ⇐ ⇒ x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) � 5 � 2 � 12 � 2 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 13 13 x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) � 5 � 2 � 12 � 2 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 13 13 x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) � 5 � 2 � 12 � 2 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 13 13 15 2 + 8 2 = 17 2 ⇐ ⇒ x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) � 5 � 2 � 12 � 2 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 13 13 � 8 � 15 � 2 � 2 15 2 + 8 2 = 17 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 17 17 x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) � 5 � 2 � 12 � 2 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 13 13 ( 15 17 , 8 17 ) � 8 � 15 � 2 � 2 15 2 + 8 2 = 17 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 17 17 x 1 6 / 8
Geometric interpretation � b � 2 � a � 2 a 2 + b 2 = c 2 ⇒ x 2 + y 2 = 1 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 ⇐ c c a, b, c ∈ N x, y ∈ Q (rational) ���� ���� x y y � 3 � 2 � 4 � 2 ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) 3 2 + 4 2 = 5 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 5 5 ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) � 5 � 2 � 12 � 2 5 2 + 12 2 = 13 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 13 13 ( 15 17 , 8 17 ) � 8 � 15 � 2 � 2 15 2 + 8 2 = 17 2 ⇐ ⇒ + = 1 17 17 x 1 Problem Find examples of x, y ∈ Q such that x 2 + y 2 = 1 . 6 / 8
Hunting rational points y x 1 7 / 8
Hunting rational points y ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) x 1 7 / 8
Hunting rational points y ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) x 1 7 / 8
Hunting rational points y ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) ( 15 17 , 8 17 ) x 1 7 / 8
Hunting rational points y ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) ( 15 17 , 8 17 ) ( − 1 , 0) x 1 7 / 8
Hunting rational points y ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) ( 15 17 , 8 17 ) ( − 1 , 0) x 1 7 / 8
Hunting rational points y slope m = ( 5 13 , 12 13 ) ( 3 5 , 4 5 ) ( 15 17 , 8 17 ) ( − 1 , 0) x 1 7 / 8
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.