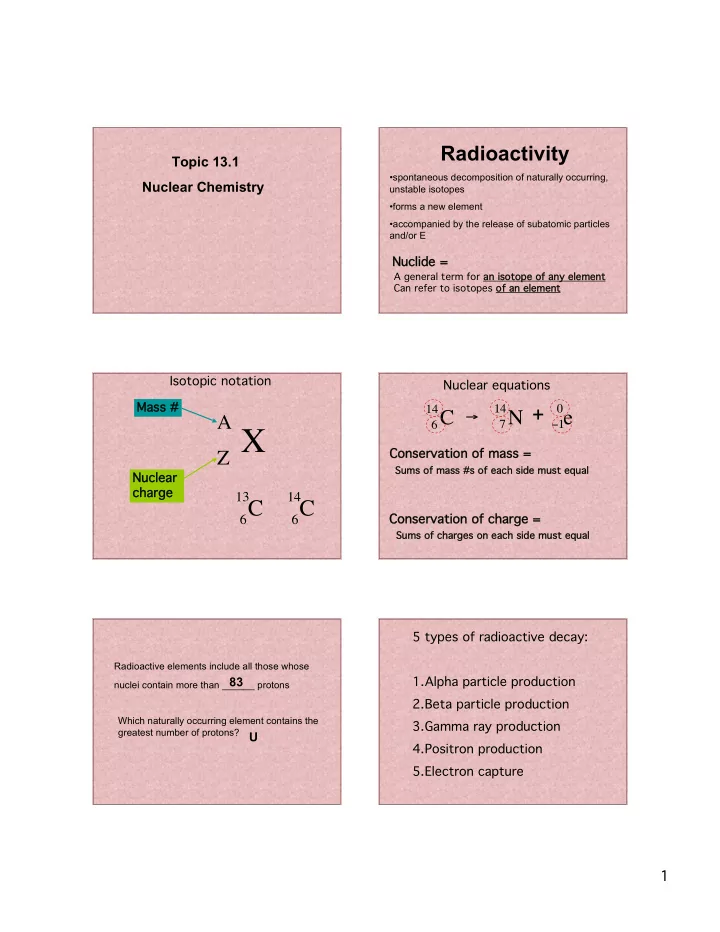

Radioactivity Topic 13.1 •spontaneous decomposition of naturally occurring, Nuclear Chemistry unstable isotopes •forms a new element •accompanied by the release of subatomic particles and/or E Nuclide = Nuclide = A general term for an isotope of any element Can refer to isotopes of an element Isotopic notation Nuclear equations Mass # Mass # A X 14 N + − 1 14 C → 7 0 e 6 Conservation of mass = Conservation of mass = Z Sums of mass #s of each side must equal Nuclear Nuclear charge charge 13 C 14 C Conservation of charge = Conservation of charge = 6 6 Sums of charges on each side must equal 5 types of radioactive decay: Radioactive elements include all those whose 1.Alpha particle production 83 nuclei contain more than ______ protons 2.Beta particle production Which naturally occurring element contains the 3.Gamma ray production greatest number of protons? U 4.Positron production 5.Electron capture 1
Types of radioactive decay: 226 Ra 230 Th � + 2 4 He 90 88 1. alpha particle: an element spontaneously releases a helium nucleus with no electrons 4 He + 2 ( α ) or 2 218 Po � + 2 214 Pb 4 He 238 U � 2 4 He 234 Th He + 84 82 92 90 What happens to ratio of n 0 /p /p + ? ? ↑ ratio: from 146/92 to 144/90 234 Pa � 234 U 0 e + � 1 2. Beta particle production ( β or e - ) 91 92 an element releases an e - and gains a p + • a neutron splits into a p + and an e - • the e - is released 0 e 234 Th � 234 Pa Pa + 210 Pb � 210 Bi 0 e + � 1 90 91 � 1 82 83 What happens to ratio of n 0 /p + ? ↓ ratio: from 144/90 to 143/91 3. Gamma rays ( γ ) Excited nucleus � ground state nucleus + 0 0 � ( excess energy ) ( lower energy ) • very high E photon of nonvisible light • Unstable nuclide has too much energy (excited state) • Excess E can be released by producing 238 U � 2 4 He + 234 Th + 2 0 0 � γ -rays 92 90 • This often accompanies other forms of nuclear decay no change of mass or nuclear charge 2
0 e 4. Positron emission ( β + or ) 11 C � + 1 11 B 0 e 1 same mass as electron 6 5 • opposite charge (anti-electron) • 22 Na � 22 Ne 0 e Ne + 1 11 10 118 Xe � + 1 118 I 0 e How: 54 53 •p + decays into a n 0 and β + , , β + + emitted What happens to ratio of n 0 /p + ? ↑ ratio: from 11/11 to 12/10 5. Electron capture 73 As + � 1 0 e � 73 G e 0 � e + 0 an inner shell e - is pulled into nucleus • 33 32 merges with a p + to form a n 0 • Always accompanied by γ -rays • 204 Po + � 1 0 e � 204 Bi 0 � Bi + 0 84 83 201 Hg + � 1 0 e � 201 Au 0 � Au + 0 80 79 What happens to ratio of n 0 /p + ? ↑ ratio: from 121/80 to 122/79 1. Alpha emission from Cm-242 process symbol Change in Change in Change in nuclear mass # n 0 2. Alpha emission from Np-237 charge -2 -4 -2 α 4 He 3. Beta emission from Mg-28 2 emission 0 e +1 0 -1 β 4. Beta emission from Ru-106 -1 emission 5. Positron emission from N-13 0 0 0 γ 0 � 0 emission 6. Positron emission from Ta-165 0 e β + -1 0 +1 +1 7. Electron capture of Sm-138 emission 0 e e - -1 0 +1 8. Electron capture of Ar-36 -1 capture 3
Write nuclear equations for the following processes: Beta emission from Mg-28 Alpha emission from Cm-242 4 He 242 Cm � 238 Pu + 2 28 Mg � 28 Al 0 e Al + � 1 96 94 12 13 Alpha emission from Np-237 Beta emission from Ru-106 237 Np � 233 Pa + 2 4 He 106 Ru � 106 Rh 0 e Rh + � 1 93 91 44 45 Positron emission from N-13 Electron capture of Sm-138 138 Sm 0 e � 138 Pm + 0 0 � Sm + � 1 13 N � 13 C 0 e C + 1 62 61 7 6 Positron emission from Ta-165 Electron capture of Ar-36 36 Ar 0 e � 17 36 Cl 0 � Ar + � 1 Cl + 0 165 Ta � 165 Hf 0 e Hf + 1 73 18 72 Write the nuclear equation that represents the fusion of He-3 with H-1 to yield a positron, a gamma ray and one additional product. 3 He + 1 3 He + 1 3 He + 1 3 He + 1 3 He 1 H � 1 H � 1 H � 1 H � 0 � + 1 0 � + 1 0 � 0 e 0 e + 2 4 He 2 2 2 2 2 0 0 0 4
Recommend
More recommend