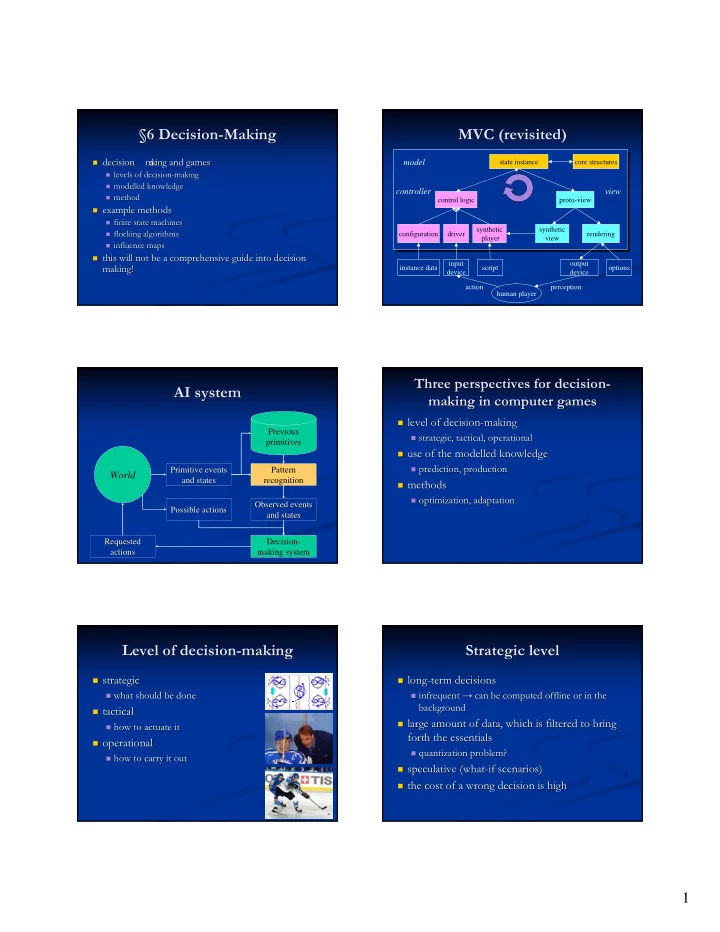

§6 Decision- -Making Making MVC (revisited) §6 Decision MVC (revisited) � decision decision - - m m a a king and games king and games � model state instance core structures � levels of decision levels of decision- -making making � � modelled knowledge modelled knowledge � controller view � method method � control logic proto-view � example methods example methods � � finite state machines finite state machines � synthetic synthetic � flocking algorithms flocking algorithms � configuration driver rendering player view � influence maps influence maps � � this will not be a comprehensive guide into decision this will not be a comprehensive guide into decision - - � input output making! making! instance data script options device device action perception human player Three perspectives for decision- Three perspectives for decision - AI system AI system making in computer games making in computer games � level of decision level of decision- -making making � Previous � strategic, tactical, operational strategic, tactical, operational � primitives � use of the modelled knowledge use of the modelled knowledge � � prediction, production prediction, production � Primitive events Primitive events Pattern World and states and states recognition � methods methods � � optimization, adaptation optimization, adaptation � Observed events Observed events Possible actions Possible actions and states and states Requested Requested Decision- actions actions making system Level of decision- Level of decision -making making Strategic level Strategic level � strategic strategic � long long- -term decisions term decisions � � � what should be done what should be done � infrequent → can be computed offline or in the infrequent → can be computed offline or in the � � background background � tactical tactical � � large amount of data, which is large amount of data, which is filtered to bring filtered to bring � � how to actuate it how to actuate it � forth the essentials forth the essentials � operational operational � � quantization problem? quantization problem? � � how to carry it out how to carry it out � � speculative (what speculative (what- -if scenarios) if scenarios) � � the cost of a wrong decision is high the cost of a wrong decision is high � 1
Tactical level Operational level Tactical level Operational level � medium medium- -term decisions term decisions � short short- -term decisions term decisions � � � reactive, real reactive, real - time response time response � intermediary between strategic and operational intermediary between strategic and operational - � � levels levels � concrete and closely connected to the game concrete and closely connected to the game � world world � follow the plan made on the strategic level follow the plan made on the strategic level � � convey the feedback from the operational level convey the feedback from the operational level � considers individual entities considers individual entities � � � considers a group of entities considers a group of entities � the cost of a wrong decision is relatively low the cost of a wrong decision is relatively low � � � a selected set of data to be scrutinized a selected set of data to be scrutinized � of course not to the entity itself of course not to the entity itself � � � co co - - o o peration within the group peration within the group � Use of the modelled knowledge Prediction Use of the modelled knowledge Prediction � time series data time series data � � world = a generator of events and states, which world = a generator of events and states, which � can be labelled with symbols can be labelled with symbols Modeller � prediction prediction � � what the generator will produce next? what the generator will produce next? � � production production � � simulating the output of the generator simulating the output of the generator maximum � Generator probability � how to cope with uncertainty? how to cope with uncertainty? � Production Production Methods: Optimization Methods: Optimization � elements: elements: � � objective function to be maximized/minimized objective function to be maximized/minimized � � variables affecting the value of the objective function variables affecting the value of the objective function � Modeller � constraints limiting feasible variable values constraints limiting feasible variable values � � goal: find among the feasible solutions the one goal: find among the feasible solutions the one � that gives an optimum value for the objective that gives an optimum value for the objective function function random � time consuming? time consuming? selection from � probability → heuristic rules to guide the search → heuristic rules to guide the search distribution 2
Methods: Optimization (cont’d) Methods: Adaptation Methods: Optimization (cont’d) Methods: Adaptation � hill hill- -climbing climbing � ability to make appropriate responses to ability to make appropriate responses to � � changed circumstances → learning changed circumstances → learning � how to escape local optima? how to escape local optima? � � searches for a function behind given solutions searches for a function behind given solutions � tabu search tabu search � � � optimization: solution for a given function optimization: solution for a given function � simulated annealing simulated annealing � � � affecting factors are unknown or dynamic affecting factors are unknown or dynamic � genetic algorithms genetic algorithms � � � pattern recognition pattern recognition � � multiple search traces multiple search traces � � swarm algorithms swarm algorithms � Methods: Adaptation (cont’d) Soft computing Methods: Adaptation (cont’d) Soft computing � neural networks neural networks � L. Zadeh: methodologies that try to solve problems L. Zadeh: methodologies that try to solve problems � � arising from the complexity of the natural world arising from the complexity of the natural world � training training � � approximation approximation � � supervised learning supervised learning � � partial truth partial truth � � unsupervised learning (e.g., self unsupervised learning (e.g., self- -organizing maps) organizing maps) � � imprecision imprecision � � execution execution � � uncertainty uncertainty � � hidden Markov model hidden Markov model � � computer games have used ‘hard’ computing computer games have used ‘hard’ computing � � recurring structures recurring structures � � as the game worlds get more complex, perhaps soft as the game worlds get more complex, perhaps soft � computing methods would suit better computing methods would suit better Soft computing methods Soft computing methods Finite state machine (FSM) Finite state machine (FSM) � probabilistic reasoning probabilistic reasoning � components: components: � � � genetic algorithms genetic algorithms � � states states � � Bayesian networks Bayesian networks � � transitions transitions � � artificial neural networks artificial neural networks � � events events � � back back - - p p ropagation networks ropagation networks � � actions actions � � self self - - o o rganizing maps rganizing maps � � state chart: fully connected directed graph state chart: fully connected directed graph � � fuzzy logic fuzzy logic � � vertices = states vertices = states � � fuzzy sets fuzzy sets � � edges = transitions edges = transitions � � approximate reasoning approximate reasoning � 3
Recommend
More recommend