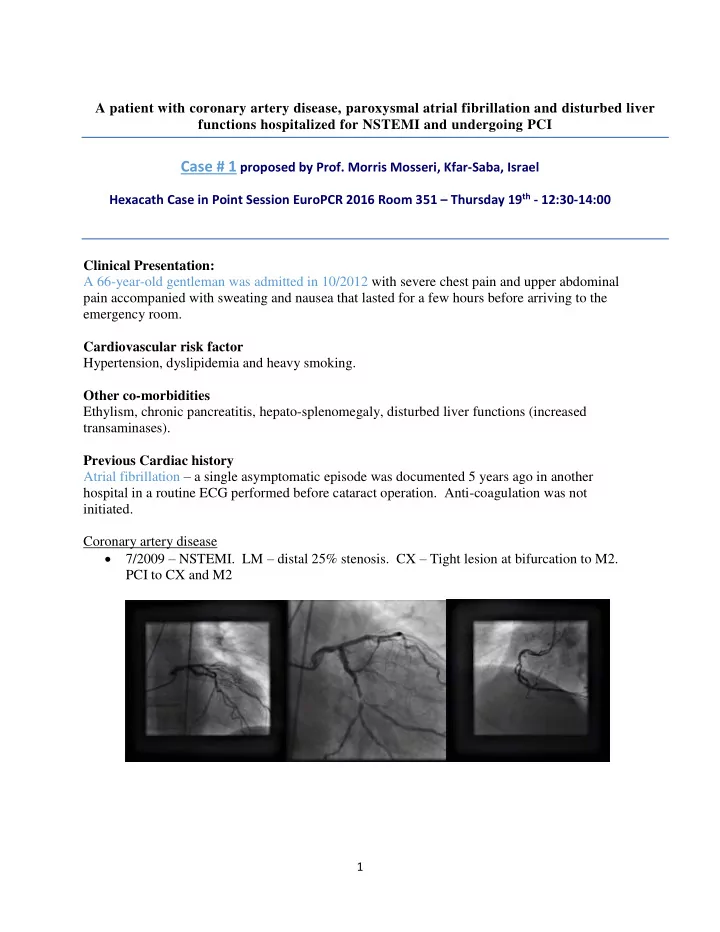

A patient with coronary artery disease, paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and disturbed liver functions hospitalized for NSTEMI and undergoing PCI Case # 1 proposed by Prof. Morris Mosseri, Kfar-Saba, Israel Hexacath Case in Point Session EuroPCR 2016 Room 351 – Thursday 19 th - 12:30-14:00 Clinical Presentation: A 66-year-old gentleman was admitted in 10/2012 with severe chest pain and upper abdominal pain accompanied with sweating and nausea that lasted for a few hours before arriving to the emergency room. Cardiovascular risk factor Hypertension, dyslipidemia and heavy smoking. Other co-morbidities Ethylism, chronic pancreatitis, hepato-splenomegaly, disturbed liver functions (increased transaminases). Previous Cardiac history Atrial fibrillation – a single asymptomatic episode was documented 5 years ago in another hospital in a routine ECG performed before cataract operation. Anti-coagulation was not initiated. Coronary artery disease 7/2009 – NSTEMI. LM – distal 25% stenosis. CX – Tight lesion at bifurcation to M2. PCI to CX and M2 1
4/2010 – Angina pectoris, posterior wall ischemia per thalium scintigraphy. CX – 90% stenosis proximal to stent. PCI to CX. 2/2011 – Echocardiography: mildly reduced global LV function, septal and inferior hupokinesis. 2/2012 – Coronary CT-angiography (performed to follow up the LM): LM stenosis unchanged, 50% stenosis in mid LAD, prox RCA and mid RCA. 9/2012 – Chest pain. Coronary angiography: LM distal 25-50% stenosis irregularities in all coronaries. 2
Medical treatment until hospitalization included: Aspirin 100 mg Bisoprolol 10 mg X2 /d Enaladex 20 mg X2 /d Amlodipine 5 mg/d Atorvastatin 80 mg/d Allopurinl 100 mg /d Clinical examination on admission on 10/2012: Good general status, 168cm x 65kg. BP (15minutes rest): 125/75 mmHg Heart sound: regulars, 60 bpm, normal, Lungs: clear Abdomen: normal Peripheral pulses normal No carotid murmur No clinical sign of thyroid dysfunction ECG on admission Sinus rythm, biphasic T wave in anterior leads, inverted and peaked T in lateral leads. Key bio-chemical markers: Troponin = positive Clinical assessment : NSTEMI The patient was treated at the ER with Aspirin 300 mg, SC Clexan and nitrates and his chest pain subsided. Coronary angiography one day after admission: Right femoral access LM – distal 25-50% stenosis; LAD – mid 75% stenosis; RCA – distal 90-99% stenosis. 3
Discussion Point 1 Do you treat this patient with a single episode of asymptomatic atrial fibrillation with long-term oral anti coagulation? Discussion Point 2 This patient undergoes PCI: DES is the best option for this particular patient? □ Yes □ No Non drug eluting stent is the best option for this particular patient? □ Yes □ No 4
Come & discuss this clinical case during the Case in Point Session at EuroPCR 2016 Room 351 Thursday 19 th 12:30-14:00 5
Recommend
More recommend