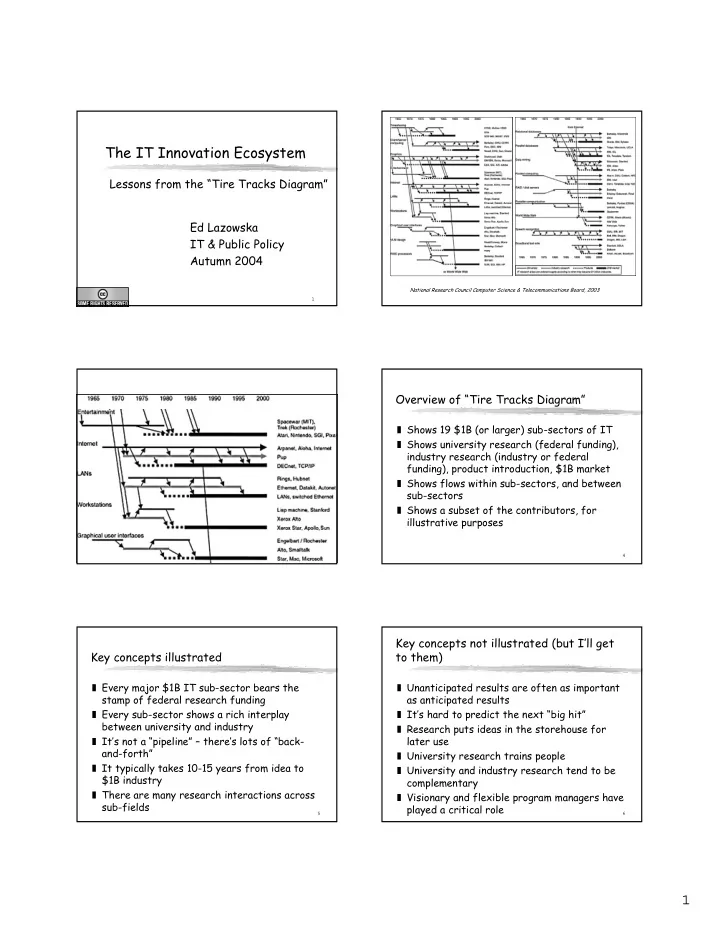

The IT Innovation Ecosystem Lessons from the “Tire Tracks Diagram” Ed Lazowska IT & Public Policy Autumn 2004 National Research Council Computer Science & Telecommunications Board, 2003 1 Overview of “Tire Tracks Diagram” ❚ Shows 19 $1B (or larger) sub-sectors of IT ❚ Shows university research (federal funding), industry research (industry or federal funding), product introduction, $1B market ❚ Shows flows within sub-sectors, and between sub-sectors ❚ Shows a subset of the contributors, for illustrative purposes 4 Key concepts not illustrated (but I’ll get Key concepts illustrated to them) ❚ Every major $1B IT sub-sector bears the ❚ Unanticipated results are often as important stamp of federal research funding as anticipated results ❚ Every sub-sector shows a rich interplay ❚ It’s hard to predict the next “big hit” between university and industry ❚ Research puts ideas in the storehouse for ❚ It’s not a “pipeline” – there’s lots of “back- later use and-forth” ❚ University research trains people ❚ It typically takes 10-15 years from idea to ❚ University and industry research tend to be $1B industry complementary ❚ There are many research interactions across ❚ Visionary and flexible program managers have sub-fields played a critical role 5 6 1
The Internet ❚ 1966: First experiments in digital packet switched technology ❚ 1968: ARPA issues RFQ for IMPs ❙ AT&T says it’ll never work, and even if it does, no one will care ❚ 1969: ARPANET inaugurated with 4 hosts ❙ Len Kleinrock’s student/programmer Charley Kline attempts remote login from UCLA SDS Sigma 7 to SRI SDS 940 ❙ System crashed partway through – thus, the first message on the Internet was “lo” 7 ❚ 1988: ARPANET becomes NSFNET ❚ 1975: ARPANET has 100 hosts ❙ Regional networks established ❚ 1977: Crufty internetworking demonstration ❙ Backbone speed 56kbps ❙ 4-network demonstration of ARPANET, SATNET, ❙ Roughly 100,000 hosts and 200 networks Ethernet, and PRnet – from a truck on 101 to ❚ 1989: CNRI interconnects MCImail to the England Internet ❚ 1980: Design of TCP/IP completed ❙ Wise policy choice ❚ 1983: Conversion to TCP/IP completed ❚ 1990: Backbone speed increased to 1.5Mbps ❙ Routers allowed full internetworking – “network of by IBM and MCI networks” ❙ Roughly 250,000 hosts and 1,500 networks ❙ Roughly 500 hosts ❙ Note: There still was “a backbone”! 9 10 M i l l i ons of I nt er net host s 250 ❚ 1992: NCSA Mosaic stimulates explosive 200 growth of WWW ❚ 1995: Full commercialization, at 45Mbps 150 ❙ 6,000,000 hosts, 50,000 networks 100 50 0 1969 1974 1979 1984 1989 1994 1999 11 2
Key concepts illustrated ❚ Bears the stamp of federal research funding ❚ Shows a rich interplay between university and industry ❚ Not a “pipeline” – there’s lots of “back-and- forth” ❚ 10-15 years from idea to $1B industry 13 14 (D)ARPA I(P)TO IPTO under Bob Kahn, 1979-85 ❚ VLSI program JCR Licklider, 1962-64 Jack Schwartz, 1987-89 ❚ ❚ Ivan Sutherland, 1964-65 Barry Boehm, 1989-91 ❚ ❚ ❙ Mead-Conway methodology Bob Taylor, 1965-69 Steve Squires, 1991-93 ❚ ❚ ❙ MOSIS (Metal Oxide Silicon Implementation Larry Roberts, 1969-73 John Toole (acting), 1993-94 ❚ ❚ Service) Al Blue (acting), 1973-74 Howard Frank, 1994-97 ❚ ❚ ❚ Berkeley Unix JCR Licklider, 1974-75 David Tennenhouse, 1997-99 ❚ ❚ Dave Russell, 1975-79 Shankar Sastry 1999-01 ❙ Needed Unix with virtual memory for the VLSI ❚ ❚ Bob Kahn, 1979-85 Kathy McDonald (acting), program (big designs) and the Image Understanding ❚ ❚ 2001-02 Saul Amarel, 1985-87 program (big images) ❚ Ron Brachman, 2002-present ❚ ❙ Also a Trojan horse for TCP/IP ❙ And a common platform for much systems and application research 15 16 Additional key concepts illustrated ❚ SUN workstation ❚ Many research interactions across sub-fields ❙ Baskett said no existing workstations could ❙ Graphics, workstations, VLSI, computer adequately handle VLSI designs (Bechtolsheim’s architecture, operating systems, and networking frame buffer approach was unique) were being synergistically advanced! ❙ Kahn insisted that it run Berkeley Unix ❚ Clear byproducts ❙ Sun ❙ SGI ❙ RISC (MIPS, SPARC) ❙ TCP/IP adoption ❙ Internet routers (Cisco) 17 18 3
❚ Visionary and flexible program managers have played a critical role 20 St udy Char t er I SAT St udy: • Revi ew i m pact of AI t echnol ogy on DoD I m pact of AI on DoD – M aj or syst em s enabl ed by AI t echnol ogy – Si gni f i cant dem onst r at i ons and new capabi l i t i es August 2004 – Spi n- of f s – DoD t o ci vi l i an – “ Spi n- ons”– ci vi l i an t o DoD Co- Chai r s: Ed Lazowska Al M cLaughl i n 21 22 Language Under st andi ng/ Tr ansl at i on Language Under st andi ng/ Tr ansl at i on Phr Phr asel asel at at or or TI DES+EARS: Aut om at ed pr ocessi ng of Ar abi c t ext & audi o Aut om at ed t r ansl at i on and Phr ase Tr ansl at i on Devi ce Phr ase Tr ansl at i on Devi ce cl assi f i cat i on of f or ei gn l anguage f f or or M i M i l l i i t t ar ar y y Use Use t ext and audi o – – User User speaks speaks a a phr phr ase ase • TI DES: Tr ansl at i on – f or ei gn l anguage t ext t o – – Aut Aut om at om at i i c c Speech Speech Recogni Recogni zer zer Engl i sh t ext , i ncl udi ng docum ent cl assi f i cat i on m at m at ches ches i i t t t t o o pr pr er er ecor ecor ded ded • EARS: Tr anscr i pt i on – conver t s Ar abi c and t t r r ansl ansl at at i i on on Chi nese speech t o t ext – Tr – Tr ansl ansl at at i i on on pl pl ayed ayed t t hr hr ough ough speaker speaker •TI DES and EARS i nt egr at i on: St at i st i cal – – Possi Possi bl bl e e due due t t o o decades decades of of ASR ASR EARS l ear ni ng – r obust f or ei gn l anguage pr ocessi ng t o and and syst syst em s em s r r esear esear ch ch ext r act i nt el l i gence f r om open sour ces. I m pact St at us I m pact St at us I m pact St at us • CENTCO M usi ng aut om at ed pr ocessi ng t o • Aut om at i c speech r ecogni t i on of Engl i sh Depl Depl oyed oyed i i n n O per O per at at i i on on Endur Endur i i ng ng – Cont Cont i nued use i n I r aq and – i nued use i n I r aq and pul l i nt el l i gence f r om Ar abi c t ext and audi o i m pr oved dr am at i cal l y f r om 1984 t o 1993. Now, Fr eedom and I r aqi Fr eedom Af ghani st an Fr eedom and I r aqi Fr eedom Af ghani st an equal l y dr am at i c i m pr ovem ent f or Ar abi c ASR • Engl i sh- onl y oper at or s can now f or m a – – Faci Faci l l i i t t at at ed ed t t i i m e m e- - cr cr i i t t i i cal cal i i nf nf or or m at m at i i on on – – Joi Joi nt nt For For ces ces Com m and Com m and f f i i el el di di ng ng t hr ough EARS pi ct ur e i n t hei r m i nd of what i s bei ng exchange exchange when when i i nt nt er er pr pr et et er er s s not not 800+ 800+ uni uni t t s s di scussed i n Ar abi c sour ce m at er i al •Text and audi o pr ocessi ng of Ar abi c now avai avai l l abl abl e e – – SO CO M SO CO M f f i i el el di di ng ng 400 400 uni uni t t s s possi bl e end- t o- end. Two depl oym ent uni t s t o – Accept – Accept ed ed by by br br oad oad set set of of user user s s • 100’ s of docum ent s f r om dozens of sour ces – – Cl Cl ear ear need need f f or or 2- 2 - way way voi voi ce ce m achi m achi ne ne CENTCO M i n 2004 f or i nf or m at i on expl oi t at i on t r ansl at ed dai l y; 5- 10 sent t o NVTC f or hum an – – I I nt nt er er act act i i on on wi wi t t h h ci ci vi vi l l i i ans ans – – t t r r ansl ansl at at i i on on ( ( VM T) VM T) f r om Ar abi c open sour ce m at er i al t r ansl at i on i i nf nf or or m at m at i i on on on on UXO s UXO s and and weapons weapons caches caches • Technol ogy f i r st used by US For ces Kor ea 24 4
Recommend
More recommend