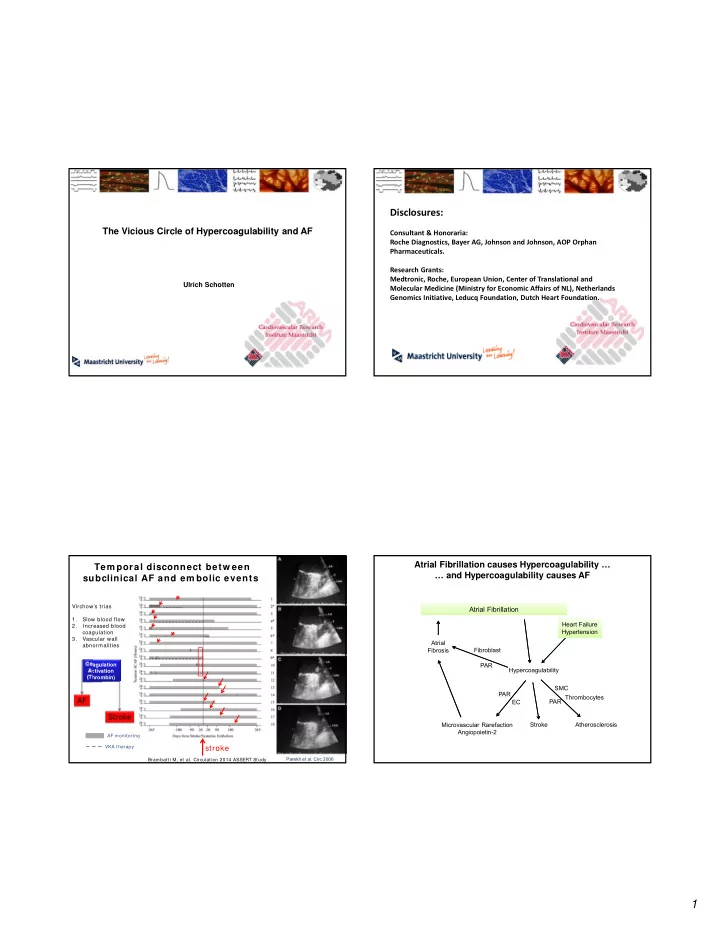

Disclosures: The Vicious Circle of Hypercoagulability and AF Consultant & Honoraria: Roche Diagnostics, Bayer AG, Johnson and Johnson, AOP Orphan Pharmaceuticals. Research Grants: Medtronic, Roche, European Union, Center of Translational and Ulrich Schotten Molecular Medicine (Ministry for Economic Affairs of NL), Netherlands Genomics Initiative, Leducq Foundation, Dutch Heart Foundation. Atrial Fibrillation causes Hypercoagulability … Tem poral disconnect betw een WP1 Pro ‐ coagulant … and Hypercoagulability causes AF subclinical AF and em bolic events Mechanisms Virchow’s trias Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation 1. Slow blood flow Heart Failure Heart Failure 2. Increased blood Hypertension Hypertension coagulation 3. Vascular wall Atrial abnormalities Fibrosis Fibroblast PAR Coagulation Hypercoagulability Activation (Thrombin) SMC PAR Thrombocytes EC PAR Microvascular Rarefaction Stroke Atherosclerosis Angiopoietin-2 AF monitoring VKA therapy stroke Parekh et al. Circ 2006 Brambatti M, et al. Circulation 2014 ASSERT Study 1
I schem ia Causes Upregulation of TF in Cardiom yocytes AF Causes Atrial Supply-Dem and I schem ia Sinus 200ms 3-6 fold increase AF in frequency Control Rhythm Demand Supply LA LV I schemic Zone Van Bragt, Verheule, Cardiovasc Res 2014;101:9–19 Erlich et al Am J Pathol 2000; 1 5 7 :1 8 4 9 – 1 8 6 2 Thrombin induces Expression of IL-6 and MCP-1 Profibrotic Effects of PAR Activation in Cardiac Fibroblasts WP2 Pro ‐ fibrotic Effects WP2 Pro ‐ fibrotic Effects Thrombin Hyper- coagulability Xa Cardiac fibroblast IL-6 TGF- β MCP-1 Pro-fibrotic and Differentiation Collagen synthesis inflammatory (Myofibroblasts) cytokines MCP-1 α -SMA 3 H-proline IL 6 incorporation TGF- β Anne Margreet de Jong, Thesis at UMCG 2014 2
Thrombin Promotes Inducibility / Stability of AF in Mice Nadroparin Inhibits the Development of a Substrate for AF AF Mapping Control (saline, n=9) Wt burst normal sinus rhythm 4 Weeks of AF 15 AF Goats Histology P Nadroparin (anti-Xa/IIa, n=6) Immunohistochemistry QRS 0.5 s Thrombin Generation High Density Mapping Histology α -SMA TMpro/pro Thrombin Generation burst 40 atrial fibrillation Baseline AF 30 P Thrombin (nM) ] Thrombin [nM A QRS 20 10 0 0 10 20 30 40 Ctr Nadroparin Ctr Nadroparin Time (min) Time [min] Activation Time max TF-ind. Thrombin Cell-Cell Distances nM/min ms µm AU 400 40 8 * 300 30 6 * nM/min * ms µm 200 20 4 * * 100 10 2 0 0 0 Base- e o Ctr Nadro- l n o Ctr l Nadro- n Ctr o l Nadro- n Ctr Nadro- n i r r i r r r i l i t r a t a t a e n p n p n p s line o o parin o o parin o o parin parin a C r C r C r B d d d a a a N N N Direct Thrombin / Xa Inhibitors, but not VitK Antagonists, Gla Domain Deficient Xa still Stimulates 3 H-proline Incorporation Inhibit PAR Signaling Vit K Antagonists Vit K Antagonists Thrombin Inhibitor Thrombin Inhibitor Xa Inhibitor Xa Inhibitor Physiological Physiological II II II II PAR2 PAR2 PAR2 PAR2 Gla Gla Xa Xa Xa Xa IIa IIa IIa IIa Gla Gla PAR1 PAR1 PAR1 PAR1 PAR1-Inhibition - - + + + PAR2-Inhibition - - - - + + + Anti-coagulation NOAC: Anticoagulation plus Upstream Therapy? 3
AF as ElectroVasculoCoagulopathy Stroke Hypercoagulability Atrial Cavity Diabetes TF Heart FIIa Coagulation Factors Induce Expression of Profibrotic and Fribrinolysis Failure Thrombocyte Activation TF Proinflammatory Responses in Fibroblasts. Shear PAI ‐ 1 VCAM ‐ 1 IL ‐ 6 FXII Obesity TF In Transgenic Mice with Enhanced Thrombin Activity Inducibility Coronary Hypocontractility Artery and Stability of AF is Enhanced. Inflammation AngII Disease Atrial Stretch TF PAR Hypertension FIIa Nadroparin can Inhibit the Development of a Substrate for AF. Atrial Vascular remodeling Ischemia Fibrosis Fatty Tachycardia Aging Infiltration Atrial Myocardium Hypercoagulability Causes Atrial Fibrosis and Promotes Atrial Fibrillation. Ca 2+ ‐ handling Conduction Ion channel instability Heterogeneities Remodeling NOACs but not Vit K Antagonists Inhibit PAR-mediated Collagen Synthesis. Ectopy Reentry Atrial Fibrillation 4
Recommend
More recommend