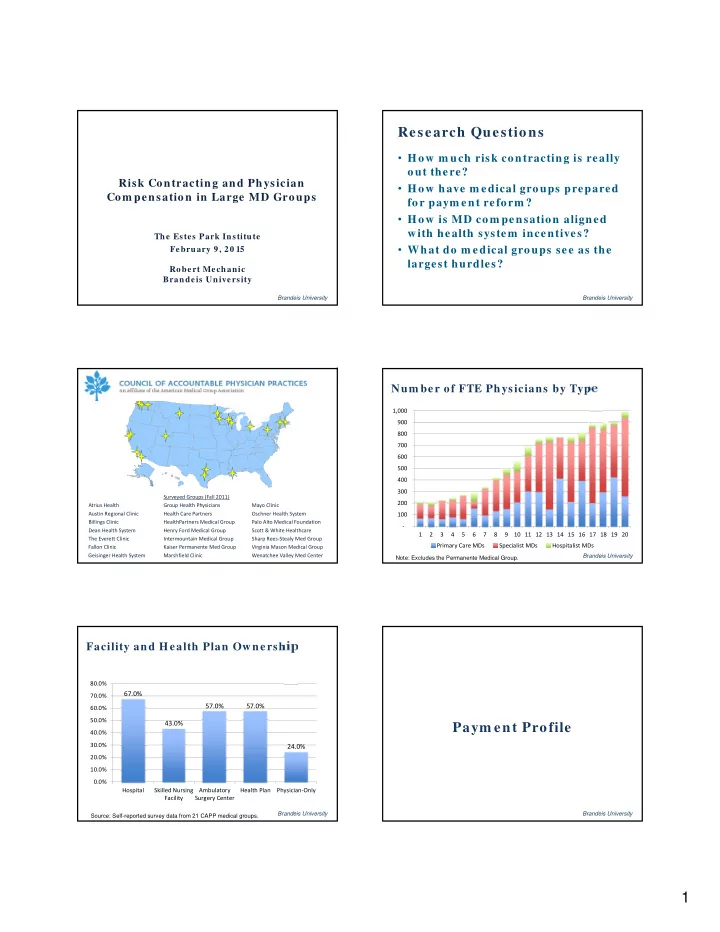

Research Questions • How m uch risk contracting is really out there? Risk Contracting and Physician • How have m edical groups prepared Com pensation in Large MD Groups for paym ent reform ? • How is MD com pensation aligned with health system incentives? The Estes Park Institute • What do m edical groups see as the February 9, 20 15 largest hurdles? Robert Mechanic Brandeis University Brandeis University Brandeis University Num ber of FTE Physicians by Type 1,000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 Surveyed Groups (Fall 2011) 200 Atrius Health Group Health Physicians Mayo Clinic Austin Regional Clinic Health Care Partners Oschner Health System 100 Billings Clinic HealthPartners Medical Group Palo Alto Medical Foundation ‐ Dean Health System Henry Ford Medical Group Scott & White Healthcare 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 The Everett Clinic Intermountain Medical Group Sharp Rees ‐ Stealy Med Group Primary Care MDs Specialist MDs Hospitalist MDs Fallon Clinic Kaiser Permanente Med Group Virginia Mason Medical Group Geisinger Health System Marshfield Clinic Wenatchee Valley Med Center Brandeis University Brandeis University Note: Excludes the Permanente Medical Group. Facility and Health Plan Ownership 80.0% 67.0% 70.0% 57.0% 57.0% 60.0% 50.0% 43.0% Paym ent Profile 40.0% 30.0% 24.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% Hospital Skilled Nursing Ambulatory Health Plan Physician ‐ Only Facility Surgery Center Brandeis University Brandeis University Source: Self-reported survey data from 21 CAPP medical groups. 1
Type of contract as a percent of 20 10 Patient Revenue by Contract Type total patient revenue FFS-based Risk-based Global Capitation, 25% 100% 90% 80% Partial Capitation, Fee for Service, 70% 5% 54% 60% 50% Shared Risk, 3% 40% Shared Savings, 30% 2% 20% 10% FFS ‐ Affiliated 0% Plan, 8% FFS w/P4P, 3% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 FFS Affiliated Health Plan Risk Note: Calculated as a simple (unweighted) average (n= 21). Brandeis University Brandeis University Source: Self-reported survey data from 21 CAPP medical groups. 20 10 PCP Com pensation Method FFS-based Risk-based 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% Physician Com pensation 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 Production Salary Performance Other Brandeis University Brandeis University Source: Self-reported survey data from 21 CAPP medical groups. One example: Dean Clinic transition toward a value- Group Paym ent vs. PCP Com pensation based compensation plan (specialty) 100% Percent of Compensation Based on 90% 80% 70% Productivity 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Value FFS/Volume Risk Contracts as Percent of Total Revenue Source: Craig Sammit, MD Based Based Brandeis University Page 12 2
One example (continued) Dean Clinic Realignment of Primary Care Compensation Dean PCMH Compensation Model Transition 100% 95% 115% 115% 10% 10% 100% 2% 10% 10% 15% 15% 80% Efficiency 20% 20% Quality Operating Characteristics 60% Service 20% 98% 95% 40% Panel Size 60% RVUs - 5% 20% 40% RVUs 0% Salary 2009 2010 2010 Future? Option A Option B Source: Craig Sammit,,MD Brandeis University Page 13 Data Managem ent Capacity System Assets by Type of Group Percent of Groups Reporting “Fully Im plem ented” 90.0% 80.0% 80.0% 80.0% 73.0% Shared electronic health record 70.0% 64.0% 60.0% Results management 50.0% 50.0% 45.0% 40.0% 36.0% 40.0% Data warehouse & analytic software 30.0% Patient disease registries 20.0% 10.0% Physician and patient reminders 0.0% Hospital Skilled Nursing Ambulatory Health Plan 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 120% Facility Surgery Center Risk ‐ Based (N=11) FFS ‐ Based (N=10) FFS Groups Risk Groups Source: Author’s analysis of self-reported survey data from 21 CAPP medical groups. Brandeis University Brandeis University Source: Self-reported survey data from 21 CAPP medical groups. Attitude toward expanding Perform ance Im provem ent Initiatives future risk contracting (n=15) Percent of Groups Reporting They are “Far Along” • All expect expanded risk contracting Reduce avoidable admissions & • 11 groups seeking new risk contracts readmissions • 3 were preparing for paym ent Reduce network leakage system change Establish preferred relationships with efficient hospitals & specialists • 1 group not interested Mgmt. Programs for High Risk Patients Patient engagement initiatives 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Risk ‐ Based (N=11) FFS ‐ Based (N=10) Brandeis University Brandeis University Source: Author’s analysis of self-reported survey data from 21 CAPP medical groups. 3
What are the largest challenges to increasing your Conclusions and Issues revenue from alternative paym ent contracts? (N=14) • “Many large m edical groups will need Need to improve care management to acquire new skills and tools to be capabilities ready for paym ent reform ”, Hea lth Need to improve data management and information systems Affa irs Sept 20 12 PPO ‐ dominated market not • Significant challenges and cost to appropriate for risk contracting im plem ent these changes broadly Payer willness to offer risk contracts • Sources of capital for infrastructure? Physician and staff resistance – Insurers? – Hospitals? 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 120% – Governm ent? Very Important Somewhat Important Brandeis University Brandeis University Source: Author’s analysis of self-reported survey data from 21 CAPP medical groups. Thank You Robert Mechanic Senior Fellow Heller School for Social Policy & Mgm t. Brandeis University m echanic@brandeis.edu http:/ healthforum .brandeis.edu Brandeis University 4
Recommend
More recommend