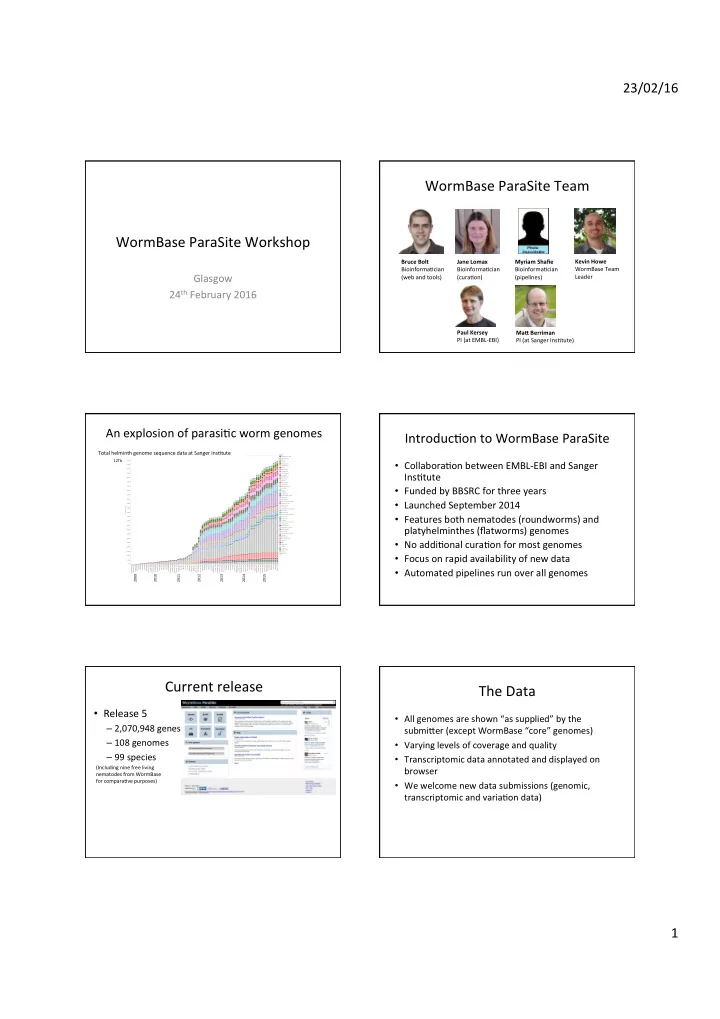

23/02/16 WormBase ParaSite Team WormBase ParaSite Workshop Kevin Howe Bruce Bolt Jane Lomax Myriam Shafie WormBase Team BioinformaCcian BioinformaCcian BioinformaCcian Glasgow (web and tools) (curaCon) (pipelines) Leader 24 th February 2016 Paul Kersey Ma< Berriman PI (at EMBL-EBI) PI (at Sanger InsCtute) An explosion of parasiCc worm genomes IntroducCon to WormBase ParaSite Total helminth genome sequence data at Sanger InsCtute Cumulative bases sequenced for helminth tracking Run date Genus Allobilharzia visceralis 12Tb Angiostrongylus 12000B Anisakis • CollaboraCon between EMBL-EBI and Sanger Ascaris Atractolytocestus 11500B Austrobilharzia Brugia 11000B Caenorhabditis InsCtute Cyathostomum 10500B Cylicostephanus Dicrocoelium Diphyllobothrium 10000B Dracunculus Dugesia 9500B Echinococcus Echinostoma • Funded by BBSRC for three years 9000B Elaeophora elaphi Enterobius 8500B Fasciola Globodera Gongylonema 8000B Griphobilharzia amoena Haemonchus • Launched September 2014 7500B Halicephalobus Haplobothrium globuliforme 7000B Heligmosomoides Homo sapiens Cumulative bases Hymenolepis 6500B Macrobilharzia macrobilharzia Mansonella 6000B Mesocestoides • Features both nematodes (roundworms) and Nippostrongylus brasiliensis 5500B Onchocerca Opisthorchis Parascaris 5000B Parastrongyloides trichosuri Protopolystoma platyhelminthes (flatworms) genomes 4500B Rhabditophanes Sanguinicola cf. inermis 4000B Schistocephalus Schistosoma 3500B Schistosomatium douthitti Spirometra Strongyloides 3000B Strongylus vulgaris • No addiConal curaCon for most genomes Syphacia Taenia 2500B Teladorsagia Thelazia 2000B Toxocara Trichobilharzia 1500B Trichuris • Focus on rapid availability of new data Wuchereria 1000B 500B 0B September 2008 December 2008 January 2009 March 2009 April 2009 May 2009 June 2009 July 2009 August 2009 September 2009 October 2009 November 2009 December 2009 January 2010 February 2010 March 2010 April 2010 May 2010 June 2010 July 2010 August 2010 September 2010 October 2010 November 2010 December 2010 February 2011 March 2011 April 2011 May 2011 June 2011 July 2011 August 2011 September 2011 October 2011 November 2011 December 2011 January 2012 February 2012 March 2012 April 2012 May 2012 June 2012 July 2012 August 2012 September 2012 October 2012 November 2012 December 2012 January 2013 February 2013 March 2013 April 2013 May 2013 June 2013 July 2013 August 2013 September 2013 October 2013 November 2013 December 2013 January 2014 February 2014 March 2014 April 2014 May 2014 June 2014 August 2014 September 201.. October 2014 November 2014 December 2014 January 2015 February 2015 March 2015 April 2015 May 2015 June 2015 July 2015 August 2015 • Automated pipelines run over all genomes 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 Current release The Data • Release 5 • All genomes are shown “as supplied” by the – 2,070,948 genes submi]er (except WormBase “core” genomes) – 108 genomes • Varying levels of coverage and quality – 99 species • Transcriptomic data annotated and displayed on (Including nine free living browser nematodes from WormBase for comparaCve purposes) • We welcome new data submissions (genomic, transcriptomic and variaCon data) 1
23/02/16 WormBase “Core” Parasite Genomes The Website • Genome Browser • These are: • Transcriptomic Data Display – Brugia malayi • Gene, transcript and protein informaCon pages – Onchocerca volvulus • ComparaCve Genomics – Pris4onchus pacificus • Sequence Similarity Search (BLAST) – Strongyloides ra: • Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) * • Receive more care and a]enCon • Advanced Search Tool (BioMart) • Community driven manual curaCon • Access to BioMart data using R * • Displayed in both WormBase and WormBase • ProgrammaCc Access (REST API) * ParaSite * = Not covered today – speak to us for more informaCon WormBase and WormBase ParaSite This aeernoon’s agenda… • wormbase.org is the 13:00 – 13:10 • IntroducCon to WormBase ParaSite home for highly curated 13:10 – 13:50 • data from C. elegans and Using the website other related nematodes • 13:50 – 14:30 Sequence search with BLAST • Genes from “core” • 14:30 – 15:00 parasites also displayed Coffee Break here • 15:00 – 15:15 ComparaCve Genomics • More genomic data for • 15:15 – 15:50 parasites available from Data Mining with BioMart parasite.wormbase.org • 15:50 – 16:00 Opportunity to ask quesCons Workshop Feedback • Feedback form located on last page of workshop booklet Part 1: Browsing and searching • Your feedback helps tailor future workshops • We would be very grateful if you could complete this before leaving 2
23/02/16 Part 1: summary Front page 1. Front page 2. LocaCng genomes 3. Searching 4. NavigaCng genes, transcripts and scaffolds 5. Adding your data 6. User accounts Front page Front page Front page Front page: browse genomes 3
23/02/16 LocaCng genomes Genomes list Genome pages Searching Search results Search results 4
23/02/16 Filtering search results Gene pages Gene pages GO terms Transcript pages: summmary Transcript pages: navigaCng 5
23/02/16 Transcript pages: protein domains LocaCon view: zooming LocaCon view: zooming LocaCon view: gene/transcript info LocaCon view: jump to… LocaCon view: configure 6
23/02/16 LocaCon view: export data LocaCon view: export data Data tracks - RNASeq Data tracks - RNASeq Adding your own data Adding your own data 7
23/02/16 Adding your own data User accounts • Saving a]ached data tracks • Sharing data tracks with collaborators • Saving configuraCon senngs User accounts User accounts: registering User accounts Part 2: ComparaCve Genomics in WormBase ParaSite 8
23/02/16 IntroducCon A word of cauCon… • During each release, we compute • Trees are re-calculated between each release phylogeneCc trees • Homologies which are poorly defined may not • Every gene is included from 120 species: be defined in next release – 99 helminths • Always check the %ID of each alignment – 9 free-living nematodes – 12 comparator species (e.g. human, mouse, etc) • Determine orthologues and paralogues Homology types Understanding the gene tree • Orthologues: any gene pairwise relaCon where the ancestor node is a speciaCon event – 1-to-1 orthologue – 1-to-many orthologue – Many-to-many orthologue • Paralogues: any pairwise relaCon where the ancestor node is a duplicaCon event Visual access to the trees Tabular access to tree data 9
23/02/16 What is BLAST? • BLAST = B asic L ocal A lignment S earch T ool Part 3: Sequence Similarity • Sequence similarity tool • Allows comparison of a query sequence, Search using BLAST against a database of sequences • Query = your nucleoCde or protein sequence • Database = the genome or proteome of any species What is BLAST? Types of BLAST BLAST Type Query Sequence Target Database • Input: BLASTN Nucleotide Genome (nucleotide) NucleoCde or protein sequence BLASTP Peptide Proteome (peptide) Search Parameters BLASTX Six frame translation of a Proteome (peptide) nucleotide sequence TBLASTX (slowest) Six frame translation of a Six frame translation of • Output: nucleotide sequence genome List of all hits ranked in order of staCsCcal TBLASTN Peptide Six frame translation of genome significance Using the ParaSite BLAST Using the ParaSite BLAST Defaults to the species you are currently browsing 10
23/02/16 Using the ParaSite BLAST Using the ParaSite BLAST Making sense of the results Making sense of the results • Score Used to assess the biological relevance by describing the alignment quality Higher score = higher similarity • E -value Probability that event occurred by chance (in short, a p -value that has been corrected for mulCple tesCng) Lower E -value = more significant result • %ID Percentage of your query sequence that matches the genome/proteome database Data-mining with BioMart Part 4: Data-mining with BioMart 11
Recommend
More recommend