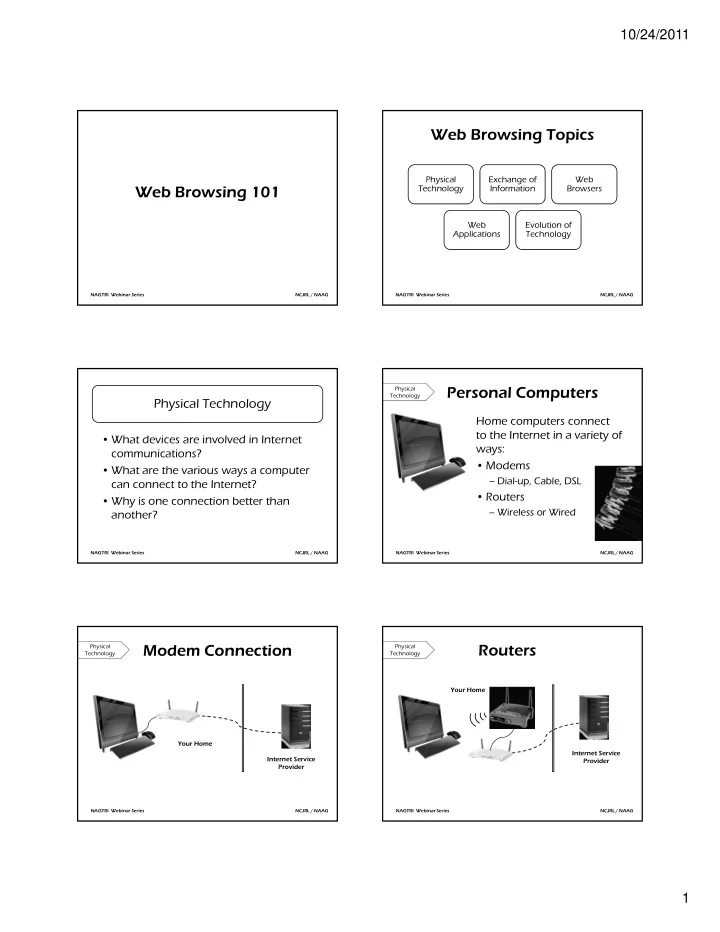

10/24/2011 Web Browsing Topics Physical Exchange of Web Web Browsing 101 Technology Information Browsers Web Evolution of Applications Technology NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG Personal Computers Physical Technology Physical Technology Home computers connect to the Internet in a variety of • What devices are involved in Internet ways: communications? • Modems • What are the various ways a computer – Dial-up, Cable, DSL can connect to the Internet? • Routers • Why is one connection better than – Wireless or Wired another? NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG Modem Connection Routers Physical Physical Technology Technology Your Home Your Home Internet Service Internet Service Provider Provider NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG 1
10/24/2011 Routers Cell Phones Physical Physical Technology Technology • Home routers may take two forms: – Wired – each computer connects to the router with a cable •Speeds of 100 Mbps – Wireless – computers connect through a User’s Cell Nearest Cell Cell signal that is broadcasted by the router Phone Towers Providers’ •Home wireless networks allow sharing of a Server connection as far as 750 feet •Unauthorized access is much easier •Speeds up to 125 Mbps NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG Internet Connections Office Networks Physical Physical Technology Technology • Many businesses utilize the same • At one time, dial-up was the predominant connection types as home users, but often way to connect to the Internet. Today, subscribe to a higher connection speed dial-up has been replaced so the user is constantly connected and receives higher • Larger businesses use a T1 or T3 speeds connection – Dial-up – 56 Kbps – Requires direct fiber optic connection – DSL – 245 Kbps to 20 Mbps – May cost more than $10,000 per month – T-3 – 44 Mbps • Even faster networks are available – 3G – 200 Kbps – Cost can exceed $5 million per month NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG The Path QUIZ Physical Physical Technology Technology 2 1 Which is a device that may be involved in a computer’s connection to the Internet? 3 A. Modem Home Computer Home Router B. Router C. User’s computer 4 5 D. ISP’s server Internet Service Provider E. All of the above Website Host Internet Exchange Point NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG 2
10/24/2011 QUIZ Physical Technology Exchange of Information Which Internet connection has the fastest speed? • What is the Internet? A. DSL • How do computers communicate with B. Dial-up each other? C. T3 • How is information sent across the Internet? D. 3G • Is it possible to track actions back to a specific person? NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG What is the Internet? What is TCP/IP? Exchange of Exchange of Information Information • A network of computers? • A set of rules governing the communication of computers online • A network of networks? • TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) – It is a network of millions of networks – Converts data into packets and reassembles • World Wide Web them into files for the user to read – Plus lots more. WWW is the most obvious • IP (Internet Protocol) part of the Internet, but it isn’t all of it – Handles addressing so that information is • Each computer on the Internet uses sent to the correct computer TCP/IP to communicate NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG IP Addressing IP Addressing Exchange of Exchange of Information Information • Each device on the Internet has a unique • Some businesses and organizations have IP address, such as this one: a range of IP addresses assigned to them – 317.23.90.134 – Government agency ranges can easily be found on the Internet • Computers, servers, and even printers – Disney, for example, uses 224.0.19.0 - have an IP address 224.0.19.63 • Addresses are usually temporary • ISPs also have a range of IP addresses to – In some cases, “static” addresses are assigned assign to their users permanently NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG 3
10/24/2011 IP Addressing IP Addressing Exchange of Exchange of Information Information Ro Rout uter • If a network utilizes a router, there are Internal: 172.168.1.4 two IP addresses involved External: 190.56.292.002 – Inte Internal al: each computer has an internal IP address that distinguishes the computers on Comp mput uter 1 1 Comp mput uter 3 3 the network Internal: 172.168.1.1 Internal: 172.168.1.3 External: 190.56.292.002 External: 190.56.292.002 – Ex Exter ternal al: the unique IP address assigned to the router by the ISP •Data is received at the external IP address by the router, and then the router sends the information Comp mput uter 2 2 to the correct internally-addressed computer Internal: 172.168.1.2 External: 190.56.292.002 NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG IP Tracking Exchange of Coffee Shop Coffee Shop Information Internal: 172.168.1.102 External: 235.71.90.123 • Since every computer has a unique address, actions on the Internet can The Office The Office [somewhat] easily be traced back to the Internal: 172.168.1.195 user. External: 190.56.292.002 – A range of IP addresses is assigned to ISPs. If given a certain IP address, the ISP can be Home Ho me easily determined. External: 453.23.234.901 – The ISP can track the IP address to the account holder at a designated time. NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG MAC vs. IP Exchange of Coffee Shop Coffee Shop Information Internal: 172.98.1.102 External: 235.71.90.123 • While an IP address is assigned by a network, each computer also has a The Office The Office unique MAC address which is assigned Internal: 172.16.1.195 by the computer’s manufacturer External: 190.56.292.002 – IP = software – MAC = hardware Home Ho me • Example: External: 453.23.234.901 – 70-F3-95-38-1F-06 NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG 4
10/24/2011 TCP – Packet Switching TCP – Packet Switching Exchange of Exchange of Information Information A B A B File is broken into smaller Sending File from pieces called “packets” Computer A to Computer B NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG TCP – Packet Switching TCP – Packet Switching Exchange of Exchange of Information Information A A B B The packets are not sent through The packets are labeled with the same path. There are billions of addressing information paths they may take. NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG TCP – Packet Switching QUIZ Exchange of Exchange of Information Information Which is not a step in packet switching? A. Attaching addressing information A B B. Sending packets C. Putting the packets back together D. Encrypting the information so it cannot be received by the wrong person When the packets arrive, they must be put back together. NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG NAGTRI Webinar Series NCJRL / NAAG 5
Recommend
More recommend