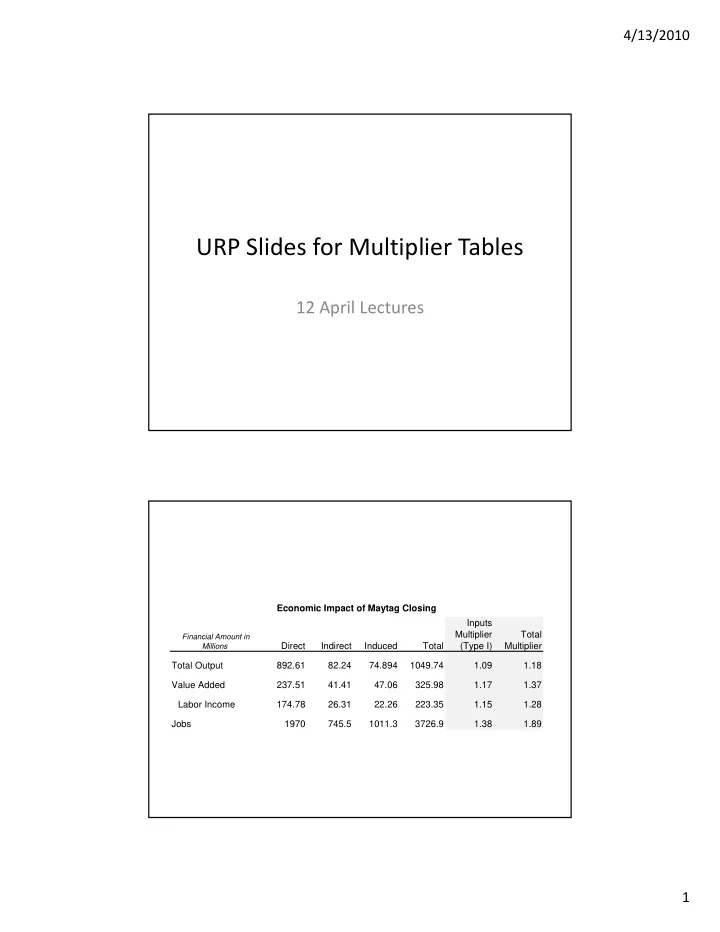

4/13/2010 URP Slides for Multiplier Tables 12 April Lectures Economic Impact of Maytag Closing Economic Impact of Maytag Closing Inputs Multiplier Total Financial Amount in Direct Indirect Induced Total (Type I) Multiplier Millions Total Output 892.61 82.24 74.894 1049.74 1.09 1.18 Value Added 237.51 41.41 47.06 325.98 1.17 1.37 Labor Income 174.78 26.31 22.26 223.35 1.15 1.28 Jobs 1970 745.5 1011.3 3726.9 1.38 1.89 1
4/13/2010 Using Multipliers There are two kinds that are generated by our model: d l Type I (or Type Inputs) Type Total Type 1 = (direct + indirect) / direct Type Total = (total effects) / direct Type Total = (total effects) / direct Refer to previous table Using the Multipliers Say we had a new plastics manufacturer wanting t l to locate in Iowa. In its application for t i I I it li ti f economic development assistance it told the state that it would employ 45 workers, pay out a total of $1.96 million in labor incomes, and have gross sales (output) of $8.68 million. We could build a table that lets us apply our multipliers from a table of multipliers 2
4/13/2010 Table of Multipliers for Misc. Plastics Output Multiplier Direct Indirect Induced Type I Type Total 1.0 0.2516 0.2182 1.2516 1.4699 Labor Income Per $1,000,000 of Output Direct Indirect Induced Total Type I Type Total 0.2261 0.0714 0.0662 0.3636 1.3158 1.6085 Jobs Jobs Per $1,000,000 of Output Direct Indirect Induced Total Type I Type Total 5.1805 1.6207 2.2627 9.0639 1.3129 1.7496 So, we could calculate impacts Direct Values X Multiplier = Impact Output = $8.68 M X 1.4699 = $12.76 M Labor income = $1.96 M X 1.6085 = $ 3.15 M Jobs = 45 X 1.7496 = 78.7 3
4/13/2010 New scenario Now suppose that a new cookie factory was going to open but the only thing that it would i t b t th l thi th t it ld tell you was that it would employ 100 workers. What kinds of impacts could you calculate? Begin, again with a table of multipliers for the cookie industry Table of Multipliers for Cookie Manufacture Output Multiplier Di Direct I di Indirect I d Induced d T Type I Type Total I T T l 1.0 0.3724 0.1690 1.3724 1.5414 Labor Income Per $1,000,000 of Output Direct Indirect Induced Total Type I Type Total 0.1222 0.1078 0.0512 0.2812 1.8822 2.3017 Jobs Per $1,000,000 of Output Direct Indirect Induced Total Type I Type Total 2.6131 2.5238 1.7525 6.8894 1.9658 2.6365 4
4/13/2010 Interpolating the impacts Steps: 1 The table tells us that there are 2 631 jobs 1. The table tells us that there are 2.631 jobs per $1 million in direct output. So, 100 jobs / 2.631 = $38.01 million in expected direct output. 2. The table tells us that we would expect, per $1 million in direct output, $.1222 in direct $1 illi i di $ 1222 i di labor income. So. 38.01 in output X .1222 = $4.645 M in labor income Impacts continued Now we can do the direct values times the multipliers now just like before: lti li j t lik b f Output = $38.01 M X 1.5414 = $58.6 M Labor Inc. = $4.645 M X 2.3017 = $10.69 M Jobs = 100 X 2.635 = 263.5 5
4/13/2010 Comparisons The cookie multipliers are higher than th the plastic multipliers. l ti lti li Why is that? What is going on in the Iowa accounts that would make cookies worth more to an economy than plastics? than plastics? Why do we need to be careful when we are declaring our economic impacts? 6
4/13/2010 Furniture Store Sales Economic Impact Demonstration Per Dollar of Sales 0.6 0.4 0 09 0.09 0.2 0.16 0.10 0 -0.06 -0.14 -0.2 -0.56 Indirect taxes Other value added -0.4 0 Labor income Local inputs -0.6 -0.08 Other imports Cost of goods sold -0.8 Initial Round Inputs Round Household Round 7
4/13/2010 A bill of goods approach First, read the REGIONAL MULTIPLIERS:A User Handbook for the Regional Input ‐ Output Modeling Handbook for the Regional Input ‐ Output Modeling System (RIMS II) ‐‐ Read the introduction through page 9 plus the case examples. Pay particular attention to Case Studies 3 and 4 as that is all that we will cover in this class. We have already used a multipliers approach to an economic impact. Now we are going to shift away from the multipliers to another approach. Using industry inputs Sometimes we do not know much about an industry or the industry is not well described i d t th i d t i t ll d ib d in our modeling system. To compensate, we can look at the balance sheet of an industry to identify its major inputs into production, and the estimated p p , percent of those inputs that are purchased locally, along with its payments to labor. 8
4/13/2010 Bill of Goods Analysis • This gives us a “Bill of Goods” or “Analysis of I Inputs” method for estimating impacts t ” th d f ti ti i t • It is a little more complicated but it is very useful, especially when there is limited information about an industry or the industry is a new type that does not resemble old yp industries. Needs • We need a multiplier table – I will have one for the state of Iowa h f th t t f I available for use • We also need to translate household spending (the earnings of workers) properly. That too will be made p p y available for use. 9
4/13/2010 Multiplier Table Vegetable Oilseed Grain and melon farming farming farming Direct 1.0 1.0 1.0 Indirect Indirect 0.2828 0.2828 0.3014 0.3014 0.1851 0.1851 Output Induced 0.2669 0.2511 0.3931 Multiplier Type I 1.2828 1.3014 1.1851 Type Total 1.5497 1.5525 1.5782 Direct 0.2718 0.2432 0.4490 Per $1.0 Indirect 0.0677 0.0781 0.0560 Million of Labor Induced 0.0809 0.0761 0.1192 Output Income Total 0.4203 0.3975 0.6241 Type I 1.2490 1.3212 1.1247 Type Total 1.5467 1.6342 1.3901 Direct 5.7378 8.9062 3.3600 Per $1.0 Indirect 1.9780 2.4502 1.8734 Million of Induced 2.7666 2.6036 4.0755 Jobs Output Total 10.4824 13.9600 9.3088 Type I 1.3447 1.2751 1.5575 Type Total 1.8269 1.5674 2.7705 Example Furniture Economic Impact Per $1,000,000 in Output Total Impacts Percent of Input Inputs (Sector) Inputs Amounts Output Labor Income Jobs Sawmill (112) 20% 351,360 60,520 1.96 Wholesale (390) 10% 155,000 55,730 1.25 Plastic parts (177) 5% 73,495 18,180 0.45 Trucking (394) 8% 132,368 44,400 1.14 Labor 30% 297,912 88,731 3.03 Imports 27% * * * 10
4/13/2010 First we calculate the input values Furniture Economic Impact Per $1,000,000 in Output Total Impacts Percent of Input Inputs (Sector) Inputs Amounts Output Labor Income Jobs Sawmill (112) 20% 200,000 351,360 60,520 1.96 Wholesale (390) 10% 100,000 155,000 55,730 1.25 Plastic parts (177) 5% 50,000 73,495 18,180 0.45 Trucking (394) 8% 80,000 132,368 44,400 1.14 Labor b 30% % 300,000 297,912 88,731 3.03 Imports 27% 270,000 * * * Next input amounts are translated into total impacts for those sectors using multipliers Output Multiplier Output Multiplier Direct Indirect Induced Type I Type Total 112 Sawmills 1.0 0.5736 0.1831 1.5736 1.7568 390 Wholesale trade 1.0 0.2140 0.3360 1.2140 1.5500 Plastics plumbing fixtures 177 and all other plas 1.0 0.2516 0.2182 1.2516 1.4699 394 Truck transportation 1.0 0.3185 0.3361 1.3185 1.6546 11
4/13/2010 For the total output impacts Furniture Economic Impact Per $1,000,000 in Output p $ , , p Total Impacts Percent of Input Inputs (Sector) Inputs Amounts Output Labor Income Jobs Sawmill (112) 20% 200,000 351,360 60,520 1.96 Wholesale (390) 10% 100,000 155,000 55,730 1.25 Plastic parts (177) 5% 50,000 73,495 18,180 0.45 Trucking (394) 8% 80,000 132,368 44,400 1.14 Labor 30% 300,000 297,912 88,731 3.03 Imports 27% 270,000 * * * For the labor income impacts: Multiplier Table Labor Income Per $1.0 Million of Output Direct Indirect Induced Total Type I Type Total 112 Sawmills 0.1440 0.1031 0.0555 0.3026 1.7158 2.1013 390 Wholesale trade 0.3781 0.0773 0.1019 0.5573 1.2045 1.4738 Plastics plumbing fixtures 177 and all other plas 0.2261 0.0714 0.0662 0.3636 1.3158 1.6085 394 Truck transportation 0.3396 0.1135 0.1019 0.5550 1.3344 1.6344 12
4/13/2010 We multiply the input value times the “Total” labor income multiplier per $1 million Furniture Economic Impact Per $1,000,000 in Output F rnit re Economic Impact Per $1 000 000 in O tp t Total Impacts Percent of Input Inputs (Sector) Inputs Amounts Output Labor Income Jobs Sawmill (112) 20% 200,000 351,360 60,520 1.96 Wholesale (390) 10% 100,000 155,000 55,730 1.25 Plastic parts (177) 5% 50,000 73,495 18,180 0.45 Trucking (394) g ( ) 8% 80,000 , 132,368 , 44,400 , 1.14 Labor 30% 300,000 297,912 88,731 3.03 Imports 27% 270,000 * * * Last we do the same thing for the jobs multipliers Jobs Per $1.0 Million of Output Direct Indirect Induced Total Type I Type Total 112 Sawmills 3.9471 3.9635 1.8986 9.8092 2.0042 2.4852 390 Wholesale trade 6.7986 2.1935 3.4834 12.4756 1.3226 1.8350 Plastics plumbing fixtures 177 and all other plas 5.1805 1.6207 2.2627 9.0639 1.3129 1.7496 394 Truck transportation 8.1225 2.6591 3.4847 14.2663 1.3274 1.7564 13
Recommend
More recommend