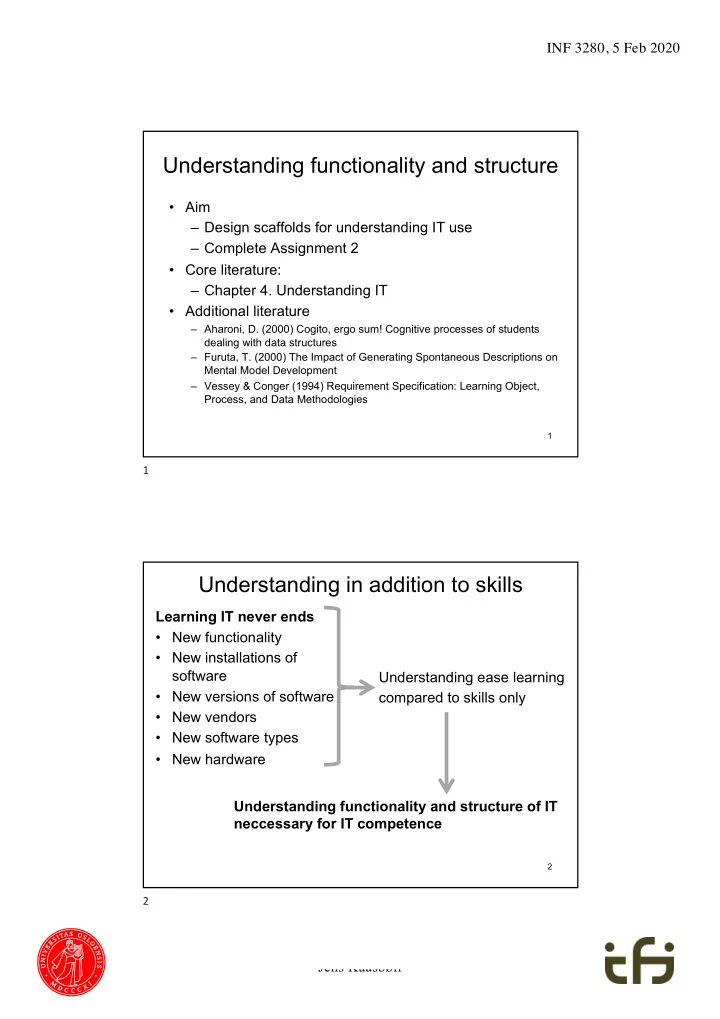

INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Understanding functionality and structure • Aim – Design scaffolds for understanding IT use – Complete Assignment 2 • Core literature: – Chapter 4. Understanding IT • Additional literature – Aharoni, D. (2000) Cogito, ergo sum! Cognitive processes of students dealing with data structures – Furuta, T. (2000) The Impact of Generating Spontaneous Descriptions on Mental Model Development – Vessey & Conger (1994) Requirement Specification: Learning Object, Process, and Data Methodologies 1 1 Understanding in addition to skills Learning IT never ends • New functionality • New installations of software Understanding ease learning • New versions of software compared to skills only • New vendors • New software types • New hardware Understanding functionality and structure of IT neccessary for IT competence 2 2 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Type the Column letter. Type the Row number. In order to have one cell refer to another, one has to get the coordinates of the other cell into the formula Cell-referencing is an ingredient in formulas 3 3 Levels of ease of understanding Process modeling Easy Restaurant Data and Occupancy Room Cleaning expense object modelling Restaurant Customer Reservation Invoicee Difficult Event Travel Agent Organiser 4 Vessey & Conger, 1994 4 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Structural models – scaffolds for structural understanding • Recognisable • Simple – Only essentials 5 5 Data structures • 1-many relationship between customer and address – Not explicitly stated Restrictions on values 6 6 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 1. Find the data structures • Outline views • Data models • Deduce from user interface 7 7 2. Decide main and sub structure types • Sequence • Grid (array, matrix) Combinations? • Hierarchy • Network 8 8 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 3. Decide user group • Most users Visit Visit-ID • Entering and reporting à Only data Patient Visit-type • Superusers • Setting up data structures à Include types 9 9 4. Include abstract entities • Events in the Domain represented by a record Occupancy From date # nights # guests Reservation • Planned events From date # nights # guests Room type 10 10 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 5. Include examples • In the model Customer Reservation Name: Fjoralba From date: 24.03.14 Address: Oslo # nights: 3 Phone: 123456 # guests: 2 Email: fj@mail.com Room type: Luxe • Relate to New reservation recognisable places Name Fjoralba in the user interface # guests 2 From 24 March 2014 # nights 2 Room type Luxe 11 11 Structural models for intermediate level users Occupancy Room From date Type # nights # beds # guests Price Customer Reservation Name From date Address # nights Phone # guests Email Room type 12 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Types and Instances •Description of a common •A unit of data adhering to set of symbols and the type operations Integer 234 -2 1 000 000 Number without decimals Calculation operators :Account Account 18 473.32 Balance Kari Owner Class Objects :Account Deposit 3 292.00 Withdraw Ola 13 13 Obtaining a structrural understanding You know recipies for Sure. making food? And knitting Yes, I normally patterns and follow patterns. sweaters? Styles and paragraphs are similar. Styles determine the layout of paragraphs. 14 14 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Structural model of IT – Generalisation-specialisation Data link Specialisations Cross reference - inside a document Hyperlink - between files 15 15 • Recognisable • Simple – Only essentials 16 Unknown notation Recognisable 16 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Functional and Structural model of IT – Discrimination Hyperlink P C a s o t p e y - Inconsistencies when Inconsistencies avoided 17 updating the spread sheet 17 Microsoft Help Word > Page breaks and section breaks > Insert a section break 18 18 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Hyperlink 19 19 Video • Make learners feel being in a conversation – We and you – Learning agent – Natural voice • Describe complex visuals with audio only 20 20 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Exploiting both the visual and oral channels Pictures Visual Eyes processing Written Long term Very limited text memory capacity Phonetic Ears processing Speech • Teaching and videos à Minimum of written text 21 21 Testing understanding A style is a … Questioning the learners a. document which looks good. – What is a … b. collection of formatting for a document. c. common set of formatting for all paragraphs. – What is the result of … d. collection of formatting for a paragraph. – What is the difference between … e. sequence of characters of the same shape. f. uniformly looking document. Not – How do you … – Where do we find … 22 22 Jens Kaasbøll
INF 3280, 5 Feb 2020 Summary Which types of learning material c does this Excel tutorial consist of? 3. Provide functional and structural models and confront misconceptions. 23 23 Jens Kaasbøll
Recommend
More recommend