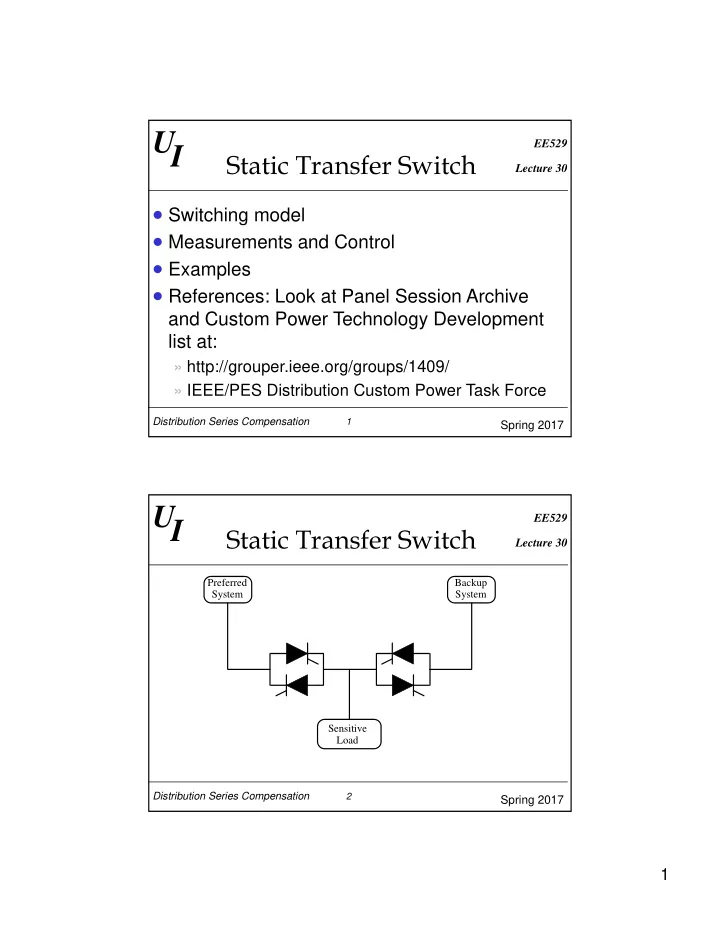

UI EE529 Static Transfer Switch Lecture 30 Switching model Measurements and Control Examples References: Look at Panel Session Archive and Custom Power Technology Development list at: » http://grouper.ieee.org/groups/1409/ » IEEE/PES Distribution Custom Power Task Force Distribution Series Compensation 1 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Static Transfer Switch Lecture 30 Preferred Backup System System Sensitive Load Distribution Series Compensation 2 Spring 2017 1
UI EE529 Static Transfer Switch Lecture 30 Fire thyristors continually on preferred Fire thyristors continually on preferred source » No phase delay » Synchronize on the current Continually measure voltage (PLL or other y g ( scheme) and track voltage magnitude Stop gating when sag detected Distribution Series Compensation 3 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Static Transfer Switch Lecture 30 Gate thyristors on alternate source when Gate thyristors on alternate source when stop on preferred source Won’t clear first source until natural current zeros » Fast detection of sag is key g y » Assumes generally don’t see a sag on two separate distribution feeders very often Distribution Series Compensation 4 Spring 2017 2
UI EE529 Modeling the STS Lecture 30 Type 11 switches for the devices Type 11 switches for the devices Synchronization and gate pulse generation Magnitude and phase calculation Distribution Series Compensation 5 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Example Case Lecture 30 Use PLL defined earlier for » Sychronization » Computing magnitude of phase A voltage Identify sag based on this magnitude compared to a reference level Check phase angle difference between Ch k h l diff b t sources before transfer Distribution Series Compensation 6 Spring 2017 3
UI EE529 Example Case Lecture 30 Preferred Source Voltage 12 [kV] 8 4 0 -4 -8 Alternate Source Voltage 12 [kV] -12 8 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 [ms] 80 (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) v:STSLA v:STSLB v:STSLC 4 0 -4 -8 -12 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 [ms] (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) v:STSRA v:STSRB v:STSRC Distribution Series Compensation 7 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Example Continued Lecture 30 Preferred Source Current Load Voltage 40 12 [A] [kV] 30 8 20 4 10 0 0 -10 -4 -20 -8 -30 -12 -40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 0 15 30 45 60 75 90 [ms] [ms] (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) v:LOADA v:LOADB v:LOADC (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) c:BUS1LA-STSLA c:BUS1LB-STSLB c:BUS1LC-STSLC Alternate Source Current 50 [A] 35 20 5 -10 -25 Distribution Series Compensation 8 Spring 2017 -40 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 [ms] (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) c:BUS2RA-STSRA c:BUS2RB-STSRB c:BUS2RC-STSRC 4
UI EE529 Example Continued Lecture 30 Firing Permission for Main Sw itches 1.1 0.8 0.5 0 5 0.2 -0.1 -0.4 Magnitude Calculation--Left Source -0.7 12 *10 3 -1.0 0 15 30 45 60 75 [ms] 90 10 (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) t: TRANS 8 6 4 2 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 [ms] (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) t: MAGNL Distribution Series Compensation 9 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Unbalanced Faults Lecture 30 Phase B to Ground Phase A to Ground 12 12 *10 3 *10 3 10 10 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 [ms] 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 [ms] (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) t: MAGNL (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) t: MAGNL B-C to Ground 12 *10 3 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 [ms] (file sts2.pl4; x-var t) t: MAGNL Distribution Series Compensation 10 Spring 2017 5
UI EE529 ATPDraw Circuit Lecture 30 GT1RA GT1LA I I I I GT2LA GT2RA GT1LB GT1RB LOAD V I GT2LB GT2RB GT1LC GT1RC GT2LC GT2RC Distribution Series Compensation 11 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Sag Detection Lecture 30 Sag Detection Logic g g Convert to components MAGL x T VLOW F T x y MAGL OUTOLL y MAGR F T x T MAGR x y VLOW VMINOK y VMINOK INTOLR T T 0.75 pu 0.9 pu TFLATC ANGMIN T T 0.5 15 deg Distribution Series Compensation 12 Spring 2017 6
UI EE529 Transfer Qualification Lecture 30 Transfer Logic ONE8T x x T ANGLR T y x + |x| PI * y + ANGDIF * -360 x THETAR + + x y K - - y POS180 THETAL * -360 x POS180 NEG180 NEG180 x y y K y T T Distribution Series Compensation 13 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Transfer Qualification Lecture 30 ANGMIN TRANSF x PLUS1 T + x y Two - y OUTOLL K INTOLR TRANSF TFLATC ZERO x T LEFTOK MINUS1 x y G u y DELAYT 58 Distribution Series Compensation 14 Spring 2017 7
UI EE529 Control Right Side Lecture 30 TFLATC TFLATC x TRIGA TFLATC x y BUS1LA x TRIGA |x| MINUS1 TRTA y x T T G u RAOK x y T 58 LEFTOK ZERO RFIRA y 54 TRIGB TFLATC TFLATC x MINUS1 TRTB x T x y G u RBOK x BUS1LB TRIGB |x| x y y 58 ZERO RFIRB y 54 T LEFTOK TRIGC TFLATC TFLATC x MINUS1 TRTC x T x y x y G u G u RCOK RCOK x BUS1LC TRIGC |x| x y y 58 ZERO RFIRC y 54 T LEFTOK Distribution Series Compensation 15 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Firing Circuit Lecture 30 RFIRA GT1RA GT2RA GT2RA LEFTOK GT2LA LEFTOK GT1LA RFIRA * * * T * T x T VARSYN T VALSYN x x y x y ZERO y ZERO y RFIRB GT1RB GT2LB GT2RB LEFTOK RFIRB LEFTOK GT1LB * * * T * T T VBRSYN x T VBLSYN x x y x y ZERO y ZERO y RFIRC GT1RC LEFTOK GT2LC GT2RC LEFTOK LEFTOK GT1LC GT1LC RFIRC RFIRC * * * T * T T VCRSYN x x T VCLSYN x y x y ZERO y ZERO y Distribution Series Compensation 16 Spring 2017 8
UI EE529 Lecture 29 M d li Modeling and Analysis of a d A l i f Flywheel Energy Storage System with a Power Converter Interface Series Compensation Fall 2003 UI Static Series Compensator EE529 Lecture 30 with Stored Energy Supply Correct oltage sags seen b critical loads Correct voltage sags seen by critical loads Isolate loads from the faulted system Respond before loads trip Presently slow protection and slow breakers Scheme that can be implemented with S h th t b i l t d ith present day technology Distribution Series Compensation 18 Spring 2017 9
UI EE529 Storing Energy Lecture 30 Chemical Energy (Batteries) Electrostatic Energy (Ultracapacitors) Electromagnetic Energy (SMES coil) Kinetic Energy (Flywheels) Ki ti E (Fl h l ) Distribution Series Compensation 19 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Advantages of Flywheel Lecture 30 Low cost High power density Greater number of charge-discharge cycles Longer life Longer life Distribution Series Compensation 20 Spring 2017 10
UI EE529 Energy Stored in Flywheel Lecture 30 1 2 E 2 I I is moment of inertia I is moment of inertia is angular velocity Distribution Series Compensation 21 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Types of Flywheel Lecture 30 High Speed Hi h S d » use high angular velocity » vacuum with magnetic bearings Low Speed » use large inertia Distribution Series Compensation 22 Spring 2017 11
UI EE529 Basic Circuit Diagram Lecture 30 DVR Voltage Supply Voltage + = Load Voltage Distribution Series Compensation 23 Spring 2017 UI EE529 FESS single line diagram Lecture 30 M Distribution Series Compensation 24 Spring 2017 12
UI EE529 Method of Operation Lecture 30 Charge mode g » energy flows from the power system to the flywheel » increasing flywheel speed to rated Floating Mode » at rated speed only supply energy to overcome losses Discharge mode » energy flows from the flywheel to the shipboard system » decreasing flywheel speed Distribution Series Compensation 25 Spring 2017 UI EE529 FESS Modeling Lecture 30 EMTDC Models EMTDC M d l Field oriented control AC drive model Static series compensator model Laboratory version in near future Distribution Series Compensation 26 Spring 2017 13
UI EE529 Field Oriented Control Lecture 30 AC Drive M Field Oriented Control AC Drive Distribution Series Compensation 27 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Static Series Compensator Lecture 30 M Static Series Compensator Distribution Series Compensation 28 Spring 2017 14
UI Field Oriented Control EE529 Lecture 30 AC Drive Induction machine model Indirect field oriented controller Space vector PWM pulse generator S t PWM l t Distribution Series Compensation 29 Spring 2017 Basic Voltage UI EE529 Source Converter Lecture 30 + 6 switches 1 5 3 8 combinations Vdc A B C 6 active vectors 2 4 6 2 zero vectors - Distribution Series Compensation 30 Spring 2017 15
UI Space Vector PWM Pulse EE529 Generator Model Lecture 30 sin V s T 1 3 T z II V dc 3 III I V s sin T 2 3 T z V dc IV VI V T 0 T z T 1 T 2 Distribution Series Compensation 31 Spring 2017 UI EE529 Space Vector PWM Pulses Lecture 30 Firing Pulse for IGBT-1 /Low) 1.0 Output (High/ -0.1 1.363 1.370 1.377 Time (s) Firing Pulses for IGBT-3 Output (High/Low) 1.0 -0.1 1 363 1.363 1.370 1 370 1 377 1.377 Time (s) Firing Pulses for IGBT-5 Output (High/Low) 1.0 -0.1 1.363 1.370 1.377 Time (s) Distribution Series Compensation 32 Spring 2017 16
Recommend
More recommend