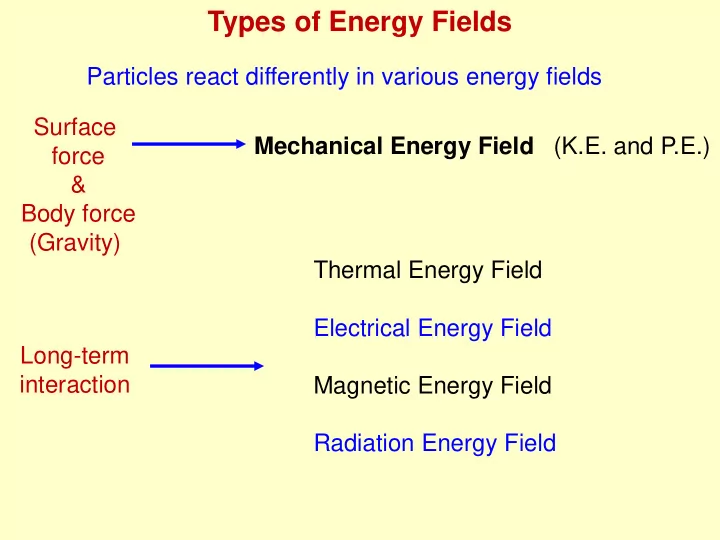

Types of Energy Fields Particles react differently in various energy fields Surface Mechanical Energy Field (K.E. and P.E.) force & Body force (Gravity) Thermal Energy Field Electrical Energy Field Long-term interaction Magnetic Energy Field Radiation Energy Field
Types of Energy Fields Particles react differently in various energy fields Surface Mechanical Energy Field (K.E. and P.E.) force & Body force Most widely used in Geotechnical Engg. (Gravity) Loading of soil mass results in high density & low volume (combination of K.E., P.E., Thermal Energy (friction between particles), Sound & Light Energies----due to crushing of grains) Total Energy of the soil mass changes (i.e. change in orientation of soil particles) Compression of gases in voids, more dissolution of gases in pore solution elastic strains of soil grains, characteristics of double layer
Mechanical Energy Field Potential Energy (Position) and Kinetic Energy (Motion) Potential Energy is stored within a physical system. Can be released or converted into other forms of energy, say Kinetic Energy. Types of PE: (each is associated with a particular kind of force). Elastic force is Elastic Potential Energy. Gravitational force is Gravitational Potential Energy Coulomb force is Electric Potential Energy Nuclear force is Nuclear Potential Energy
Potential Energy Compaction Consolidation Distortion Bending & Crushing Kinetic Energy
Bending Crushing
Potential Energy Compaction Consolidation Distortion Bending & Crushing Kneading Shearing Kinetic Energy Movement of water through porous media Vibration
Mechanical Energy Field • All short term processes • Ignore influence of the Environment Load, Deformation, Velocity, Weight, Mass, Wave, Sound Foundation design Governing Laws Flow through porous media Acid rains • Darcy’s Toxic/Hazardous wastes • Hook’s Nuclear waste storage/containment • Newton’s Land slides • Law of motion Earthquakes
Recommend
More recommend