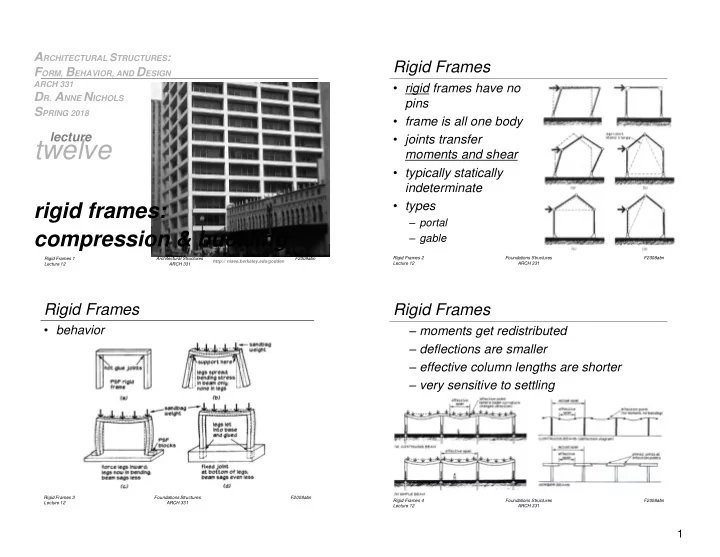

A RCHITECTURAL S TRUCTURES : Rigid Frames F ORM, B EHAVIOR, AND D ESIGN ARCH 331 • rigid frames have no D R. A NNE N ICHOLS pins S PRING 2018 • frame is all one body lecture • joints transfer twelve moments and shear • typically statically indeterminate • types rigid frames: – portal compression & buckling – gable Rigid Frames 2 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 1 Architectural Structures F2009abn http:// nisee.berkeley.edu/godden Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Rigid Frames Rigid Frames • behavior – moments get redistributed – deflections are smaller – effective column lengths are shorter – very sensitive to settling Rigid Frames 3 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 4 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 1
Moment Redistribution Rigid Frames • continuous slabs & beams with uniform • resists lateral loadings loading • shape depends on – joints similar to fixed ends, but can rotate stiffness of beams • change in moment to center = 2 wL and columns – M max for simply supported beam 8 • 90° maintained Rigid Frames 6 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 5 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Rigid Frames Rigid Frames • staggered truss • connections – rigidity – steel – clear stories – concrete http:// nisee.berkeley.edu/godden www.arcchicago.blogspot.com Rigid Frames 7 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 8 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 2
Braced Frames Braced Frames • types of bracing • pin connections – knee-bracing • bracing to prevent lateral movements – diagonal – X diagonal X – K or chevron – shear walls K (chevron) shear walls Rigid Frames 10 Foundations Structures F2008abn http:// nisee.berkeley.edu/godden Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Rigid Frames 9 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Shear Walls Compression Members • resist lateral load in plane with wall • designed for strength & stresses • designed for serviceability & deflection • need to design for stability – ability to support a specified load without sudden or unacceptable deformations Rigid Frames 11 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 12 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 3
Column Buckling Modeling • • axially loaded columns • can be modeled with a spring at mid-height • when moment • long & slender from deflection – unstable equilibrium = buckling exceeds the – sudden and not good spring capacity ... “ boing ” • critical load P Rigid Frames 13 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 14 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Effect of Length Buckling Load • short & stubby • related to deflected shape (P ) • long & slender • shape of sine wave • Euler ’ s Formula • smallest I governs 2 EI P critical 2 L Rigid Frames 15 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 16 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 4
Critical Stress Critical Stresses • short columns • when a column gets stubby, F y will limit the P load actual f F critical a • real world has loads A with eccentricity • slenderness ratio = L e /r (L/d) • C c for steel and I allowable stress r • radius of gyration = weak axis A 2 2 E 2 L 2 2 2 EA P EAr E C e critical P f r c critical F critical 2 2 2 A A L L L y e e e r r Rigid Frames 17 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 18 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Effective Length Bracing • end conditions affect shape • bracing affects shape of buckle in one direction • effective length factor, K L e K L • both should be checked! Rigid Frames 20 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 19 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 5
Centric & Eccentric Loading Combined Stresses • centric – axial + bending – allowable stress from strength or buckling P Mc f • eccentric max A I – combined stresses M P e – design f cr cr f F max F . S . Rigid Frames 21 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 22 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Stress Limit Conditions Stress Limit Conditions – in reality, as the column flexes, – ASD interaction formula the moment increases f f f a a b 1 . 0 F a F F – P- effect a b 1 – with biaxial bending f f ( Magnificat ion factor ) f f f f a b 1 . 0 by b a bx 1 1 . 0 F F F b a bx F F F a bx by interaction diagram Rigid Frames 24 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 23 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 6
Rigid Frame Analysis Rigid Frame Analysis • members see – need support reactions – free body diagram each member – shear – end reactions are equal and opposite on – axial force next member – bending – “ turn ” member • V & M diagrams like beam – plot on “ outside ” – draw V & M Rigid Frames 25 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 26 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Rigid Frame Analysis Rigid Frame Design – FBD & M • loads and combinations P • opposite end – usually uniformly distributed gravity loads reactions at joints – worst case for largest moments... – wind direction can increase moments M+ Rigid Frames 27 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 28 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 7
Rigid Frame Design Rigid Frame Design • frames & floors • floors – plates & slabs – rigid frame can have slab floors or slab – one-way behavior with connecting beams • side ratio > 1.5 • other • “ strip ” beam – two-way behavior – slabs or plates • more complex on columns Rigid Frames 29 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 30 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Rigid Frame Design Rigid Frame Design • columns in frames • column effective length, k – ends can be “ flexible ” – stiffness affected by beams A and column = EI/L EI l c G EI B – for the joint l b • l c is the column length of each column • l b is the beam length of each beam • measured center to center Rigid Frames 31 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 32 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 8
Tools – Multiframe Tools – Multiframe • in OAL and VOAL • frame window – define frame members • or pre-defined frame – select points, assign supports – select members, assign section – load window – select point or member, add point or distributed loads Rigid Frames 34 Foundations Structures F2008abn Rigid Frames 33 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Lecture 12 ARCH 331 Tools – Multiframe • to run analysis choose – Analyze menu • Linear • plot – choose options • results – choose options Rigid Frames 35 Foundations Structures F2008abn Lecture 12 ARCH 331 9
Recommend
More recommend