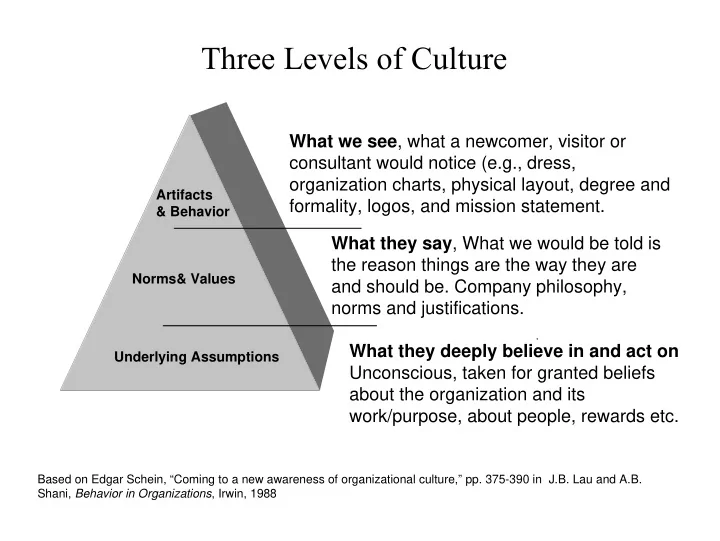

Three Levels of Culture What we see , what a newcomer, visitor or consultant would notice (e.g., dress, organization charts, physical layout, degree and Artifacts formality, logos, and mission statement. & Behavior What they say , What we would be told is the reason things are the way they are Norms& Values and should be. Company philosophy, norms and justifications. . What they deeply believe in and act on Underlying Assumptions Unconscious, taken for granted beliefs about the organization and its work/purpose, about people, rewards etc. Based on Edgar Schein, “Coming to a new awareness of organizational culture,” pp. 375-390 in J.B. Lau and A.B. Shani, Behavior in Organizations , Irwin, 1988
Company Goals Employee Goals Profit A Paycheck Long Term Growth Success Good Benefits Long Term Contribute to Mutual A Safe Economy Prosperity Workplace Contribute to Meaningful Society Work Good Quality Mutual Trust
A Partnership between an Organization & its Employees Organization provides Stable Employment & Sustains or Improves Working Conditions Organizational Employees Respect Prosperity is Satisfaction is Partnership achieved experienced Mutual Trust through through the Continuous Continuous Continuous Improvement Improvement Improvement Process Employees Contribute Efforts to Realize Company Objectives
Make problems and opportunities for kaizen visible. Safety Quality Productivity Cost HR Standardized Work, 5-S PDCA Visual Control (Andon, Line-stop, Visual Management) Problem Solving (Daily Activities, QC Circle, Suggestions)
The Toyota Way Toyota Basic Business Practices THE TOYOTA TOYOTA W AY W AY THE by concentrating know ledge Team w ork of each & every em ployee Respect for the benefit of all for People Respect custom ers & stakeholders w e strive to realize Challenge am bitious goals Continuous Genchi through steady, fact- driven I m provem ent Genbutsu progress Kaizen pursuing highest standards of excellence guided by best Values Values possible course of action Practices
Identifying Lean Core Competencies Thinking and Operational Abilities � Grasp the Situation � � Problem Solving � � Process Management � � Company Business Perspective � � Development � � Operational and Technical Skills �
Identifying Lean Core Competencies Leadership & Teamwork Abilities � Coordinate and Communicate � � Collaborate and Cooperate � � Initiate and Influence � � Build and Maintain Relationships �
Phase 1 Advertizing & Recruitment Process for Georgetown, Kentucky Applicants Original Recruitment to Selection 142,000 Phase 2 Orientation, Application & Testing Passed 28,000 Phase 3 Assessment Center Passed 12,000 Phase 4 Final Screening Passed 8000 Phase 5 Assess Health & References Job Offers 6000 Phase 6 Probation
Example on-line Simulation for Second Phase Testing
Applicant doing simulated “welding” exercise in the Assessment Area
Step-by-Step Progression to Stable Job Performance ID Fundamental Skills for a Class of jobs Train in Fundamental Skills off of Line (GPC) Continuously Improve Job & Job Instruction Job Breakdown to Work Elements for Specific Job Off-Line Skills Training Use Toyota Job Instruction (TJI) to Train Associate On-Job- Follow-up & Support Development until Masters Job
Example Video Manual
Example Simulated Jobs Simulations and Image Painting requires rhythm Training make hidden and precision work visible
THE OBJECTIVES OF THE OBJECTIVES OF STANDARDIZATION STANDARDIZATION • Reduce variability, increase predictability • Enhance repeatability, confidence, consistency • Clarify procedures • Enhance communication • Improve Problem Solving • Set good discipline • Develop awareness • Establish “Problem Consciousness” • Establish a basis for education and training • Establish a baseline for performance • Improve Quality, Safety, Delivery, Cost • Provide the basis for Improvement
The Four Steps of JIT Step 4: FOLLOW UP Step 1: PREPARE WORKER Action Plan Major Steps Key Points Check Reasons Do Step 3: TRY OUT Step 2: PRESENT PERFORMANCE OPERATION
Sample TMMK New Hire Training Program 2008 2010 2013 PHASE II: PHASE I: New Hire or Temporary TMMK New Hire Overview: Each Step: Plan= Classroom Training Action= Extend Do= OJT/ $$$ Homework Assignment *Final Problem Solving *Business Demonstration Check= Assess./ Direction Evaluation *STW III *Process Diagnostics *Conflict *Ergonomics Resolution *Two Way Communicat. *STW II. *KPIÕ s $$ Skills/Pay *Visual. *External Hire Control *Catch-up *Meeting Facilitation *STW *PDCA *A-3 *Problem *Teamwork Solving Grow-in *STW Ready $ Complete *QC Tools to Hire *Safety *Values *TPS 2 years 5 years Start 4/3/2006 OJT/Production Experience
Toyota Training and Development General Manager and VP Level Business Planning and Policy Deployment Tools: Hoshin Planning & Toyota Business Practices (TBP) Manager Level Focus on Shop Floor and Systems Improvement. Tools: Visual Factory & TBP Team Leader and Group Leader Manage Standardized Work, Process Improvement and Develop Problem Solving Skills. Tools: FMDS, TBP & OJD Team Member Focus on Fundamental Skills & Standardized Work Tools: Skills Training, Job Instruction, Standardized Work and 5-S
What is a problem in lean? In Lean, we appreciate problems! They are considered opportunities for Kaizen. We need to aggressively uncover them. Finding problems is the first step for problem solving. Otherwise there will be neither Kaizen ideas nor evolution in the future. At times it is our tendency to ignore or mask problems, in hopes they will disappear. This action could lead to increasing costs and muda. “No one has more trouble “No one has more trouble than the person who claims to have no trouble.” than the person who claims to have no trouble.” (Having no problems is the biggest problem of all.) (Having no problems is the biggest problem of all.) Taiichi Ohno Taiichi Ohno
Western versus Toyota View of Problems Traditional Western Toyota What is a problem? Result of someone messing Deviation from standard up What is the cause? Individual (5 Whos) System (5 Whys) Who is responsible? Person who makes mistake Management What should individual who Solve problem on own if Call attention to problem makes mistake do? possible for assistance and to avoid the problem in the future Assumptions about People They will not accept blame They will feel empowered if unless forced to they get positive support for solving problems Problem solving skill Some have it, some donÕ t It can and must be taught
PDCA in our Daily Work Business Planning Business Planning Project Management Project Management Problem Solving/Kaizen Problem Solving/Kai en Daily Work ily Work A P A P GtS GTS TOOLS C D TOOLS C D TO A-3 R 3 Repor eport A-3 A 3 Action Plans-Master on Plans-Master Schedule Schedule Hoshin Kanri
Toyota Continuous Improvement Culture Engineers & Pilot Teams Create Initial Standards Learning from Past Problems Work Teams Work Broader Problem to Standard and Solving to Level Up Detect Deviations System From Standards Continuous Improvement Work Team Root Work Teams Cause Problem Contain Solving Disruptions to Improves Standards Production Underlying Assumption: Human and Technical Processes are interrelated and dynamic so initial designs are only a rough starting point which must be continuously improved by every team member. Results: High levels of engagement at all levels in the actual process leads to continuous strengthening of the system and high congruence between expectations and reality.
Three Stages of Problem Solving Maintenance Kaizen Kaizen “Raising” New Goal “Maintaining” Goal “Reaching” • Problem Solving that focuses on increasing capability beyond the goal or to achieve a new • Problem Solving that focuses goal- “Kaizen”. • Problem Solving that results in on maintaining the goal. • Make efforts to challenge and improve upon the getting to the goal. • Establish system / procedures to standards. maintain the standards • Must establish standards and train t o the standards. Strict follow-up.
Recommend
More recommend