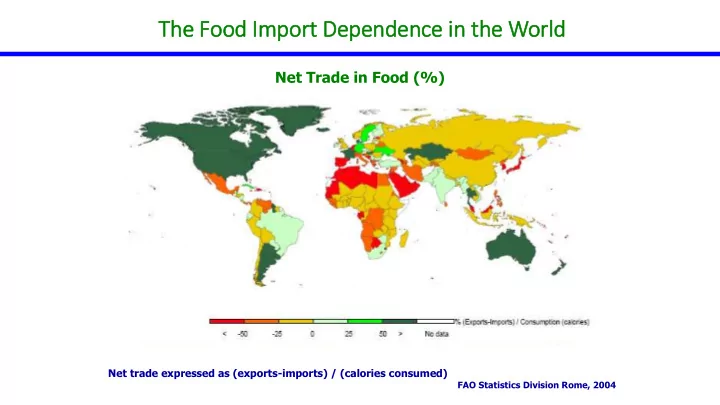

Th The Food Im Import t Dependence in in th the World Net Trade in Food (%) Net trade expressed as (exports-imports) / (calories consumed) FAO Statistics Division Rome, 2004
Food Surpluses and Deficit in Different Regions of the World Food Surplus and Deficit in Different Parts of the World From the Economist Online, 28 May 2012
Global Cereal Trade: Cereal imports and exports (in million MT) in different parts of the world in 2007, 2010 and 2013. ARAB ENVIRONMENT IN 10 YEARS
Food insecurity in developing regions of the world Cereals imports of developing regions 1970-2030 Historical Development Projections 240 East Asia South Asia 190 million tonnes Near East/North Africa (Arab countries) Latin America 140 S.S.Africa 90 40 -10 1970 1980 1990 2000 2015 2030 Source: FAO, 2002 World Agriculture: Towards 2015/30. http://www.fao.org/es/ESD/gstudies.htm
Implications of the Food Crisis Most developing countries are moving from self-reliance to self sufficiency
Potential of Arab countries to enhance food security based on agricultural potential (renewal water resources, arable land area, soil fertility and irrigated area) ARAB ENVIRONMENT IN 10 YEARS
Total renewable water resources per capita (2007-2014) in Arab countries (FAO AQUASTAT, 2017) Average Per Capita Water Resources − World average: 7000 m3 − Arab world average: 813 m3 (2011) Absolute water scarcity level: 500 m 3 − Water Poverty level ARAB ENVIRONMENT IN 10 YEARS
Policies and Actions Finance, Governance and Innovation Drivers Food Energy Policies Production Impacts Economic Food & Improving Livelihoods Natural Nutritional Security & National Resources (renewal Environmental Economic water resources) Sustainability Growth Climate Change Poverty Reduction Technological Health Institutional Labor Market Gender Equity Expertise & Labor force Demographic Water
Importance of Mountains Ecosystem to Global Environment, Food Security and Livelihoods Mountains are important towers of water reservoirs that provide 70% of world fresh water including irrigation water; Mountain ecosystems are key source of different types of renewal energy including hydropower, solar energy, wind power and biomass fuels such as wood. Water streams and rivers along with the mountains altitude gradient provide hydropower: Wind flow and circulation and high solar radiation in the mountains provide renewal sources of solar and wind energy.
Importance of Mountain Ecosystem to Water, Energy and Food Nexus Moutains & River Basin Source: ICIMOD
Recommend
More recommend