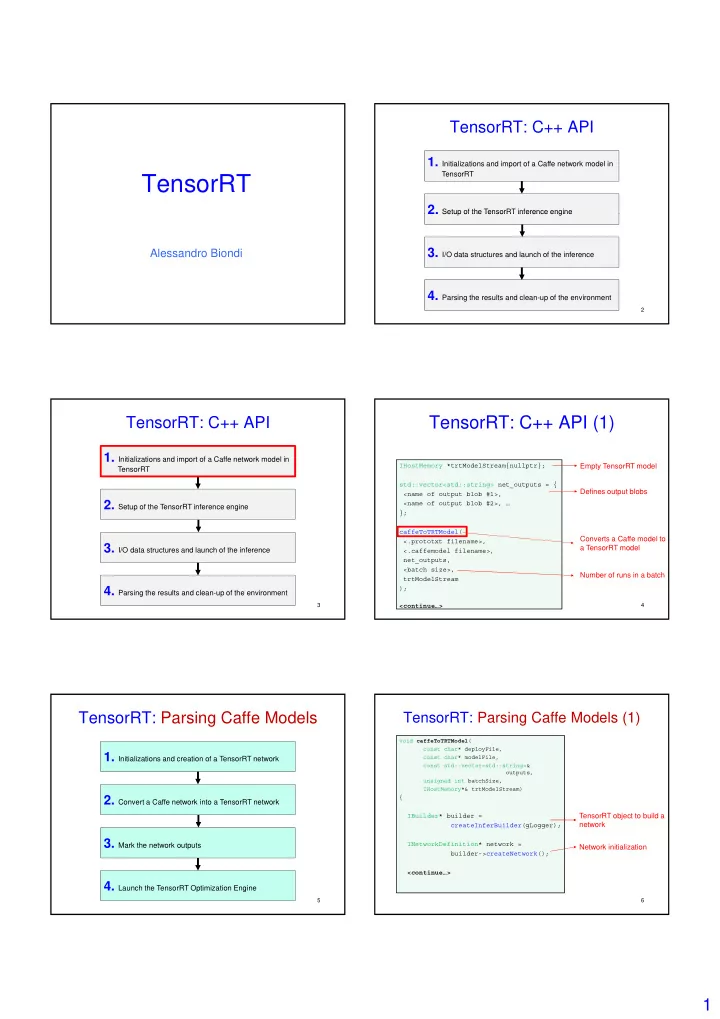

TensorRT: C++ API 1. Initializations and import of a Caffe network model in TensorRT TensorRT 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine 3. I/O data structures and launch of the inference Alessandro Biondi 4. Parsing the results and clean-up of the environment 2 TensorRT: C++ API TensorRT: C++ API (1) 1. Initializations and import of a Caffe network model in IHostMemory *trtModelStream{nullptr}; Empty TensorRT model TensorRT std::vector<std::string> net_outputs = { Defines output blobs <name of output blob #1>, 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine <name of output blob #2>, … }; caffeToTRTModel( Converts a Caffe model to <.prototxt filename>, 3. I/O data structures and launch of the inference a TensorRT model <.caffemodel filename>, net_outputs, <batch size>, Number of runs in a batch trtModelStream ); 4. Parsing the results and clean-up of the environment 3 <continue…> 4 TensorRT: Parsing Caffe Models TensorRT: Parsing Caffe Models (1) void caffeToTRTModel ( const char* deployFile, 1. Initializations and creation of a TensorRT network const char* modelFile, const std::vector<std::string>& outputs, unsigned int batchSize, IHostMemory*& trtModelStream) 2. Convert a Caffe network into a TensorRT network 2. Convert a Caffe network into a TensorRT network { IBuilder* builder = TensorRT object to build a createInferBuilder(gLogger); network 3. Mark the network outputs INetworkDefinition* network = Network initialization builder->createNetwork(); <continue…> 4. Launch the TensorRT Optimization Engine 5 6 1
TensorRT: Parsing Caffe Models (2) TensorRT: Parsing Caffe Models (3) void caffeToTRTModel ( void caffeToTRTModel ( const char* deployFile, const char* deployFile, const char* modelFile, const char* modelFile, const std::vector<std::string>& const std::vector<std::string>& outputs, outputs, unsigned int batchSize, unsigned int batchSize, IHostMemory*& trtModelStream) IHostMemory*& trtModelStream) { { <…> <…> ICaffeParser* parser = TensorRT object to parse for(auto& s : outputs) Caffe networks createCaffeParser(); network->markOutput( Tells TensorRT which are *blobNameToTensor->find( the output blobs const IBlobNameToTensor* s.c_str() blobNameToTensor = parser->parse( )); deployFile, modelFile, builder->setMaxBatchSize( Parse the network Sets the maximum batch *network, maxBatchSize); size DataType::kFLOAT); <continue…> 7 <continue…> 8 TensorRT: C++ API TensorRT: Parsing Caffe Models (4) void caffeToTRTModel ( const char* deployFile, 1. Initializations and import of a Caffe network model in const char* modelFile, TensorRT const std::vector<std::string>& outputs, unsigned int batchSize, IHostMemory*& trtModelStream) { 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine <…> Launches the TensorRT ICudaEngine* engine = optimization engine builder->buildCudaEngine(*network); 3. I/O data structures and launch of the inference The optimized network is trtModelStream = engine->serialize(); serialized for portability network->destroy(); parser->destroy(); engine->destroy(); 4. Parsing the results and clean-up of the environment builder->destroy(); } 9 10 TensorRT: C++ API (2) TensorRT: C++ API 1. Initializations and import of a Caffe network model in <…> TensorRT IRuntime* runtime = Creates TensorRT runtime createInferRuntime(gLogger); engine 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine ICudaEngine* engine = Retrieves the optimized runtime->deserializeCudaEngine( network trtModelStream->data(), trtModelStream->size(), NULL 3. I/O data structures and launch of the inference ); Initializes the execution IExecutionContext* context = context for TensorRT engine->createExecutionContext(); 4. Parsing the results and clean-up of the environment <continue…> 11 12 2
TensorRT: C++ API (3) TensorRT: Launching inference void doInference (…) <…> { float inputData[<batch size> * Allocates the input buffer const ICudaEngine& engine = Retrieves the network <input size>]; context.getEngine(); void* buffers[<num input blobs> + struct OUTPUT_RESULT outputData; Allocates the output buffers Pointers to GPU input and <num output blobs>]; output buffers fillImageData(inputData); fillImageData(inputData); Fills the input buffer // for each input blob Get id of input buffer int inputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex doInference( (<name of input blob>); *context, cudaMalloc(&buffers[inputIndex], Allocate input buffer on <batch size>, <input size>); GPU memory inputData, Launches the inference! outputData // for each output blob ); Get id of output buffer int outputIndex = engine.getBindingIndex <continue…> (<name of output blob>); cudaMalloc(&buffers[outputIndex], Allocate output buffer on <output size>); GPU memory 13 14 <continue…> TensorRT: Launching inference TensorRT: C++ API void doInference ( IExecutionContext& context, 1. Initializations and import of a Caffe network model in int batchSize, float* input, TensorRT struct OUTPUT_RESULT& output) { <…> 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine 2. Setup of the TensorRT inference engine // for each input cudaMemcpy(buffers[inputIndex], input, Copy input buffer to the inputSize, GPU input buffer cudaMemcpyHostToDevice) Launch the inference! 3. I/O data structures and launch of the inference context.execute(batchSize, buffers); (blocking call) // for each output cudaMemcpy(output.<buffer>, Copy GPU output buffer to buffers[outputIndex], output buffer 4. Parsing the results and clean-up of the environment <output size>, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost) 15 16 <free buffers> TensorRT: C++ API (4) ResNet18 • DNN for object classification and detection • Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun, “Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition” • Available as a Caffe model • We use a pre-trained version that detects 3 classes ( people, two wheelers, <…> and cars ) Extract the output data parseResult(outputData); (details will follow) context->destroy(); engine->destroy(); Cleaning up the runtime->destroy(); environment <delete allocated dyn memory> 17 18 3
ResNet18: input ResNet18: outputs Input size = 1*3*368*640 640 368 19 20 ResNet18: outputs ResNet18: outputs X columns • For each class, one bbox for each cell The number of columns and rows are fixed parameters of the DNN Y rows Each Bbox is For each class c , each cell characterized by (x,y) is assigned to a confidence of top-left edge , and in [0, 1] with which an item (x,y) of bottom-right of c is detected edge 21 22 ResNet18: outputs ResNet18: outputs • Confidence values are meant to be compared with thresholds • Final bboxes are built with post-processing 0.2 0.35 0.8 0.9 0.9 0.7 0.9 With a threshold 0.8 0.6 set to 0.3 , this 0.35 0.8 bbox is discarded 23 24 4
Recommend
More recommend