Survey of Concepts for QoS Improvements via SDN Atanas Mirchev - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit at M unchen Survey of Concepts for QoS Improvements via SDN Atanas Mirchev Chair for Network Architectures and Services Department for Computer Science Technische
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Survey of Concepts for QoS Improvements via SDN Atanas Mirchev Chair for Network Architectures and Services Department for Computer Science Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen April 9, 2015 Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 1
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Outline Motivation Introduction to SDN and QoS Overview of existing QoS approaches Resource reservation Per-flow path optimization Enqueuing of packets Policy enforcement Framework comparison and assessment Concluding remarks Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 2
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Motivation ◮ Traditional approaches to providing Quality of Service for single services or specific tenants are limited and inflexible [4] Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 3
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Motivation ◮ Traditional approaches to providing Quality of Service for single services or specific tenants are limited and inflexible [4] ◮ A scalable solution is needed that allows for fine-grained traffic tuning Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 3
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Motivation ◮ Traditional approaches to providing Quality of Service for single services or specific tenants are limited and inflexible [4] ◮ A scalable solution is needed that allows for fine-grained traffic tuning ◮ Software Defined Networking (SDN) brings a lot of freedom and monitoring possibilities [5] [2] Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 3
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Software Defined Networking ◮ Without SDN each forwarding device has to be configured separately Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 4
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Software Defined Networking ◮ Without SDN each forwarding device has to be configured separately ◮ SDN introduces a control plane, decoupled from the forwarding plane Figure: Simplified representation of the SDN architecture Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 4
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Software Defined Networking ◮ Without SDN each forwarding device has to be configured separately ◮ SDN introduces a control plane, decoupled from the forwarding plane ◮ the SDN controller is centralized Figure: Simplified representation of the SDN architecture Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 4
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Quality of Service ◮ QoS consists of all quality aspects of data transmission (response time, jitter, interrupts, etc.) Figure: Quality of Service is based on priorities Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 5
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Quality of Service ◮ QoS consists of all quality aspects of data transmission (response time, jitter, interrupts, etc.) ◮ Application flows need to be differentiated and assigned priorities Figure: Quality of Service is based on priorities Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 5
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Quality of Service ◮ QoS consists of all quality aspects of data transmission (response time, jitter, interrupts, etc.) ◮ Application flows need to be differentiated and assigned priorities ◮ Defining policies should be a simple task Figure: Quality of Service is based on priorities Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 5
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Traditional approaches to QoS ◮ Integrated Services : fine-grained but not well scalable ◮ Differentiated Services: scalable but coarse-grained (only 8 classes of flows in the DiffServ field, part of the IP header) Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 6
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen SDN-enabled approaches Technische Universit¨ at M¨ Figure: QoS via SDN unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 7
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Resource reservation Frameworks of this type consist of: ◮ Flow classifier (considers any of DiffServ field, 5-Tuple, Port number) ◮ Rate shaper - installs rules for each classified flow type Example frameworks: ◮ FlowQoS - small scale framework for home routers [3] ◮ EuQoS - large scale, adaptable to the current Internet, differentiates only tenant flows [4] ◮ Princeton - large scale, proposes an adaptive flow aggregator for application flows with similar priority [6] Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 8
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Per-flow path optimization ◮ dynamic placement of high priority flows on QoS guaranteed routes Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 9
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Per-flow path optimization ◮ dynamic placement of high priority flows on QoS guaranteed routes ◮ the path determination is done using the overall network state obtained by the controller Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 9
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Per-flow path optimization ◮ dynamic placement of high priority flows on QoS guaranteed routes ◮ the path determination is done using the overall network state obtained by the controller ◮ scalability issues are expected Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 9
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Per-flow path optimization ◮ dynamic placement of high priority flows on QoS guaranteed routes ◮ the path determination is done using the overall network state obtained by the controller ◮ scalability issues are expected ◮ OpenQoS [2] is a framework representing this class Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 9
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Enqueuing of packets ◮ the standard queue type in OpenFlow 1.3 is FIFO [7] ◮ in a lot of cases, putting packets with higher priority in front is beneficial (e.g. congested node) ◮ QoSFlow [7] is a framework that creates a separate bucket for each priority and sends the packages via a Round Robin approach Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 10
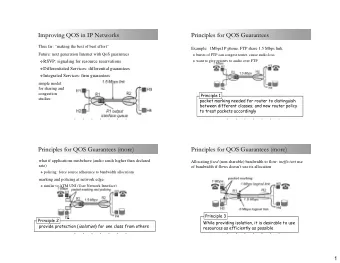
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Policy enforcement ◮ a robust approach for applying predefined SLA (Service-level Agreements) to the network is required, most of the traditional technologies are proprietary Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 11
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Policy enforcement ◮ a robust approach for applying predefined SLA (Service-level Agreements) to the network is required, most of the traditional technologies are proprietary ◮ SDN represents the possibility of a single standardized API for configuring policies Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 11
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Policy enforcement ◮ a robust approach for applying predefined SLA (Service-level Agreements) to the network is required, most of the traditional technologies are proprietary ◮ SDN represents the possibility of a single standardized API for configuring policies ◮ the framework PolicyCop [5] utilizes the Northbound API of an SDN controller to define policies in a standard way, which are then enforced on the forwarding plane Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 11
Chair for Network Architectures and Services Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen Framework comparison and assessment FlowQoS [3]: Pros: Cons: ◮ small framework which ◮ not a generalized solution every user could apply at for the Internet home ◮ lack of tests and thus any ◮ focus on multimedia performance figures streaming ◮ no performance guarantees ◮ prototype Technische Universit¨ at M¨ unchen – Chair for Network Architectures and Services 12
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.