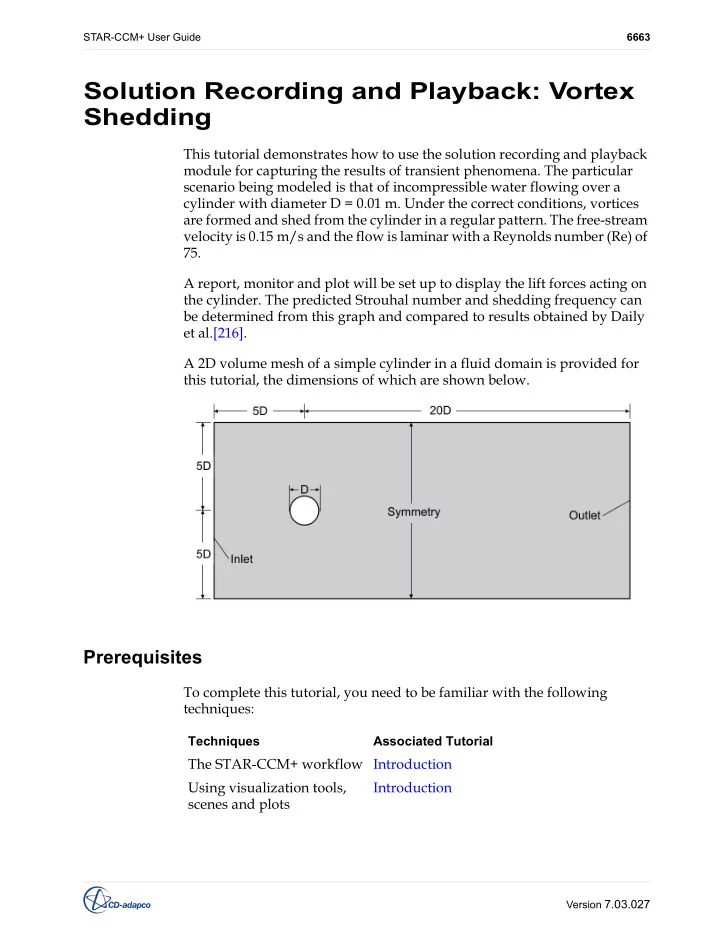

STAR-CCM+ User Guide 6663 Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding This tutorial demonstrates how to use the solution recording and playback module for capturing the results of transient phenomena. The particular scenario being modeled is that of incompressible water flowing over a cylinder with diameter D = 0.01 m. Under the correct conditions, vortices are formed and shed from the cylinder in a regular pattern. The free-stream velocity is 0.15 m/s and the flow is laminar with a Reynolds number (Re) of 75. A report, monitor and plot will be set up to display the lift forces acting on the cylinder. The predicted Strouhal number and shedding frequency can be determined from this graph and compared to results obtained by Daily et al.[216]. A 2D volume mesh of a simple cylinder in a fluid domain is provided for this tutorial, the dimensions of which are shown below. Prerequisites To complete this tutorial, you need to be familiar with the following techniques: Techniques Associated Tutorial The STAR-CCM+ workflow Introduction Using visualization tools, Introduction scenes and plots Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6664 Importing the Mesh • Start up STAR-CCM+ in a manner that is appropriate to your working environment and create a New Simulation . • Save the new simulation to disk with the file name vortexShedding.sim We will begin by importing the volume mesh. • Select File > Import > Import Volume Mesh from the menu. The Open dialog will appear. • Navigate to the /doc/tutorials/simpleFlow subdirectory of your STAR-CCM+ installation directory and select vortexSheddingDomainMesh.ccm A geometry scene is automatically created after the mesh has been successfully imported. The boundaries have been pre-defined, so no further action is required. • Create a mesh scene and examine the 2D mesh. Selecting Physics Models A physics continuum was added to the object tree when the volume mesh was imported. We will select the physics models required to run this case. Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6665 The fluid used in this tutorial is water, and the flow is incompressible and laminar. Vortex shedding is a periodic phenomenon and will require the use of a transient solver. • Rename the Continua > Physics 1 continuum to Fluid . • Right-click on the Fluid > Models node and choose Select models... The Fluid Model Selection dialog will guide you through the model selection process. Select the following models: • Implicit Unsteady from the Time box. • Liquid from the Material box. • Coupled Flow from the Flow box. • Constant Density from the Equation of State box. • Laminar from the Viscous Regime box. • Click Close . The selected models are shown in the Fluid > Models node in the object tree. Modifying Material Properties and Setting Initial Conditions Modify the material properties of water, so that the correct Reynolds number is obtained. • Within the Fluid continuum, select the Models > Liquid > H2O > Material Properties > Density > Constant node and set its Value property to Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6666 1 kg/m^3 • Select the Dynamic Viscosity > Constant node and set its Value property to 2.0E-5 Pa-s Set the initial conditions so that the simulation will begin with the fluid in a state of motion. • Select the Fluid > Initial Conditions > Velocity > Constant node. In the Properties window, set the Value property to [0.15, 0.0, 0.0] m/s Setting Boundary Conditions Set the required velocity at the inlet boundary. • Select the Regions > Fluid_Domain > Boundaries > Inlet > Physics Conditions > Velocity Specification node. In the Properties window, Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6667 set the Method property to Components . • Select the Inlet > Physics Values > Velocity > Constant node and set its Value property to [0.15, 0.0, 0.0] m/s • Save the simulation . Creating a Scalar Scene Create a scalar scene displaying vorticity. This will be used to visualize the solution while the simulation is running. • Create a new scalar scene. • Click on the scene/plot button located above the object tree. Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6668 • Select the Displayers > Scalar 1 > Scalar Field node. • In the Properties window set the Function property to Vorticity > Magnitude . • In the same window, set the following properties: Property Value Min 0 Max 28 Clip Off • Select the Displayers > Scalar 1 node. In the Properties window, set the Contour Style property to Smooth Filled . • Click on the simulation button to return to the STAR-CCM+ simulation object tree. We will add an annotation displaying solution time to the scene. • Expand the Tools > Annotations node and drag the Solution Time node Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6669 into the scene. The Solution Time annotation is added to the bottom left of the scene. Preparing the Lift Plot We will monitor the lift that the cylinder wall is experiencing. This will be used to determine the period of oscillation for the vortex shedding. First create a report: • Right-click on the Reports node and select New Report > Force Coefficient . • Rename the new plot to Coefficient of Lift . In the Properties window of the Coefficient of Lift node, do the following: • Set the Reference Velocity to 0.15 m/s • Set the Reference Area to 0.01 m^2 • Set the Force Option to Pressure . • Set the Direction to [0.0, 1.0, 0.0] • Click to the right of the Parts property. In the object selection dialog, tick Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6670 the checkbox next to Regions > Fluid_Domain > Cylinder . The completed Properties window is shown below. Create a monitor and plot from this report. • Right-click on the Coefficient of Lift node and select Create Monitor and Plot from Report . Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6671 A new monitor and plot is added to the Monitors and Plots nodes respectively. We will now modify the monitor so that the data is plotted against time; the default setting would plot the data against iterations. • Select the Monitors > Coefficient of Lift Monitor node. In the Properties window, set the Trigger property to Time Step . • Open the Coefficient of Lift Monitor Plot by right-clicking on its node in the object tree and selecting Open . Modifying Solver Settings Modify the solver settings to more appropriate values for this case. Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6672 • Select the Solvers > Implicit Unsteady node. • In the Properties window, set the Time-Step to 0.02 s • In the same window, set the Temporal Discretization to 2nd-order . • Select the Solvers > Coupled Implicit node and set its Courant Number property to 100 Setting Up Stopping Criteria Reduce the number of inner iterations for each time step and extend the maximum time the solver will be allowed to run. • Select the Stopping Criteria > Maximum Inner Iterations node and set its Maximum Inner Iterations property to 15 • Select the Stopping Criteria > Maximum Physical Time node and set its Maximum Physical Time property to 8 s • Save the simulation Setting Up the Solution History File Create a new solution history ( .simh ) file and use it to store selected solution data at specified time intervals. Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6673 • Right-click on the Solution Histories node and select New... The Save dialog appears. Choose a location where you would like to store the solution history file. • Enter vortexSheddingData.simh as the name of the solution history file. • Click Save . Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6674 A new sub-node containing the name of the solution history file is added to the object tree below the Solution Histories node. The red asterisk next to this node means that data will be actively written to the file when the simulation runs. Choose what data to save to the solution history file. As this is a vortex shedding case it would be appropriate to store the results for pressure, velocity and vorticity. • Select the Solution Histories > vortexSheddingData node. In the Properties window, click on the ( property customizer ) button next to the Scalar Functions property. The Scalar Functions dialog appears. • Use the > ( Add selected ) button to select the following items: • Pressure • Velocity Version 7.03.027
STAR-CCM+ User Guide Solution Recording and Playback: Vortex Shedding 6675 • Vorticity The selections are added to the right-hand side column, as shown below. • Click OK to close the dialog. Set the frequency with which the selected data will be written to the solution history file. We would like the data to be written every time step. • Select the Solution Histories > vortexSheddingData > Update node and set its Update Policy property to Time Step . • Select the Update > Update Frequency node. In the Properties window, Version 7.03.027
Recommend
More recommend