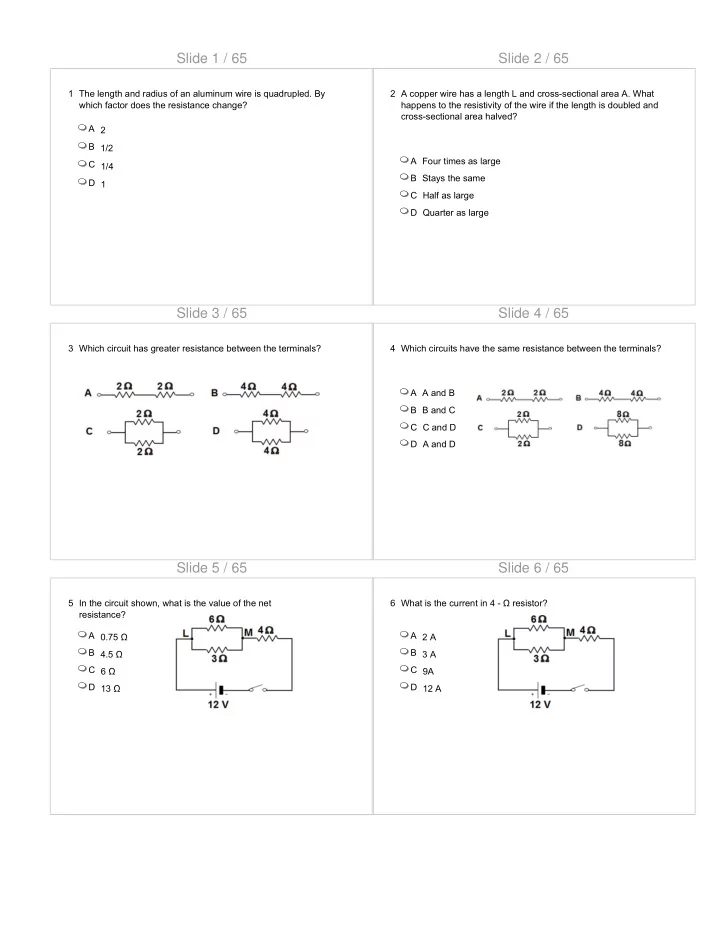
Slide 1 / 65 Slide 2 / 65 1 The length and radius of an aluminum - PDF document
Slide 1 / 65 Slide 2 / 65 1 The length and radius of an aluminum wire is quadrupled. By 2 A copper wire has a length L and cross-sectional area A. What which factor does the resistance change? happens to the resistivity of the wire if the
Slide 1 / 65 Slide 2 / 65 1 The length and radius of an aluminum wire is quadrupled. By 2 A copper wire has a length L and cross-sectional area A. What which factor does the resistance change? happens to the resistivity of the wire if the length is doubled and cross-sectional area halved? A 2 B 1/2 A Four times as large C 1/4 B Stays the same D 1 C Half as large D Quarter as large Slide 3 / 65 Slide 4 / 65 3 Which circuit has greater resistance between the terminals? 4 Which circuits have the same resistance between the terminals? A A A and B B B B and C C C C and D D D A and D Slide 5 / 65 Slide 6 / 65 5 In the circuit shown, what is the value of the net 6 What is the current in 4 - Ω resistor? resistance? A 0.75 Ω A 2 A B 4.5 Ω B 3 A C 6 Ω C 9A D 13 Ω D 12 A
Slide 7 / 65 Slide 8 / 65 7 What is the voltage between points L and M? 8 A lamp L1, a voltmeter V, an ammeter A, and a battery with zero internal resistance are connected as shown above. Connecting another lamp L2 in series with the first lamp as shown by the A 2 V dashed lines would B 4 V A Increase the ammeter reading C 8 V B Increase the voltmeter reading D 12 V C Decrease the ammeter reading D Decrease the voltmeter reading Slide 9 / 65 Slide 10 / 65 9 The four resistors shown below have the lengths and cross- 10 The circuit shown above left is made up of a variable resistor and a sectional areas indicated and are made of material with the same battery with negligible internal resistance. A graph of the power P resistivity. Which has the smallest resistance? dissipated in the resistor as a function of the current I supplied by the battery is given above right. What is the emf of the battery? A A 0.125 V B B 5 V C C 8 V D D 40 V Slide 11 / 65 Slide 12 / 65 11 The total equivalent resistance of the circuit shown on the diagram 12 A heating spiral of resistance R converts elec-trical energy into is: thermal energy that is transferred to the liquid in which the spiral is immersed. If the voltage across the spiral is V, the thermal energy trans-ferred to the liquid in time t is: A 2 Ω B 6 Ω A Vrt C 9 Ω B V 2 Rt D 18 Ω C VR 2 t D V 2 t/R
Slide 13 / 65 Slide 14 / 65 13 In the circuit two identical resistors R are connected in series with 14 Questions 14-16 relate to the following circuit diagram which 8-W resistor and 12- V battery. What is the value of R if the current shows a battery with an internal resistance of 2.0 ohms connected in the circuit I = 1 A? to an 8-ohm and a 10-ohm resistor in series. The current in the 10- ohm resistor is 0.2 amperes. What is the emf of the battery? A 2 Ω B 4 Ω A 0.4 V C 8 Ω B 3.6 V D 12 Ω C 4 V D 12 V Slide 15 / 65 Slide 16 / 65 15 Questions 14-16 relate to the following circuit diagram which 16 Questions 14-16 relate to the following circuit diagram which shows a battery with an internal resistance of 2.0 ohms connected shows a battery with an internal resistance of 2.0 ohms connected to an 8-ohm and a 10-ohm resistor in series. The current in the 10- to an 8-ohm and a 10-ohm resistor in series. The current in the 10- ohm resistor is 0.2 amperes. What is the potential difference ohm resistor is 0.2 amperes. What power is dissipated by the 2- across the terminals A and B of the battery? ohm internal resistance of the battery? A 1.2 V A 0.08 W B 2.4 V C 3.6 V B 0.8 W C 1.2 W D 12.2 V D 6.5 W Slide 17 / 65 Slide 18 / 65 17 In the diagrams above, resistors R1 and R2 are shown in two 18 The product 3 amperes x 3 volts x 3 seconds is equal to different connections to the same source of emf e that has no internal resistance. How does the power dissipated by the resistors A 27 C in these two cases compare? B 27 N A It is greater for the series connection. C 27 J B It is greater for the parallel connection. D 27 W C It is the same for both connections. D One must know the values of R1 and R2 to know which is greater.
Slide 19 / 65 Slide 20 / 65 19 The electrical resistance of the part of the circuit shown between 20 When there is a steady current in the circuit, the amount of charge point X and point Y is passing a point per unit of time is: A 1.4 ohms B 2.5 ohms C 6.2 ohms A the same everywhere in the circuit D 10 ohms B greater at point X than at point Y C greater in the 2 ohm resistor than in the 5 ohm resistor D the same in the 2 ohm resistor and in the 5 ohm resistor Slide 21 / 65 Slide 22 / 65 21 A certain coffeepot draws 2.0 A of current when it is operated on 22 Five identical light bulbs are connected to a 120 V power supply. 110 V household lines. If electrical energy costs 10 cents per Each light bulb has a resistance of 15 Ω. The switch is closed. kilowatt-hour, how much does it cost to operate the coffeepot for 5 What is the net resistance of the circuit? hours? A 3 Ω A 2.4 cents B 30.1 Ω B 4.8 cents C 40 Ω C 8.0 cents D 75 Ω D 11 cents Slide 23 / 65 Slide 24 / 65 23 Five identical light bulbs are connected to a 120 V power supply. 24 Five identical light bulbs are connected to a 120 V power supply. Each light bulb has a resistance of 15 Ω. The switch is closed. Each light bulb has a resistance of 15 Ω. The switch is closed. What is the current in the light bulb L 1 ? Which light bulb or bulbs could burn out without causing any others to go out? A 1.6 A A Only L 1 B 3 A B Only L 2 C 8 A C Only L 4 D 40 A D Only L 5
Slide 25 / 65 Slide 26 / 65 26 A circuit, shown above, has three resisters R-1 = 60Ω, R2 = 30Ω, 25 A circuit, shown above, has three resisters R-1 = 60Ω, R2 = 30Ω, and R3 = 20Ω, an internal resistance r = 4Ω, and a battery 120V. and R3 = 20Ω, an internal resistance r = 4Ω, and a battery 120V. If V 1 represents the potential difference across the first resistor, What is the relationship between the three labeled currents? V2 across the second resistor, V3 across the third resistor and V the terminal voltage in the battery. What is the relationship between the V 1 , V 2 , V 3 , and V? A I 1 =I 2 < I < I 3 B I 1 + I 2 + I 3 = I A V 1 = V 2 = V – V 3 C I 2 > I 1 > I 3 > I B V 1 + V 2 + V 3 = V D I 1 + I 2 = I 3 = I C V 1 = V 2 = V 3 < V D V > V 3 > V 2 > V 1 Slide 27 / 65 Slide 28 / 65 27 A circuit, shown above, has three resisters R-1 = 60Ω, R2 = 30Ω, 28 A battery has an emf of ε and an internal resistance of r. What and R3 = 20Ω, an internal resistance r = 4Ω, and a battery 120V. resistance R, when connected across the terminals of the battery What is the ratio of current I1 in resistor R1 to the current in I2 in will make the terminal voltage to be ½ ε? resistor R2? A ½ r B 2r C r D 4r A B C D Slide 29 / 65 Slide 30 / 65 29 Multi-correct Section: For each question or incomplete statement, 30 For each question or incomplete statement, two of the answers are two of the answers are correct. For each questions you must correct. For each questions you must select both answers. A select both answers. In reference to the circuit above, which of the single resistor is connected across the terminals of a battery. follow statements are true? Choose two answers. Which of the following will leave the power output unaffected? Choose two answers. A Reducing both the resistance and the voltage by a factor of 4. B Reducing the resistance by a factor of 4 and the voltage by A The current in R1 must be the same as the current in R2. a factor of 2. B The current in R3 must be the same as the current in the C Doubling both the resistance and the voltage. battery. D Doubling the voltage and increasing the resistance by a C The voltage across R1 must be the same as the voltage factor of 4. across R2. D The voltage across R3 must be the same as the voltage across the battery.
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.


















![CernVM[FS] and CMS Open Data Pilot Jakob Blomer, Gerardo Ganis, Adam Huffman, Kati](https://c.sambuz.com/777067/cernvm-fs-and-cms-open-data-pilot-s.webp)
