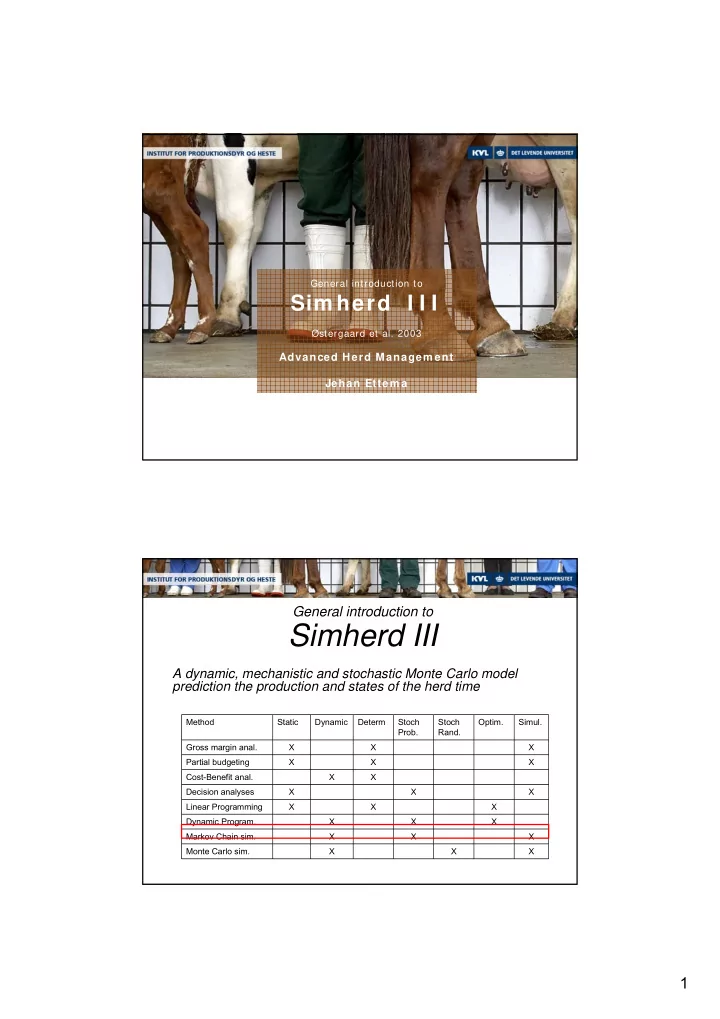

General introduction to Sim herd I I I Østergaard et al. 2003 Advanced Herd Managem ent Jehan Ettem a General introduction to Simherd III A dynamic, mechanistic and stochastic Monte Carlo model prediction the production and states of the herd time Method Static Dynamic Determ Stoch Stoch Optim. Simul. Prob. Rand. Gross margin anal. X X X Partial budgeting X X X Cost-Benefit anal. X X Decision analyses X X X Linear Programming X X X Dynamic Program. X X X Markov Chain sim. X X X Monte Carlo sim. X X X 1
General introduction to Simherd III A dynamic, mechanistic and stochastic Monte Carlo model prediction the production and states of the herd time ’89-’91: Research tool: Jan Tind Sørensen, DIAS ’91-’92: Further developed as advisory tool ’98: Simherd II, mimic four production diseases: Søren Østergaard ’98-’03: Simherd III: 8 diseases, modification feed intake, efficiency and body condition score. Østergaard, Sørensen and Hans Houe Input and output • What does the model do: • Simulation of technical and economical consequences of production strategies in dairy herds •Production strategie: postpone insemination start •Technical: disease prevalence, replacement rate •Economical: Margin per cow-year, income from milk sale 2
Many different projects and publications • Meaning of disease leves (1988) • Mortality and disease prevalence (1991) • SimHerd I + feedings, reproduction and culling strategy (1992) • Increase dry period (1993) • Replacement and reproductive strategies (1995) • BVD (1995) • Organic vs. Conventional production (1998) • Time of first insemination (1998) • Preventive strategies against stafylokokmastitis (1999) • SimHerd II + Interaction between feeding, health and production (2000) • AMS and replacement (2002) • Prolonged lactation (2003) • SimHerd III + control strategies against Milk Fever (2004) • Control strategies against ParaTB (2004) • Value of progesteron measurements (2004) • Early treatment of mastitis and ketose (2004) • Different types of mastitis • Clinical mastitis in different weeks of lactation (Sweden) • Incorporation of Bayesian analysis Herd data Outline of SimHerd III Statistical analysis SimHerd Simulation and SimCow HerdView presentation of annual Description of Description of results. feeding and event rates for other production the production Simulation of samples. strategy. strategy. Description and Presentation of Presentation of editing of initial herd. effects at cow short term level. simulations. Short term simulation of cow events. SimTest Technical-economic comparison of production strategies based on samples simulated by SimHerd. Overview of the Simherd-programmes and their interrelations 3
Input and output Input • State of nature: – Complete set of input parameters – Simherd: List of the cows’ and heifers’ ”starting values” on the starting date of simulation • Parameter values for relations in the model – Biological parameters – Parameters describing production system (capacity of the stable) – Parameters describing production strategy (feeding plan, culling decisions) Output: • Technical annual results – 10 years, 500-1000 replications Overview of steps in the simulation • Each cow at each week-step (dynamic) – Lactation stage – Reproduction status (Heat; Pregnancy; Abortion; Calving) – Diseases, death, culling for replacement and involuntary replacement – Net energy intake = Feed intake capacity + Feed available – Milk yield and weight gain = Utilized net energy - Maintenance – Fetus • Each heifer at each week-step – Age, Reproduction, Replacement, Feeding 4
Overview of steps in the simulation • The herd at each week-step – Replacement (Max cow number, Culled cows, Available down calving heifers, Strategy of buying and selling heifers) • State is updated and production and consumption are calculated • The herd after each year of simulation – File annual results • Ten years of simulation – Analyze averages of the last 5 years Outline of SimHerd III Events: stochastic – Probability of events happening is calculated with a logistic regression model • Conception • Culling • Disease • ... – Drawing samples from relevant probability distributions – Number generation by computer: X diseases does not occur 5
Outline of SimHerd III Mechanistic – Events on cow level determine ’behaviour’ on herd level – Replacement rate of the herd, determined by: • Culling strategy of the farmer (min. milk yield level, max. days open) • (Re)production of the individual cow Functioning on cow level x number of year cows (årskøer) ≠ Functioning on herd level Outline of SimHerd III Herd data Statistical analysis SimCow: simulates the Herd production of an individual cow Sim Sim Herd Cow View given a production strategy -initial cow SimTest -weekly results -lactation statistics -milk production 6
Outline of Simcow: initial cow Initial settings standard cow in Simcow Outline of Simcow: weekly results 7
Outline of Simcow: milk production Actual daily yield as function of weeks after calving Outline of Simcow: lactation statistics Max. yield possible and yield currently realised 8
Outline of SimHerd III Herd data Statistical analysis Simherd: defining initial herd Herd Sim and strategy Sim Herd Cow View -biological variables SimTest -feeding and drying-off strategy -replacement strategy -milk production Simherd: defining initial herd and strategy Biological Variables Abortion (pct) 25 291 variables! Time for 50% abortion 1 : 17 Stillbirths 1. lactation (pct) 10,9 Stillbirth older cows (pct) 6 Involuntary culling (pct per cow-year) 18 Mortality in cows (pct per cow-year) 2 Age at first heat (days) 280 St.dev. first heat (1,2 or 3) 2 Change of pregnancy (pct) 50 Gestation length (days) 280 Prop. Heifer calves (pct) 50 Yield level (kg ECM 2 1-24 wpp, 3 rd lact) 34,0 St. dev. Individual yield level 2 St. dev. Individual yield level 2 Mature weight (kg) 630 9
Difference with SimFlock? SimHerd Mature weight 630 kg SimFlock Marture weight mean 1637 gram standard deviation 143 gram Simherd: Feeding and drying of strategy yield at 1st step., 1st lact. (kg/day)) 23,0 defining initial herd and strategy yield at 1st step., older cows (kg/day) 28,0 yield at 2nd step., 1st lact. (kg/day) 18,0 yield at 2nd step., older cows (kg/day) 22,0 yield at drying off 1st lact. (kg/day) 5,0 yield at drying off older cows (kg/day) 5,0 10
Simherd: defining initial herd and strategy Reproduction strategy 291 variables! Start breed of heifers (days) 450 Start breed of 1 st lactation (days after calving) 40 Start breed of other cows (days after calving) 40 of which Heat detection eff. in winter, heifers (pct) 50 Heat detection eff. in summer, heifers (pct) 40 70 decision Heat detection eff. in winter, cows (pct) 50 Heat detection eff. in summer, cows (pct) 50 variables! Pregnancy detection cows (days after insemination) 42 Pregnancy detection cows (days after insemination) 42 First calendar day in summer season, cows 119 Last calendar day in summer season, cows 238 First calendar day in summer season, heifers 119 Last calendar day in summer season, heifers 238 Simherd: defining initial herd and strategy 291 variables! Replacement strategy of which Max number of cows 120 Min number of cows 100 Max days open before culling 1 st lact 427 70 decision Max days open before culling older 427 Max age of open heifers before culling 805 variables! Max days open before culling decision 1 st lact 245 Max days open before culling decision older 245 Max days open before culling (low yield) 1 st 203 Max days open before culling (low yield) old 203 Threshold low yield 1 st lactation (kg 24) 25 Threshold low yield 2 nd lactation (kg 24) 33 Threshold low yield older cows (kg 24) 34 Milk quota: max tons per year 0 Min tons per year 0 11
Biological variables concerning health Modeling risk of disease at the cow level •Base risk (probability for parity 3, average producing, no previous cases) •Parity: 1, 2, 3, >3 •Milk yield capacity •Lactational recurrence of the disease • Other diseases •Body condition score •Season Logistic regression model and random numbers Biological variables concerning health MAS DOWN KET MF MET DA RP DYS Diseases and their interrelationships: disease complexes 12
Recommend
More recommend