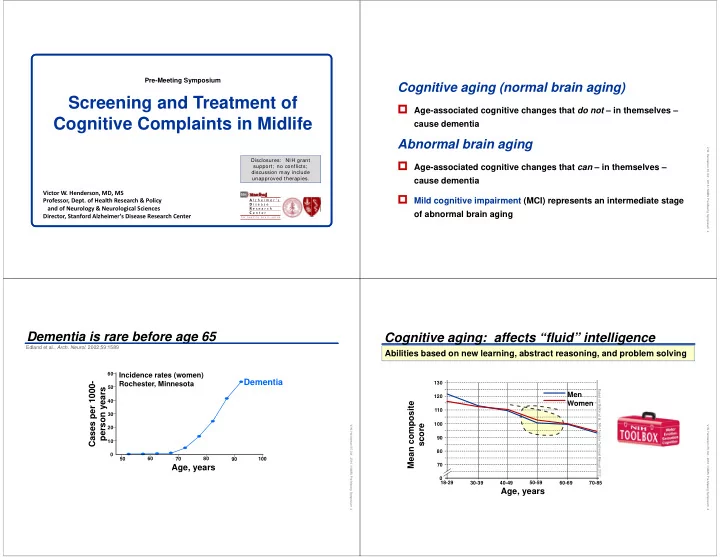

Pre-Meeting Symposium Cognitive aging (normal brain aging) Screening and Treatment of Age-associated cognitive changes that do not – in themselves – Cognitive Complaints in Midlife cause dementia Abnormal brain aging V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 2 Disclosures: NIH grant Age-associated cognitive changes that can – in themselves – support; no conflicts; discussion may include unapproved therapies. cause dementia Victor W. Henderson, MD, MS S t a n f o r d Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) represents an intermediate stage Professor, Dept. of Health Research & Policy A l z h e i m e r ’ s D i s e a s e and of Neurology & Neurological Sciences R e s e a r c h of abnormal brain aging C e n t e r Director, Stanford Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center f o r h e a l t h y b r a i n a g i n g Dementia is rare before age 65 Cognitive aging: affects “fluid” intelligence Edland et al., Arch. Neurol. 2002;59:1589 Abilities based on new learning, abstract reasoning, and problem solving 60 Incidence rates (women) Dementia Cases per 1000- Rochester, Minnesota 130 50 person years Based on Slotkin et al., NIH Toolbox Technical Manual, 2012 Men 120 40 Mean composite Women 110 30 100 score V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 3 V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 4 20 90 10 80 0 50 60 70 80 90 100 70 Age, years 0 18-29 30-39 40-49 50-59 60-69 70-85 Age, years
Memory complaints are common during midlife Memory complaints are common during midlife Mitchell ES & Woods NF, J. Womens Weber, Mapstone, Staskiewwicz, Maki, Szoeke, Clark, Guthrie, Dennerstein, Gold EB, Am. J. Epidemiol. 2000;152:463 Health Gend. Based Med . 10:351, 2001 Menopause 7:735, 2013 Henderson Seattle Midlife Melbourne Women’s Rochester, NY 100 SWAN Women’s Health Study Midlife Health Project 75 women, ages 40-60 90 16,065 women, age 40-55 years 249 women, ages 55-66 230 women, mean age Percent forgetful 80 Memory Functioning 47 70 “During the past week, Questionnaire “Forgetfulness” during past 2 weeks (yes/no) 60 have you had particular “Have you noticed any 50 trouble remembering 67% reported some changes in your V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 5 V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 6 recent events, such as 40 degree of memory loss memory over the past items in the newspaper or 30 few years?” on TV, or what someone 20 No correlation with told you?” 10 learning/ memory 62% responded YES. 36% responded YES. 0 scores; correlation with Pre- Early Peri- Post- Late Peri- Surgical attentional/ working menopausal menopausal No difference in objective memory scores episodic memory scores Associated with age, lower education, not being able to pay for basics, not being employed full-time, past smoking, and less physical activity. Memory complaints are common “Are you concerned about your memory?” after Neugarten & Kraines, Psychosomatic Medicine 1965;27:266. Bayley et al., JAGS , 2015;63:309 > High > High 100 school school 100 460 Chicago area women, no surgical menopause <High <High 80 school school High High 80 Percent passing Percent forgetful Menopause Menopause Pre- or post- Pre- or post- school school transition transition menopausal menopausal 8 .2 % 60 60 failed V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 7 V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 8 40 40 No memory concern 25% 75% Memory concern 20 1 1 .9 % 20 failed N = 2,067 No sex differences 0 OR = 1.4 13-18 20-29 30-44 45-54 45-54 55-64 0 (1.1-1.8) Age <75 75-84 >84 Age
Thus far… Approach to screening and treatment Dementia during midlife is rare History Cognitive aging begins before midlife Examination Midlife cognitive complaints are common Laboratory But cognitive complaints are not confined to midlife (or to V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 10 women) V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 9 Diagnosis/ contributing factors Biomarkers in older adults with subjective memory Management complaints are not obviously different from biomarkers in older adults without complaints or cognitive impairment. Memory complaints may be associated with objective cognitive loss, but often they are not. Patient concerns? History Informant Yes No concerns? Yes No Try to include an informant! 1. History (patient and informant) • Memory Clinician concerns Memory • Function for neuro-based • Medical and psychosocial Function impairment? • Medications • Family history Yes No V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 11 V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 12 Medical history / psychosocial history / drug history and + current meds 2. Examination • Cognition (Diagnosis) & Management Family history • Mood • Physical / neurological Refer for neurologist evaluation Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease +/ − Frontotemporal dementia 3. Laboratory Follow-up as needed
Examination Laboratory General physical exam / neurological exam General labs (metabolic panel, CBC) Cognitive and behavioral observations Thyroid functions Cognitive screening B12? Mini-cog Mood screening Toxic (drug) screen MMSE V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 13 V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 14 MoCA Brain imaging? AD8 Beck SLUMS IQCODE GDS Hamilton Zung Diagnosis / management Other management issues Henderson et al., Neurology 2016;87:699 Awareness of normal cognitive aging Vascular health What is the role of hormone therapy? Depression or anxiety ELITE (Early versus Late Menopause as time of affective vulnerabilty Intervention Trial with Estradiol) Sleep disturbance + 1 SD 1.00 0.80 Hot flashes (stress, sleep) 0.60 0.40 Family stressors 0.20 0 Adolescent children, empty nest, aging parents, marital discord 0 V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 15 V.W. Henderson 05 Oct . 2016 / NAMS Pre-Meeing Symposium 16 -0.20 -0.40 Career challenges -0.60 -0.80 Medication side-effects - 1 SD -1.00 Verbal Global Executive OTC sleep aids, prescription sedatives, anxiolytics, antidepressants, Memory Cognition Functions analgesics RCT, 643 healthy postmenopausal women Early group (<6 y) and Late group ( ≥ 10 y) Alcohol or substance abuse after menopause Mean duration 57 months Estradiol 0.5 mg/d or placebo
Recommend
More recommend