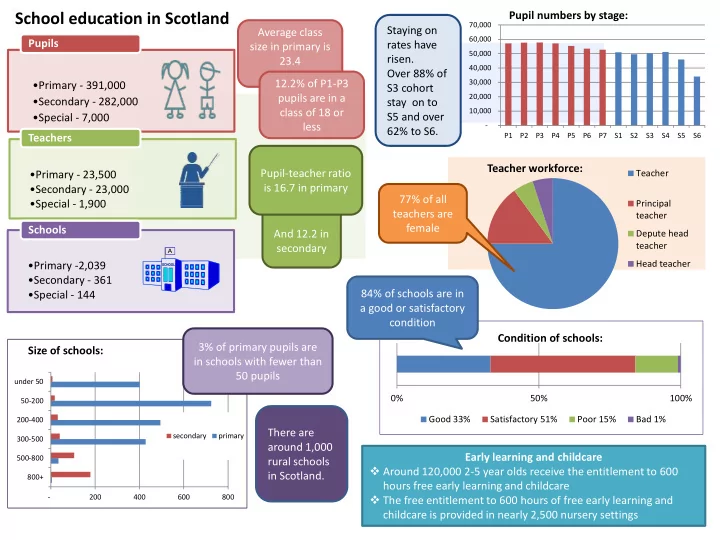

School education in Scotland Pupil numbers by stage: 70,000 Staying on Average class Pupils 60,000 rates have size in primary is 50,000 risen. 23.4 40,000 Over 88% of 12.2% of P1-P3 30,000 • Primary - 391,000 S3 cohort pupils are in a 20,000 • Secondary - 282,000 stay on to class of 18 or 10,000 S5 and over • Special - 7,000 less - 62% to S6. Teachers P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 Teacher workforce: Pupil-teacher ratio Teacher • Primary - 23,500 is 16.7 in primary • Secondary - 23,000 77% of all • Special - 1,900 Principal teachers are teacher Schools female And 12.2 in Depute head teacher secondary Head teacher • Primary -2,039 • Secondary - 361 84% of schools are in • Special - 144 a good or satisfactory condition Condition of schools: 3% of primary pupils are Size of schools: in schools with fewer than 50 pupils under 50 0% 50% 100% 50-200 Good 33% Satisfactory 51% Poor 15% Bad 1% 200-400 There are secondary primary 300-500 around 1,000 Early learning and childcare 500-800 rural schools Around 120,000 2-5 year olds receive the entitlement to 600 in Scotland. 800+ hours free early learning and childcare - 200 400 600 800 The free entitlement to 600 hours of free early learning and childcare is provided in nearly 2,500 nursery settings
Attainment No matter what data we use, or which aspect of attainment Attainment is rising: we look at, there is a clear gap Very few young people leave school with between children from more “ There is significant no or very low levels of qualifications variation in attainment deprived and less deprived (2.1% in 14/15) between individual backgrounds. 152,701 Higher passes in 2016, up more councils, schools and than 40,000 since 2006 groups of pupils.” Positive destinations for our young There are signs that the attainment people are rising - 92% of 2014/15 92% gap is reducing on some measures. school leavers were in a positive follow up destination in March 2016. There is an improving picture for those leaving school with low or no levels or qualification. The Scottish Survey of Literacy and Numeracy shows that: The difference in the proportions from the most and least deprived The majority of P4 and P7 areas achieving at least one SCQF 5 pupils are performing well or qualification or better has reduced very well in literacy and (33 percentage points in 09/10 to 21 numeracy ... points in 14/15.) ...However there were small decreases in performance in reading and writing between 2012 and 2014 at the majority of stages. But the gap in terms of those achieving 5 or more awards at SCQF5 or better has decreased at a much ...And a decreased numeracy slower rate (down 5.6 percentage performance between 2011 points since 09/10). and 2015
Spending on education by local authorities Secondary Average spend Average spend per pupil of £1,929 m Education is the largest service per pupil of £6,790 Councils spent area – The 32 councils plan to (40%) £4,814 £4.8 bn on spend 41% of service expenditure education in on education in 2016-17 Other Primary 2014-15 £156 m £1,852 m (3%) (38%) Education Over half of spend on Expenditure primary, secondary and Running school buildings, school meals, special education is on school transport, teachers Early Years textbooks etc, some Average spend Special and elements of unitary schools per child of Childcare charge payments around £2,900 £533m £346 m a year (11%) (7%) Services All Other purchased Expenditure Average spend per pupil in primary, by local authority to 28% Teachers support 54% delivery There is wide Support (e.g. IT or Services variation finance Scotland average 4% between bought Other councils in within an Employees LA) spend per pupil 14% Island authorities All non-teaching staff employed in schools and non- All teachers in schools teaching staff and those centrally employed by LA employed by LAs £- £2,000 £4,000 £6,000 £8,000 £10,000 education services
How is Education in Scotland run now? The Scottish Government, local government, national agencies and other bodies each play different roles in governing, leading and supporting the delivery of education Scottish College for Educational Children and Young Parents have a range of rights and responsibilities, including Leadership People • Responsibilities to ensure their children: are properly educated at Scottish Qualifications Authority 8 Universities • • • Children have Develops school examinations Responsible for developing school age; attend school; obey school rules. • Provide Rights to: children being educated in line with their • leadership and programmes rights to be heard and awards school teacher and involved in religious/philosophical beliefs; to choose school; to be consulted qualifications education • decisions about Also has responsibility for other and appeal against decisions on additional support needs. Scottish Social Services Council Parent Councils represent the voice of parents in their school • their education qualifications (such as HNC’s ) • Regulator for the social service workforce Early Years staff & Teachers • Deliver day to day care and General Teaching Council for Scotland learning to children in early years Child • Sets teaching standards settings and schools • Accredits teacher training • Oversees induction, professional learning Headteachers and student placement programmes • Day to day running of school Parents • Share responsibility with local Care Inspectorate authority for management and • Regulates and inspects the standard of School delivery of curriculum care services, including in early years, and • Some funding decisions residential schools Local 32 Local Authorities (as Education Authority) Education Scotland • Duty to provide “adequate and efficient” school • National Supports quality and improvement education and early years provision • Responsible for supporting schools to deliver • Employment of school and some early years staff Curriculum for Excellence and for school • Decide how much money to give to schools inspection. • Number of other duties, for example; providing for additional support needs; consulting on school Scottish Scottish Government estate, arranging school transport, school opening, Qualifications • Develops national policy and sets overall direction closing and holiday dates Authority • Gives majority of funding to local authorities for • Develops school education Others examinations • Legal duty to improve education and powers to A range of other partners support children’s learning including private and awards raise standards and third sector providers; local community organisations and charities qualifications • Legal duty to promote involvement of parents in as well as other local services such as social work, the police, employers, education colleges and universities
Recommend
More recommend