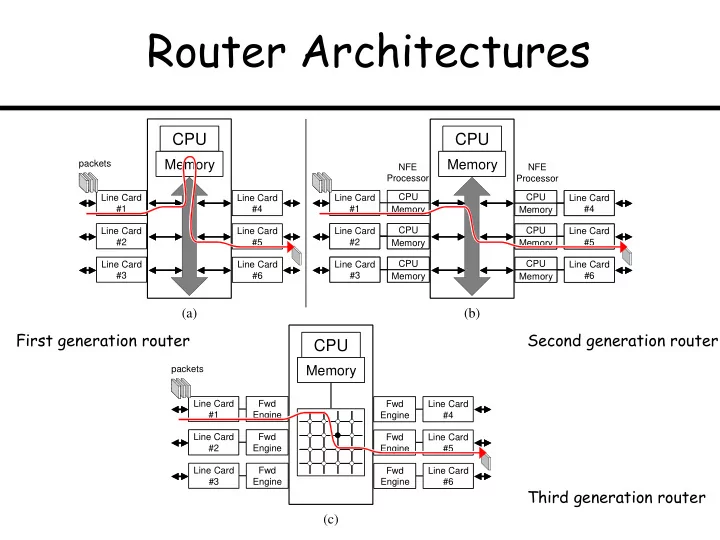

Router Architectures CPU CPU Memory Memory packets NFE NFE Processor Processor Line Card Line Card Line Card CPU CPU CPU Line Card Line Card #1 #1 #4 Memory Memory Memory #4 #4 CPU CPU CPU CPU Line Card Line Card Line Card Line Card Line Card Line Card #2 #5 #2 #2 #5 #5 Memory Memory Memory Memory CPU CPU CPU CPU Line Card Line Card Line Card Line Card Line Card Line Card #3 #6 #3 #3 #6 #6 Memory Memory Memory Memory (a) (b) First generation router Second generation router CPU Memory packets Line Card Fwd Fwd Line Card #1 Engine Engine #4 Line Card Fwd Fwd Line Card #2 Engine Engine #5 Line Card Fwd Fwd Line Card #3 Engine Engine #6 Third generation router (c)
Switching via Memory / via Bus Forwarding & Routing Forwarding & Routing CPU CPU Input port Input port processor processor Memory Memory Network layer Network layer First generation router Output port Output port Link layer Link layer Line card Line card Line card Line card packets packets System bus System bus Input port Input port Output port Output port Routing processor Routing processor CPU CPU NFE processor NFE processor NFE processor NFE processor Memory Memory Network layer Network layer packets packets Link layer Link layer Line card Line card Line card Line card Second generation router System bus System bus
Crossbar Switch Fabric Input N x N switching elements allows N simultaneous packets switched (in the best case when all packets going to different outputs) Output
Goal: Reduce # Switching Elements • System bus (in 1 st and 2 nd generation arch’s) allows only one packet switched at a time • Crossbar allows up to N packets switched at a time • Something in the middle? (+cheaper!)
Banyan Switch Fabric Input port Output port tag tag Input port Input port Output port Output port tag tag tag tag 1 1 00 00 00 00 0 0 0 0 01 01 01 01 Packet Packet 1 1 1 1 (b) with tag 1 with tag 1 (a) 10 10 10 10 11 11 11 11 8x8 Banyan has only 12 switching elements Input port Output port (while 8x8 crossbar tag tag 000 000 requires 64) 001 001 Packet But, much greater with tag 100 likelihood of collisions… 100 010 010 011 011 (c) 100 100 101 101 Packet with tag 001 001 110 110 111 111
Reducing Collisions • (Show slide with a collision example) • Collisions can be reduced if packets are ordered on input ports by their output port number • The router cannot choose the ordering of arriving packets, but we can insert a sorting hardware between the input network ports and the switching fabric …
Batcher Network Comparator Comparator 5 5 Input Input Output Output 7 7 L L L L 3 3 numbers numbers numbers numbers 3 3 5 5 H H H H 5 5 5 5 Low Low 3 3 L L 4 4 (b) 3 3 High High 5 5 H H 5 5 7 7 3 3 L L L L 4 4 (a) 4 4 4 4 H H H H 7 7 Input Output list list 5 4 9 1 4 1 4 5 2 2 9 5 4 6 3 6 2 3 4 4 5 3 (c) 2 6 5 3 5 1 3 7 2 6 6 3 9 7 1 7 7 7 7 9
Batcher-Banyan Network Batcher Trap Shuffle Banyan sort network exchange network network network
Why Batcher-Banyan Network Packets Empty input Batcher sorter Banyan network with tags 1, 0, 0, 2 0 0 0 1 Trap 1 0 0 network 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 2 2 2 2 3 2 2 This figure is meant to illustrate why a concentrator is needed, because otherwise the gap in the input sequence will cause collision in the Banyan, but the example does not work for a 4x4 network -- need an 8x8 network example!!!!
Recommend
More recommend