
Review of DNA ( D eoxyribo n ucleic a cid)
What do you remember from Biology?
Who are these people?
James Watson and Francis Crick • 1953 – Determined the structure of DNA using Rosalind Franklin’s data • Awarded the Nobel Prize in 1962
What is DNA?
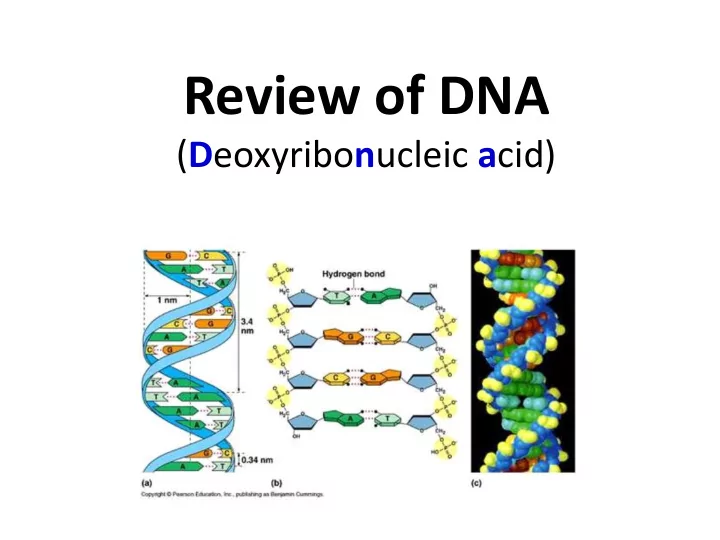
DNA ( D eoxyribo n ucleic a cid) • Nucleic acid • Consists of monomers called nucleotides • Found in all cells, some organelles, and some viruses
DNA ( D eoxyribo n ucleic a cid) • Stores genetic information • Determines an organisms traits by directing the synthesis of proteins • Each organisms genome is unique
Structure of DNA
Structure of DNA • Double helix • Consists of a double strand of nucleotides • Sides: Alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphates • Center: Complementary nitrogenous bases • Two strands are anti-parallel – 5’ to 3’ – 3’ to 5’
A Note About the Phosphates • DNA is a negatively charged molecule because of the phosphate groups • Important property in gel electrophoresis
Gel Electrophoresis
Nucleotide Composition • Three parts of a nucleotide – 5 carbon sugar called deoxyribose – Phosphate group – A single nitrogenous base
Four Nitrogenous Bases • Purines (double ring) • Pyrimidines (single ring) – Adenine (A) – Thymine (T) – Guanine (G) – Cytosine (C)
Purines pair with Pyrimidines
Chargaff’s Rules (Base Pairing) • A-T (2 hydrogen bonds) • C-G (3 hydrogen bonds)
Bonds Within a DNA Molecule
• Phosphodiester bonds join nucleotides together along the sides of the DNA molecule (type of covalent bond) • Hydrogen bonds join the two DNA strands together in the center of the molecule
Phosphodiester Bond
DNA and Genes • Only 2% of the human genome is protein coding • A gene is a sequence of nucleotides that contains instructions for synthesizing a particular protein • The sequence of nucleotides in an organisms genome is unique
Human Genome Project • Began in 1990, completed in April 2003 • Approximately 20,000 genes in the human genome • 3 billion base pairs
Recommend
More recommend