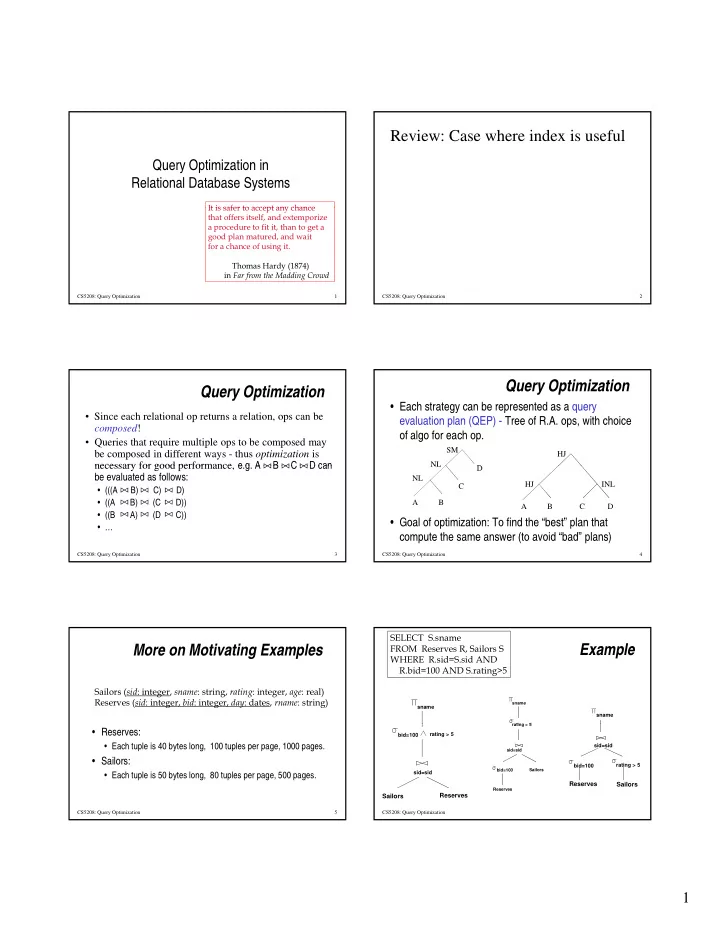

Review: Case where index is useful Query Optimization in Relational Database Systems It is safer to accept any chance It is safer to accept any chance that offers itself, and extemporize a procedure to fit it, than to get a good plan matured, and wait for a chance of using it. Thomas Hardy (1874) in Far from the Madding Crowd CS5208: Query Optimization 1 CS5208: Query Optimization 2 Query Optimization Query Optimization • Each strategy can be represented as a query • Since each relational op returns a relation, ops can be evaluation plan (QEP) - Tree of R.A. ops, with choice composed ! of algo for each op. • Queries that require multiple ops to be composed may SM be composed in different ways - thus optimization is HJ necessary for good performance e g A B C D can necessary for good performance, e.g. A B C D can NL NL D D be evaluated as follows: NL HJ INL C • (((A B) C) D) • ((A B) (C D)) A B A B C D • ((B A) (D C)) • Goal of optimization: To find the “best” plan that • … compute the same answer (to avoid “bad” plans) CS5208: Query Optimization 3 CS5208: Query Optimization 4 SELECT S.sname More on Motivating Examples FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 Sailors ( sid : integer, sname : string, rating : integer, age : real) Reserves ( sid : integer, bid : integer, day : dates, rname : string) sname sname sname rating > 5 ti > 5 • Reserves: bid=100 rating > 5 • Each tuple is 40 bytes long, 100 tuples per page, 1000 pages. sid=sid sid=sid • Sailors: bid=100 rating > 5 Sailors bid=100 sid=sid • Each tuple is 50 bytes long, 80 tuples per page, 500 pages. Reserves Sailors Reserves Reserves Sailors CS5208: Query Optimization 5 CS5208: Query Optimization 1
SELECT S.sname SELECT S.sname FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 sname sname lubber lubber sname sname sid sname rating age bid day rname sid sname rating age bid day rname rating > 5 rating 5 31 31 lubber lubber 8 8 55.5 55.5 100 100 10/11/96 10/11/96 lubber lubber rating > 5 bid=100 31 lubber 8 55.5 100 10/11/96 lubber sid sname rating age bid day rname sid=sid sid sname rating age bid day rname 31 lubber 8 55.5 100 10/11/96 lubber 31 lubber 8 55.5 100 10/11/96 lubber sid=sid 58 rusty 10 35.0 103 11/12/96 dustin bid=100 Sailors sid bid day rname sid sname rating age 22 dustin 7 45.0 31 100 10/11/96 lubber sid sname rating age sid bid day rname 28 yuppy 9 35.0 Reserves Sailors Reserves 22 dustin 7 45.0 31 100 10/11/96 lubber 31 lubber 8 55.5 sid bid day rname 28 yuppy 9 35.0 44 guppy 5 35.0 58 103 11/12/96 dustin 31 100 10/11/96 lubber 31 lubber 8 55.5 58 rusty 10 35.0 58 103 11/12/96 dustin 44 guppy 5 35.0 CS5208: Query Optimization CS5208: Query Optimization 58 rusty 10 35.0 SELECT S.sname SELECT S.sname FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example (Cont) WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 Query Evaluation Plan: sname • Cost? lubber (On-the-fly) sname sid sname rating age bid day rname sname 31 31 lubber lubber 8 8 55.5 55.5 100 100 10/11/96 10/11/96 lubber lubber (On-the-fly) rating > 5 bid=100 sid bid day rname sid sname rating age 31 100 10/11/96 lubber 22 dustin 7 45.0 sid=sid 28 yuppy 9 35.0 31 lubber 8 55.5 (Page Nested Loops) 58 rusty 10 35.0 bid=100 rating > 5 sid=sid sid sname rating age Reserves Sailors 22 dustin 7 45.0 Sailors Reserves sid bid day rname 28 yuppy 9 35.0 31 lubber 8 55.5 31 100 10/11/96 lubber 44 guppy 5 35.0 58 103 11/12/96 dustin 58 rusty 10 35.0 CS5208: Query Optimization CS5208: Query Optimization 10 SELECT S.sname SELECT S.sname FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example (Cont) FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example (Cont) WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 Query Evaluation Plan: Query Evaluation Plan: • Cost: 500+500*1000 I/Os • Cost: 500+500*1000 I/Os (On-the-fly) (On-the-fly) sname sname • Memory? rating > 5 (On-the-fly) rating > 5 (On-the-fly) bid=100 bid=100 (Page Nested Loops) (Page Nested Loops) sid=sid sid=sid Reserves Reserves Sailors Sailors CS5208: Query Optimization 11 CS5208: Query Optimization 12 2
SELECT S.sname FROM Reserves R, Sailors S Example (Cont) Alternative Plans 1 (No Indexes) WHERE R.sid=S.sid AND R.bid=100 AND S.rating>5 • Main difference: push selections down Query Evaluation Plan: • Assume 5 buffers, T1 = 10 pages (100 boats, • Cost: 500+500*1000 I/Os (On-the-fly) uniform distribution), T2 = 250 pages (10 ratings, sname • Memory: 3 sname (On-the-fly) uniform distribution) (On-the-fly) rating > 5 bid=100 (Sort-Merge) sid=sid (T1) (T2) (Page Nested Loops) rating > 5 bid=100 sid=sid Reserves Sailors Sailors Reserves CS5208: Query Optimization 13 CS5208: Query Optimization 14 Alternative Plans 2 (With Indexes) Alternative Plans 1 (No Indexes) • Main difference: push selections down • Clustered index on bid of Reserves • 100,000/100 = 1000 tuples on 1000/100 = 10 pages • With 5 buffers, cost of plan: • Hash index on sid. Join column sid is a key for Sailors. • Scan Reserves (1000) + write temp T1 (10 pages, sname(On-the-fly) sname (On-the-fly) • INL with pipelining (outer is not materialized) if we have 100 boats, uniform distribution). • Project out unnecessary fields from outer doesn’t help. • Scan Sailors (500) + write temp T2 (250 pages, if S S il (500) + it t T2 (250 if 5 (On the fly) (On-the-fly) rating > 5 ti • At most one matching tuple, unclustered we have 10 ratings). (Sort-Merge) index on sid OK. sid=sid (INL • Sort T1 (2*2*10), sort T2 (2*4*250), merge sid=sid with pipelining ) • Did not push “rating> 5” before the join. Why? (10+250) (T1) (T2) bid=100 rating > 5 • Total: 4060 page I/Os. bid=100 Sailors (Use hash index; do Reserves Sailors not write Reserves result to temp) CS5208: Query Optimization 15 CS5208: Query Optimization 16 Alternative Plans 2 (With Indexes) Alternative Plans 2 (With Indexes) • Clustered index on bid of Reserves • Clustered index on bid of Reserves • 100,000/100 = 1000 tuples on 1000/100 = 10 pages • 100,000/100 = 1000 tuples on 1000/100 = 10 pages • Hash index on sid. Join column sid is a key for Sailors. • Hash index on sid. Join column sid is a key for Sailors. sname(On-the-fly) sname(On-the-fly) • INL with pipelining (outer is not materialized) • INL with pipelining (outer is not materialized) • Project out unnecessary fields from outer doesn’t help. • Project out unnecessary fields from outer doesn’t help. 5 (On the fly) (On-the-fly) 5 (On the fly) (On-the-fly) rating > 5 ti rating > 5 ti • At most one matching tuple, unclustered • At most one matching tuple, unclustered index on sid OK. index on sid OK. (INL (INL sid=sid with pipelining ) sid=sid with pipelining ) • Decision not to push rating> 5 before the join is • Decision not to push rating> 5 before the join is based on availability of sid index on Sailors. based on availability of sid index on Sailors. Sailors Sailors • Cost? bid=100 • Cost: Selection of Reserves tuples (10 I/Os); for bid=100 (Use hash (Use hash each, must get matching Sailors tuple (1000* 2.2); index; do index; do not write not write total 2210 I/Os. Reserves result to Reserves result to temp) temp) CS5208: Query Optimization 17 CS5208: Query Optimization 18 3
Plan Execution under the Iterator Model Plan Execution under the Iterator Model consumer consumer Open() Open() Open() Open() p () C C Open() Open() A B A B CS5208: Query Optimization 19 CS5208: Query Optimization 20 Plan Execution under the Iterator Model Plan Execution under the Iterator Model consumer consumer GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() C C GetNext() A B A B CS5208: Query Optimization 21 CS5208: Query Optimization 22 Plan Execution under the Iterator Model Plan Execution under the Iterator Model consumer consumer GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() C C GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() t t A B A B CS5208: Query Optimization 23 CS5208: Query Optimization 24 4
Plan Execution under the Iterator Model Plan Execution under the Iterator Model consumer consumer GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() C C GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() t t A B A B CS5208: Query Optimization 25 CS5208: Query Optimization 26 Plan Execution under the Iterator Model Plan Execution under the Iterator Model consumer consumer GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() C C GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() t t A B A B CS5208: Query Optimization 27 CS5208: Query Optimization 28 Plan Execution under the Iterator Model Plan Execution under the Iterator Model consumer consumer GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() C C GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() GetNext() t t A B A B CS5208: Query Optimization 29 CS5208: Query Optimization 30 5
Recommend
More recommend