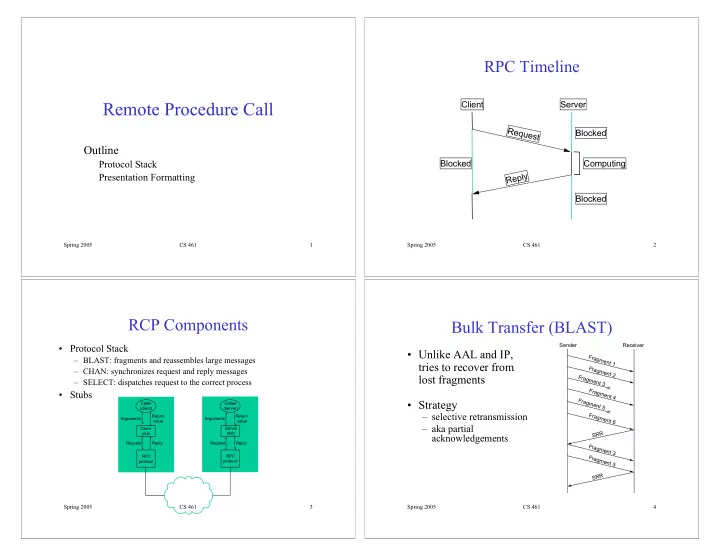

RPC Timeline Remote Procedure Call Client Server R e Blocked q u e s t Outline Protocol Stack Blocked Computing Presentation Formatting y p l e R Blocked Spring 2005 CS 461 1 Spring 2005 CS 461 2 RCP Components Bulk Transfer (BLAST) Sender Receiver • Protocol Stack • Unlike AAL and IP, Fragment 1 – BLAST: fragments and reassembles large messages tries to recover from Fragment 2 – CHAN: synchronizes request and reply messages lost fragments Fragment 3 – SELECT: dispatches request to the correct process Fragment 4 • Stubs Fragment 5 • Strategy Caller Callee (client) (server) – selective retransmission Fragment 6 Return Return Arguments Arguments value value – aka partial Client Server R stub stub R acknowledgements S Request Reply Request Reply Fragment 3 RPC RPC Fragment 5 protocol protocol R R S Spring 2005 CS 461 3 Spring 2005 CS 461 4
BLAST Details BLAST Details (cont) • Sender: • Receiver: – after sending all fragments, set timer DONE – when first fragments arrives, set timer LAST_FRAG – if receive SRR, send missing fragments and reset DONE – when all fragments present, reassemble and pass up – if timer DONE expires, free fragments – four exceptional conditions: • if last fragment arrives but message not complete – send SRR and set timer RETRY • if timer LAST_FRAG expires – send SRR and set timer RETRY • if timer RETRY expires for first or second time – send SRR and set timer RETRY • if timer RETRY expires a third time – give up and free partial message Spring 2005 CS 461 5 Spring 2005 CS 461 6 Request/Reply (CHAN) BLAST Header Format • Guarantees message delivery 0 16 31 • Synchronizes client with server • MID must protect against wrap around ProtNum MID • Supports at-most-once semantics • TYPE = DATA or SRR Length • NumFrags indicates number of fragments NumFrags Type Simple case Implicit Acks • FragMask distinguishes among fragments FragMask Client Server – if Type=DATA, identifies this fragment Client Server Data Request 1 Request – if Type=SRR, identifies missing fragments 1 y l p e K R C A Request 2 y p l e R 2 y p l e ACK R … Spring 2005 CS 461 7 Spring 2005 CS 461 8
CHAN Header Format CHAN Details typedef struct { u_short Type; /* REQ, REP, ACK, PROBE */ • Lost message (request, reply, or ACK) u_short CID; /* unique channel id */ int MID; /* unique message id */ – set RETRANSMIT timer int BID; /* unique boot id */ int Length; /* length of message */ – use message id (MID) field to distinguish int ProtNum; /* high-level protocol */ } ChanHdr; • Slow (long running) server – client periodically sends “are you alive” probe, or typedef struct { u_char type; /* CLIENT or SERVER */ – server periodically sends “I’m alive” notice u_char status; /* BUSY or IDLE */ int retries; /* number of retries */ • Want to support multiple outstanding calls int timeout; /* timeout value */ XkReturn ret_val; /* return value */ Msg *request; /* request message */ – use channel id (CID) field to distinguish Msg *reply; /* reply message */ Semaphore reply_sem; /* client semaphore */ • Machines crash and reboot int mid; /* message id */ int bid; /* boot id */ – use boot id (BID) field to distinguish } ChanState; Spring 2005 CS 461 9 Spring 2005 CS 461 10 Synchronous vs Asynchronous Dispatcher (SELECT) Protocols • Dispatch to appropriate Client Server • Asynchronous interface Caller Callee procedure call send(Protocol llp, Msg *message) upcall • Synchronous SELECT SELECT deliver(Protocol llp, Msg *message) counterpart to UDP call upcall • Implement concurrency • Synchronous interface CHAN CHAN (open multiple CHANs) call(Protocol llp, Msg *request, Msg *reply) send deliver send deliver upcall(Protocol hlp, Msg *request, Msg *reply) • CHAN is a hybrid protocol – synchronous from above: call • Address Space for Procedures – asynchronous from below: deliver – flat: unique id for each possible procedure – hierarchical: program + procedure number Spring 2005 CS 461 11 Spring 2005 CS 461 12
SunRPC Simple RPC Stack • IP implements BLAST-equivalent SunRPC SELECT – except no selective retransmit UDP CHAN • SunRPC implements CHAN-equivalent IP – except not at-most-once BLAST ETH IP • UDP + SunRPC implement SELECT-equivalent – UDP dispatches to program (ports bound to programs) – SunRPC dispatches to procedure within program ETH Spring 2005 CS 461 13 Spring 2005 CS 461 14 Presentation Formatting SunRPC Header Format • Marshalling (encoding) • XID (transaction id) is 0 31 0 31 application data into XID XID similar to CHAN’s MID Application Application messages data data MsgType = CALL MsgType = REPLY • Server does not remember • Unmarshalling RPCVersion = 2 Status = ACCEPTED last XID it serviced (decoding) messages Presentation Presentation Data Program encoding decoding into application data • Problem if client Version … retransmits request while Message Message Message Procedure reply is in transit Credentials (variable) • Data types we consider • Types of data we do not consider Verifier (variable) – integers – images Data – floats – video – strings – multimedia documents – arrays – structs Spring 2005 CS 461 15 Spring 2005 CS 461 16
Difficulties Taxonomy • Data types • Representation of base types – base types (e.g., ints, floats); must convert – floating point: IEEE 754 versus non-standard – flat types (e.g., structures, arrays); must pack – integer: big-endian versus little-endian (e.g., 34,677,374) – complex types (e.g., pointers); must linearize (2) (17) (34) (126) Application data structure Big-endian 00000010 0 0 01 001 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 (126) (34) (17) (2) Little- endian 0 111111 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 01 00 0 1 0 0 0 000 0 1 Marshaller High Low • Conversion Strategy address address • Compiler layout of structures – canonical intermediate form – receiver-makes-right (an N x N solution) Spring 2005 CS 461 17 Spring 2005 CS 461 18 Taxonomy (cont) eXternal Data Representation • Tagged versus untagged data (XDR) type = len = 4 value = 417892 INT • Defined by Sun for use with SunRPC • Stubs Interface descriptor for • C type system (without function pointers) – compiled Procedure P Call P P – interpreted • Canonical intermediate form Arguments Specification Arguments • Untagged (except array length) Code Code Client Stub Server stub compiler stub • Compiled stubs Marshalled Marshalled arguments arguments RPC RPC Message Spring 2005 CS 461 19 Spring 2005 CS 461 20
Abstract Syntax Notation One #define MAXNAME 256; #define MAXLIST 100; (ASN-1) struct item { • An ISO standard int count; char name[MAXNAME]; • Essentially the C type system int list[MAXLIST]; }; • Canonical intermediate form bool_t • Tagged xdr_item(XDR *xdrs, struct item *ptr) { • Compiled or interpretted stubs return(xdr_int(xdrs, &ptr->count) && xdr_string(xdrs, &ptr->name, MAXNAME) && • BER: Basic Encoding Rules xdr_array(xdrs, &ptr->list, &ptr->count, MAXLIST, sizeof(int), xdr_int)); (tag, length, value) } type length type length value type length value Count Name 3 7 J O H N S O N value List INT 4 4-byte integer 3 4 97 8 321 2 65 Spring 2005 CS 461 21 Spring 2005 CS 461 22 Network Data Representation XML (NDR) – IntegerRep • Defined by DCE • 0 = big-endian • Essentially the C type system <?xml version="1.0"?> • 1 = little-endian <employee> • Receiver-makes-right – CharRep • 0 = ASCII <name>John Doe</name> (architecture tag) • 1 = EBCDIC <title>Head Bottle Washer</title> • Individual data items untagged – FloatRep <id>123456789</id> • Compiled stubs from IDL • 0 = IEEE 754 <hiredate> • 1 = VAX • 4-byte architecture tag • 2 = Cray <day>5</day> • 3 = IBM <month>June</month> <year>1986</year> 0 4 8 16 24 31 </hiredate> IntegrRep CharRep FloatRep Extension 1 Extension 2 </employee> Spring 2005 CS 461 23 Spring 2005 CS 461 24
XML (cont) <?xml version="1.0"?> <xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.cs.princeton.edu/XMLSchema” …> <xs:element name="employee"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element name="name" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="title" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="id" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="hiredate"> <xs:complexType> <xs:sequence> <xs:element name="day" type="xs:integer"/> <xs:element name="month" type="xs:string"/> <xs:element name="year" type="xs:integer"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:sequence> </xs:complexType> </xs:element> </xs:schema> Spring 2005 CS 461 25
Recommend
More recommend