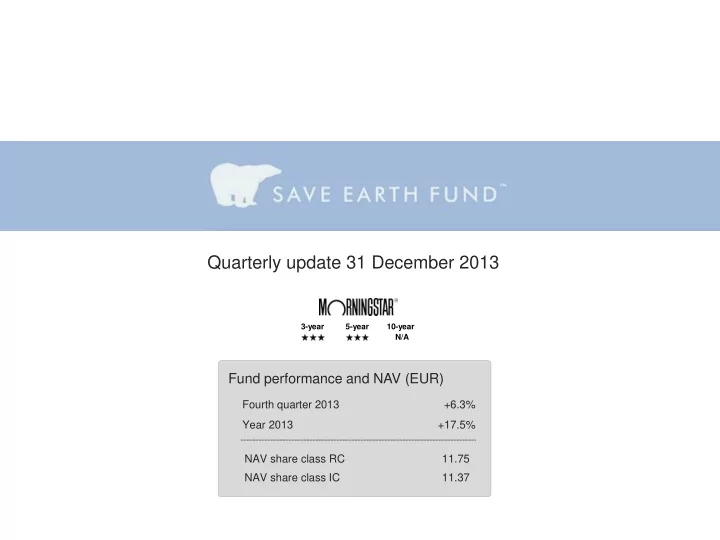

Quarterly update 31 December 2013 3-year 5-year 10-year N/A Fund performance and NAV (EUR) Fourth quarter 2013 +6.3% Year 2013 +17.5% NAV share class RC 11.75 NAV share class IC 11.37
Save Earth Fund Performance Fund performance vs MSCI World Net, 2013 (EUR) The fund gained 5.1% in the first half of 2013, which was about 5% +21.2% worse than MSCI World Net. During the period the best +17.5% performing sector exposure was renewable energy, while the worst performing regional exposure was Asia. During the second half of 2013 the fund gained 12.5%, which was about 3% better than MSCI World Net. The strong performance can be contributed mostly to the Source: MSCI, CB Fonder exposure against environmental technology in Europe, but renewable energy continued to perform very well too. Our exposure to Asia continued to underperform MSCI World. For the full year, Europe was the best contributor to the fund’s performance. Asia was the worst contributor, especially environmental technology in the region. 2
Save Earth Fund News flow during the quarter Climate change, population growth and urbanisation can make water the most valuable commodity in the world , SCA writes in its magazine Shape. Fresh water is a scarce commodity. Only 2.5% of the water on the planet is fresh and most of it is in glaciers and polar ice caps. Gustaf Olsson, professor in industrial automation at Lund university in Sweden, makes the following comparison: ”If all the water in the world would fit into a 10-liter container, all the accessible freshwater in our rivers and lakes would fill a one millilitre measuring spoon. ” Read more … Air pollution is more harmful than passive smoking according to two reports from the World Health Organization (WHO). Air pollution was responsible for 3.2 million deaths in 2010 and of those 223 000 was caused by lung cancer. Read more … China has serious problems with air pollution. NOAA has published a satellite image that very clearly shows the problem. See it here. Oil sands and the shale gas revolution lead to an increased demand for water investments from the oil and gas sector, writes RobecoSAM. Canada – known for vast reserves of oil sands - is mentioned as an example. Another mentioned fact is that one produced barrel of oil require one barrel of water. Read more … The global sea and land temperature was the highest ever in November 2013. Measurements go back 134 years and has never reached as high temperatures. The temperature was 0.78 degrees Celsius over the historical mean. Read more … 3
Save Earth Fund Picture of the quarter 1 In the green countries solar energy is competitive with conventional energy without subsidies; in the red countries solar energy is not competitive. The grey countries are not analysed. The yellow boxes show population and the cost savings, in percent, that can be achieved if conventional energy is replaced with solar energy. 60% of the world’s population live in areas where solar energy is competitive! 4
Save Earth Fund Picture of the quarter 2 Energy revolution! ”The falling satellite” below (grey line) shows how the cost of solar energy has developed over time. It is still more expensive than conventional energy, however, the trend is evident for solar energy (down) and conventional energy (up). The graph is as of 2012; according to the author of the analysis solar energy was cheaper than oil globally at the end of 2013 and cheaper than natural gas in Asia at the same time, measured as $/MMBTU. And most importantly: this trend will continue for years to come. Price development (real in $/MMBTU) for gas, coal, oil, liquefied natural gas and solar energy Source: EIA, CIA, World Bank, Bernstein analysis 5
Save Earth Fund Performance during the quarter (EUR) The fund and benchmark indices The fund and country / regional indices • Index for renewable energy (including dividends): WilderHill New Energy Global Innovation • Index for clean technology (including dividends after tax): The Cleantech Index Index • Water index (including dividends): S&P Global Water Index • World index (including dividends after tax): MSCI World 6
Save Earth Fund Performance since inception (EUR) The fund and benchmark indices +17.5% -46.9% +53.4% +1.1% +43.6% • Index for renewable energy (dividends included): WilderHill New Energy Global Innovation • Index for clean technology (dividends after tax included): The Cleantech Index Index • Water index (dividends included): S&P Global Water Index • World index (dividends after tax included): MSCI World 7
Save Earth Fund The fund compared to index - performance and standard deviation Since inception* (EUR) Since inception in June 2008, two of the three sectors we invest in have performed very poorly – the exception is the water sector that has performed well. Our ambition is that the fund shall be a low risk alternative in a high risk sector – in this we have succeeded. However, the performance has so far not met our expectations. Year 2013 (EUR) In light of the poor performance in the environmental sector since fund inception, 2013 was an encouraging year. For the first time since 2009 both environmental technology and renewable energy outperformed MSCI World – a trend reversal. The fund performed in line with the broad market indices, with low risk. Source: CB Fonder, Lipper, MSCI 8 *Monthly data from Lipper for the period 30 June 2008 – 31 December 2013, in EUR.
Save Earth Fund The fund compared to peers Performance and risk, since inception (EUR)* Sharpe, since inception* Source: CB Fonder, Lipper 9 *Monthly data from Lipper for the period 30 June 2008 – 31 December 2013, in EUR.
Save Earth Fund Sector and geographical allocation Sector allocation, 36 months As of December 2013 Geographical allocation, 36 months As of December 2013 *Including cash in underlying funds. 10
Save Earth Fund Portfolio Largest company exposures Trends Market cap Company Country Sector (billion € ) A strong trend for the water sector is USA Water 11.1 shale gas in USA that demand enormous amounts of water (11-19 million litres of Germany Cleantech water per drill hole). The water 0.3 companies take advantage mainly in two ways: Germany Cleantech Pentair American Water 0.4 The water is distributed to and Danaher from the drill holes, which requires Netherlands Cleantech infrastructure in the form of water 1.8 pipes. Austria Renewable Large amounts of chemicals are energy 4.7 added to the water, which requires treatment of the water after use. USA Water 5.4 European companies within energy Schaltbau France Cleantech efficiency have often much experience Centrotec 6.1 and also world leading technologies in Arcadis Belgium Cleantech the area, because of the demanding Valeo 0.9 European regulation. Melexis USA Water 38.8 USA Cleantech 7.2 11
Save Earth Fund Risk analysis - correlations MSCI index, 5 years* Save Earth Fund World Europe USA Asia Save Earth Fund 1.00 0.88 0.81 0.79 0.85 World 1.00 0.88 0.94 0.86 Europe 1.00 0.69 0.75 USA 1.00 0.74 Asia 1.00 The fund’s benchmark index is MSCI World, which it has the highest correlation with. Asia, Europe and USA are the regions we mainly allocate between, of which the fund has the highest correlation with Asia followed by Europe. World and sector index, 5 years* Save Earth Fund MSCI World WilderHill New Energy S&P Global Water Cleantech index Save Earth Fund 1.00 0.88 0.82 0.90 0.88 MSCI World 1.00 0.72 0.87 0.85 WilderHill New Energy 1.00 0.67 0.88 S&P Global Water 1.00 0.84 Cleantech index 1.00 The water sector is the most mature sector, with the most global and stable companies – the sector also has a high correlation with MSCI World. In the fund we have, and have had, high exposure to the sector which explains the fund’s high correlation with both MSCI World and S&P Global Water index. Renewable energy differ from both the water sector and MSCI World mainly because of the sector’s immature characteristics, with young companies and volatile stock prices. Source: CB Fonder, MSCI, Reuters 12 *Monthly data from MSCI and Reuters for the period 31 December 2008 – 31 December 2013, in EUR.
Risk analysis – standard deviation and beta Save Earth Fund Standard deviation* The fund’s standard deviation is consistently lower than that of the benchmark, MSCI World 8.1% 6.6% Beta against MSCI World* The fund’s beta is consistently below 1 +0.59 13 *36 months data on a 60-day rolling basis (EUR)
Recommend
More recommend