
PULSAR GLITCHES spin frequency time Danai Antonopoulou Centrum Astronomiczne im. Miko ł aja Kopernika
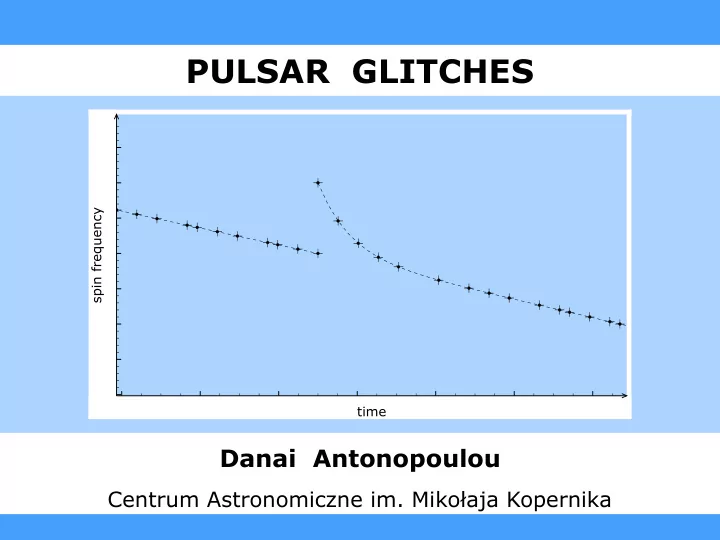
What are pulsar glitches? 11.197 ★ fast spin-up 11.1947 spin frequency ν (Hz) 10 − 3 � ∆ ν � 100 µ Hz 11.1946 11.196 51520 51540 51560 51580 51600 ★ increase in spin-down 11.195 ∆ ˙ ν < 0 11.194 ν (10 − 15 Hz/s) -15550 ★ slow relaxation -15600 (~weeks-years) spin-down rate ˙ -15650 superfluid dynamics -15700 50000 50500 51000 51500 52000 MJD (days) Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
What could be causing them? ★ Superfluid vortices interact/pin to crust lattice (and to core superconducting flux tubes) ★ Pinning holds up to a critical lag ω cr = ( Ω s − Ω c ) max Figure by Nils Andersson Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
What could be causing them? Z ★ Two weakly-coupled components I c Ω c + Ω s ( r ) dI s = L tot ★ Vortices collectively unpin and rearrange sudden exchange of angular momentum Δν { spin frequency time Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
. What could be causing them? Z ★ Post-glitch relaxation I c ˙ ˙ Ω c ( t ) + Ω s ( r, t ) dI s = N ext ˙ Ω s depends on lag ω (r,t), nature of interactions, T , ... ★ At a glitch, ω reduces and so does ˙ Ω s spin-down recovers on local characteristic timescales { spin down Δν time Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitch statistics ★ Melatos et al. 2008: power-law size distributions and exponential distributions of waiting times ★ Evidence for scale-invariance glitches as vortex avalanches events Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitch size distribution data from http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/pulsar/glitches.html, thanks to Ben Shaw Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitch size distribution data from http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/pulsar/glitches.html, thanks to Ben Shaw Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitch size distribution data from http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/pulsar/glitches.html, thanks to Ben Shaw Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitch size distribution pulsar # glitches size distribution J0537-6910 45 normal J0835-4510 (Vela) 19 normal, mixture J1902+0615 6 mixture, normal J1048-5832 6 mixture J2229+6114 6 mixture J1740-3015 35 Weibull, Pareto, lognormal J0534+2200 (Crab) 26 Pareto, Weibull, lognormal J1341-6220 23 Weibull, Pareto, lognormal J0631+1036 15 Pareto, Weibull, lognormal J1801-2304 13 Weibull, mixture J0742-2822 8 Weibull, Pareto, lognormal J1413-6141 7 Weibull, Pareto J0358+5413 6 Weibull, Pareto, lognormal J1825-0935 6 Pareto, Weibull, lognormal J1826-1334 6 Weibull, Pareto J1952+3252 6 Pareto Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitch size distribution ★ Distribution type does not appear to correlate with basic pulsar parameters 10 -14 10 -13 10 -12 10 -11 10 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 spin frequency (Hz) spin down rate (Hz/s) 10 6 10 12 10 13 1000 10000 100000 age (years) dipole B-field (Gauss) ★ Individual, well-studied, cases: J0534+2200 ( Crab ) J0537-6910 Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitch size distribution ★ Distribution type does not appear to correlate with basic pulsar parameters Crab Crab 0537 0537 10 -14 10 -13 10 -12 10 -11 10 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 spin frequency (Hz) spin down rate (Hz/s) Crab 0537 Crab 0537 10 6 10 12 10 13 1000 10000 100000 age (years) dipole B-field (Gauss) ★ Individual, well-studied, cases: J0534+2200 ( Crab ) J0537-6910 Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Crab vs J0537: Glitch sizes Crab pulsar 1 ★ Power-law size distribution, with lower Espinoza et al. 2014 0.8 cut-off single vortex unpinning ∆ ν min >> 0.6 P (s ≤ Δ ν ) ★ Trigger: local avalanches involving 0.4 Crab pulsar billions of vortices (and crustquakes?) 0.2 Power law Lognormal Antonopoulou et al. 2018 0 0.1 1 10 Δ ν ( μ Hz) J0537-6910 ★ Normal distribution, large glitches ★ Trigger: Threshold -regulated process depleting almost all angular momentum reservoir Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Crab vs J0537: Interglitch time intervals Crab pulsar J0537-6910 -15 10 Δ ν g ( μ Hz ) (e) 40 1 30 Δν ( μ Hz) 0.1 25 35 45 20 15 0.01 -0.020 5 10 Hz s -1 ) -3.70 40000 42000 44000 46000 48000 50000 52000 54000 56000 0 MJD (Days) 52000 53000 54000 55000 56000 MJD ★ Unique to J0537: Strong correlation ( Δν , Δ t post ) time to the next glitch (days) 300 Antonopoulou et al. 2018 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 glitch magnitude ( µ Hz) Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Crab vs J0537: Spin down evolution Crab pulsar Year 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 ★ Glitches have little impact on the -3.70 (a) -3.72 ν (10 -10 Hz s -1 ) long-term behaviour -3.74 -3.76 -3.78 -3.80 ★ Overall braking index n~2.5, -3.82 • -3.84 reduces to n~2.3 during period of -3.86 Lyne et al. 2014 high glitch activity (b) 0 -0.005 δ ν (10 -10 Hz s -1 ) spin down -0.010 -0.015 • time ★ Between glitches the braking index -0.020 is close to its long-term value -0.025 40000 42000 44000 46000 48000 50000 52000 54000 56000 MJD (Days) Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Crab vs J0537: Spin down evolution J0537-6910 ★ Glitches have large impact on the long-term behaviour J0537-6910 -199100 ★ Long-term n=-1.2 -199200 ν [10 − 15 Hz / s] -199300 ★ Between glitches n~20 -199400 much bigger than ˙ -199500 its long-term value Antonopoulou et al. 2018 -199600 52000 53000 54000 55000 56000 MJD [days] -15500 ★ Similar to Vela pulsar: ν [10 − 15 Hz / s] -15600 -1 ★ Long-term n~1.7 -15700 -1 Vela ★ Much bigger between ˙ -15800 -1 glitches (n>40) 40000 42000 44000 46000 48000 50000 52000 54000 MJD Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Glitches diversity in other pulsars Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Can one model fit all? ★ Dominance of local or global avalanches depending on critical lag profile (pinning strength, homogeneity, ...), driving rate (spin-down) and temperature ★ Older, lower-B, pulsars (4 objects) tend to have regular large glitches and inter glitch n >> long-term n ★ Other effects to be accounted for: } magnetic field role e.g. magnetars relation to magnetosphere crustal failure thermal effects Antonopoulou Danai POLNS18 Warsaw, 26/03/2018
Recommend
More recommend
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.