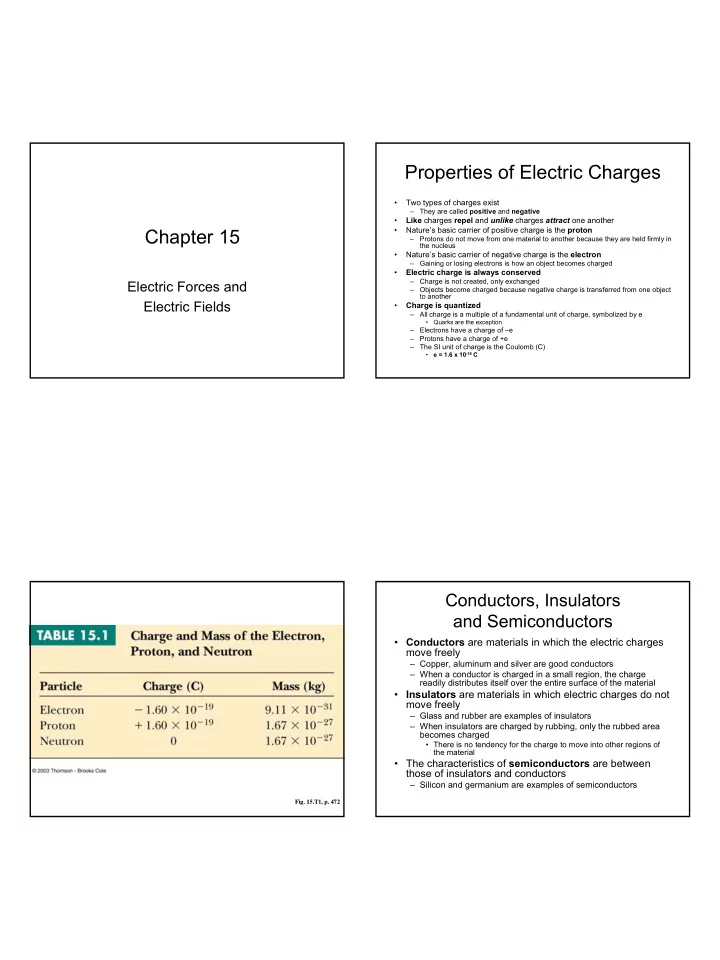

Properties of Electric Charges • Two types of charges exist – They are called positive and negative • Like charges repel and unlike charges attract one another Chapter 15 • Nature’s basic carrier of positive charge is the proton – Protons do not move from one material to another because they are held firmly in the nucleus • Nature’s basic carrier of negative charge is the electron – Gaining or losing electrons is how an object becomes charged • Electric charge is always conserved – Charge is not created, only exchanged Electric Forces and – Objects become charged because negative charge is transferred from one object to another Electric Fields • Charge is quantized – All charge is a multiple of a fundamental unit of charge, symbolized by e • Quarks are the exception – Electrons have a charge of –e – Protons have a charge of +e – The SI unit of charge is the Coulomb (C) e = 1.6 x 10 -19 C • Conductors, Insulators and Semiconductors • Conductors are materials in which the electric charges move freely – Copper, aluminum and silver are good conductors – When a conductor is charged in a small region, the charge readily distributes itself over the entire surface of the material • Insulators are materials in which electric charges do not move freely – Glass and rubber are examples of insulators – When insulators are charged by rubbing, only the rubbed area becomes charged • There is no tendency for the charge to move into other regions of the material • The characteristics of semiconductors are between those of insulators and conductors – Silicon and germanium are examples of semiconductors Fig. 15.T1, p. 472 1
Charging by Conduction Charging by Induction • When an object is connected to a conducting wire or pipe buried in the earth, it is said to be grounded • A charged object (the rod) is • A negatively charged rubber rod is brought near an placed in contact with another uncharged sphere object (the sphere) • The charges in the sphere are redistributed – Some of the electrons in the sphere are repelled from • Some electrons on the rod can the electrons in the rod move to the sphere • The region of the sphere nearest the negatively charged rod has an excess of positive charge • When the rod is removed, the because of the migration of electrons away from sphere is left with a charge this location • A grounded conducting wire is connected to the • The object being charged is sphere always left with a charge – Allows some of the electrons to move from the sphere having the same sign as the to the ground • The wire to ground is removed, the sphere is left object doing the charging with an excess of induced positive charge • The positive charge on the sphere is evenly distributed due to the repulsion between the positive charges • Charging by induction requires no contact with the object inducing the charge Examples of Polarization Polarization • In most neutral atoms or molecules, the center • The charged object of positive charge coincides with the center of (on the left) induces negative charge charge on the surface of the insulator • In the presence of a charged object, these centers may separate slightly • A charged comb attracts bits of paper – This results in more positive charge on one side of the molecule than on the other side due to polarization of the paper • This realignment of charge on the surface of an insulator is known as polarization 2
QUICK QUIZ 15.1 QUICK QUIZ 15.1 ANSWER (d). Object A could possess a net If a suspended object A is charge whose sign is opposite that of attracted to object B, which is the excess charge on B. If object A is charged, we can conclude that (a) neutral, B would also attract it by object A is uncharged, (b) object A creating an induced charge on the is charged, (c) object B is surface of A. This situation is illustrated positively charged, or (d) object A in Figure 15.5 of the textbook. may be either charged or uncharged. Coulomb’s Law Coulomb’s Law, cont. • Mathematically, q q • Coulomb shows that an electrical force has F = 1 2 k e 2 r the following properties: • k e is called the Coulomb Constant – It is inversely proportional to the square of the k e = 8.99 x 10 9 N m 2 /C 2 separation between the two particles and is along • Typical charges can be in the µC range the line joining them – Remember, Coulombs must be used in the equation – It is proportional to the product of the magnitudes of the charges q 1 and q 2 on the two • Remember that force is a vector quantity particles – It is attractive if the charges are of opposite signs and repulsive if the charges have the same signs 3
Vector Nature of Electric Forces Vector Nature of Forces, cont. • Two point charges are • Two point charges are separated by a distance r separated by a distance r • The like charges produce • The unlike charges a repulsive force between produce a attractive force them between them • The force on q 1 is equal • The force on q 1 is equal in magnitude and in magnitude and opposite in direction to opposite in direction to the force on q 2 the force on q 2 q q F = 1 2 k q q e 2 r F = 1 2 k e 2 r Electrical Forces are Field Electrical Force Compared to Forces Gravitational Force • This is the second example of a field force • Both are inverse square laws – Gravity was the first • The mathematical form of both laws is the • Remember, with a field force, the force is same exerted by one object on another object even • Electrical forces can be either attractive or though there is no physical contact between repulsive them • Gravitational forces are always attractive 4
QUICK QUIZ 15.2 QUICK QUIZ 15.2 ANSWER Object A has a charge of +2 µ C, (b). By Newton’s third law, the two and object B has a charge of +6 objects will exert forces having equal µ C. Which statement is true: magnitudes but opposite directions on (a) F AB = –3 F BA , (b) F AB = – F BA , or each other. (c) 3 F AB = – F BA The Superposition Principle • The resultant force on any one charge equals the vector sum of the forces exerted by the other individual charges that are present. – Remember to add the forces vectorially Fig. 15.8, p. 474 5
Superposition Principle Electrical Field Example • An electric field is said to exist in the region of space around a • The force exerted by charged object q 1 on q 3 is F 13 – When another charged object enters this electric field, the field • The force exerted by exerts a force on the second q 2 on q 3 is F 23 charged object • A charged particle, with charge • The total force Q, produces an electric field in exerted on q 3 is the the region of space around it vector sum of F 13 • A small test charge , q o , placed and F 23 in the field, will experience a force Electric Field Direction of Electric Field • Mathematically, • The electric field F k Q produced by a = = E e negative charge is 2 q r o directed toward the charge • Use this for the magnitude of the field – A positive test • The electric field is a vector quantity charge would be • The direction of the field is defined to be attracted to the the direction of the electric force that negative source would be exerted on a small positive test charge charge placed at that point 6
More About a Test Charge and Direction of Electric Field, cont The Electric Field • The test charge is required to be a small charge • The electric field – It can cause no rearrangement of the charges on the produced by a source charge positive charge is • The electric field exists whether or not there is a directed away from test charge present the charge • The Superposition Principle can be applied to – A positive test the electric field if a group of charges is present charge would be repelled from the positive source charge Problem Solving Strategy • Units q q 1 2 F = – When using k e , charges must be in Coulombs, k e 2 distances in meters and force in Newtons r – If values are given in other units, they must be converted • Applying Coulomb’s Law to point charges – Use the superposition principle for more than two charges – Use Coulomb’s Law to find the individual forces – Directions of forces are found by noting that like charges repel and unlike charges attract Fig. 15.12, p. 477 7
Recommend
More recommend