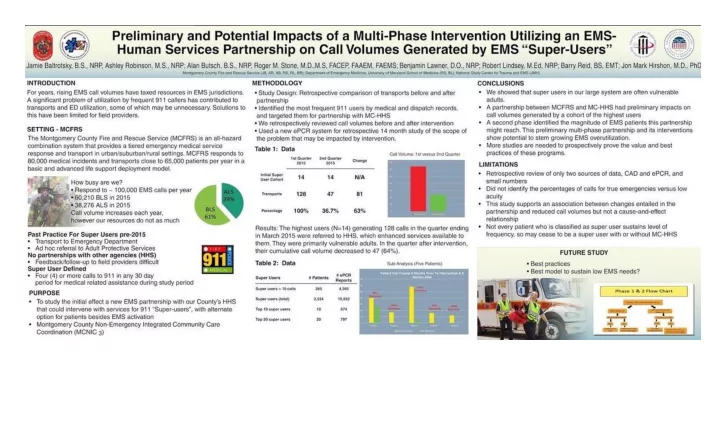

Preliminary and Potential Impacts of a Multi-Phase Intervention Utilizing an EMS-Human Services Partnership on Call Volumes Generated by EMS “Super-Users” Jamie Baltrotsky, B.S., NRP, Ashley Robinson, M.S., NRP; Alan Butsch, B.S., NRP, Roger M. Stone, M.D.,M.S, FACEP, FAAEM; Benjamin Lawner, D.O., NRP; Robert Lindsey, M.Ed, NRP; Barry Reid, BS, EMT; Jon Mark Hirshon, M.D., PhD Montgomery County Fire & Rescue (JB,AR.AB, RS, RL, BR) Department of Emergency Medicine , University of Maryland SOM(RS,BL) National Study Center for Trauma and EMS (JMH) Introduction Introduction: For years, rising EMS call volumes have taxed resources in EMS jurisdictions. A significant problem of utilization by frequent 911 callers has contributed to transports and ED utilization, some of which may be unnecessary. Solutions to this have been limited for field providers. Setting: MCFRS The Montgomery County Fire Rescue Service (MCFRS) is an all-hazard combination system that provides a tiered emergency medical service response and transport in urban/suburban/rural settings. MCFRS responds to 80,000 medical incidents and transports close to 65, 000 patients per year in a basic and advanced life support deployment model.
MCFRS Fig 1 How busy are we? Respond to ~ 100,000 EMS calls per year 60,210 BLS in 2015 38, 276 ALS in 2015 Call volume increases each year, however our resources do not as much Setting Past Practice For Super Users pre-2015 Transport to Emergency Department Ad hoc referral to Adult Protective Services No partnerships with other agencies (HHS) Feedback/follow-up to field providers difficult Super User Defined Four (4) or more calls to 911 in any 30 day period for medical related assistance during study period Purpose of Study Purpose: To study the initial effect a new EMS partnership with our County’s HHS that could intervene with services for 911 “Super-users”, with alternate option for patients besides EMS activation Montgomery County Non-Emergency Integrated Community Care Coordination MC-NIC 3
Methodology Study Design: Retrospective comparison of transports before and after partnership Identified the most frequent 911 users by medical and dispatch records, and targeted them for partnership with MC-HHS We retrospectively reviewed call volumes before and after intervention Used a new ePCR system for retrospective 14 month study of the scope of the problem that may be impacted by intervention. Results Table 1: Data Results: The highest users (N=14) generating 128 calls in the quarter ending in March 2015 were referred to HHS, which enhanced services available to them. They were primarily vulnerable adults. In the Quarter after intervention, their cumulative call volume decreased to 47 (64%). Table 1 2 nd Quarter 1st Quarter 2015 2015 Change Initial Super user Cohort 14 14 N/A Transports 128 47 81 63% Percentage 100% 36.7%
Call Volume: 1 st versus 2 nd Quarter 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 1st Quarter 2015 2nd Quarter 2015 Results In a second phase, we developed field referral and e-PCR search programs to identify super-users over a 14 month period from April 2015 to July 2016. There were 265 patients with > 10 calls in study period accounting for 4,393 e-PCRs Of those, the top super-users (N=20) accounted for 797 responses. Table 2 # ePCR Super Users # Patients reports Super users > 10 calls 265 4,393 Super users (total) 2,534 15, 933 Top 10 super users 10 674 Top 20 super users 20 797 Referrals to MC-HHS 71
Sub-Analysis Five patients Patient Call Volume 6 Months Prior To Intervention & 6 Months After 70 60 93 % Decrease 50 35% Decrease 40 30 100% 94% 100% Decrease Decrease Decrease 20 10 0 Patient 1 Patient 2 Patient 3 Patient 4 Patient 5 Before Intervention After Intervention Conclusions We showed that super users in our large system are often vulnerable adults. A partnership between MCFRS and MC-HHS had preliminary impacts on call volumes generated by a cohort of the highest users A second phase identified the magnitude of EMS patients this partnership might reach. This preliminary multi-phase partnership and its interventions show potential to stem growing EMS overutilization. More studies are needed to prospectively prove the value and best practices of these programs. Limitations Retrospective review of only two sources of data, CAD and ePCR, and small numbers Did not identify the percentages of calls for true emergencies versus low acuity This study supports an association between changes entailed in the partnership and reduced call volumes but not a cause-and- effect relationship Not every patient who is classified as super user sustains level of frequency, so may cease to be a super user with or without MC-HHS
Future Study Best practices Best model to sustain low EMS needs?
Recommend
More recommend