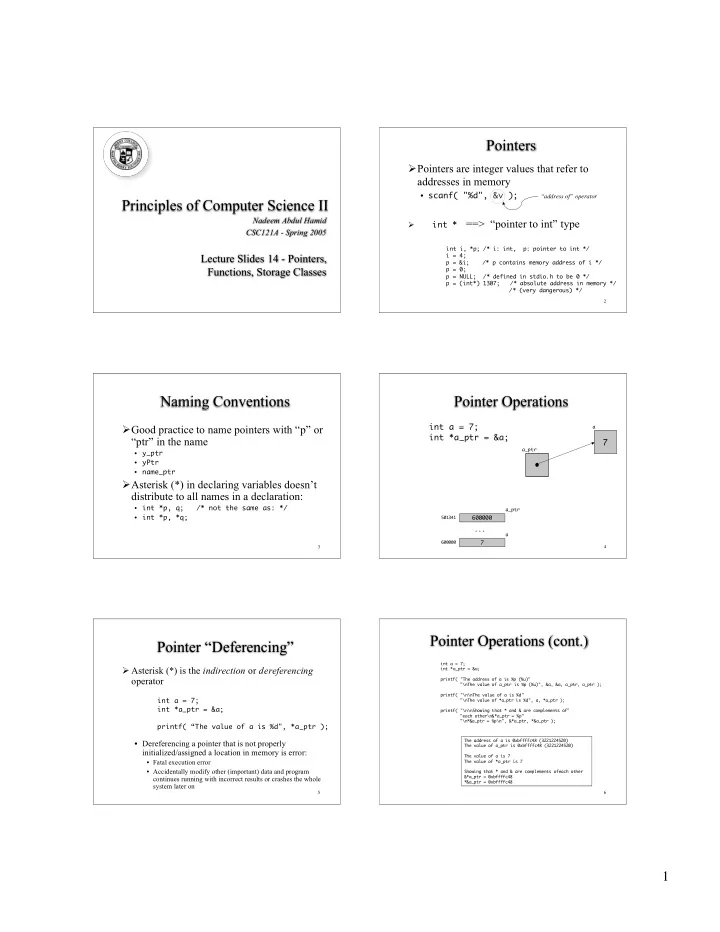

Pointers Pointers are integer values that refer to addresses in memory • scanf( "%d", &v ); “address of” operator Principles of Computer Science II Nadeem Abdul Hamid int * ==> “pointer to int” type CSC121A - Spring 2005 int i, *p; /* i: int, p: pointer to int */ Lecture Slides 14 - Pointers, i = 4; p = &i; /* p contains memory address of i */ Functions, Storage Classes p = 0; p = NULL; /* defined in stdio.h to be 0 */ p = (int*) 1307; /* absolute address in memory */ /* (very dangerous) */ 2 Naming Conventions Pointer Operations int a = 7; Good practice to name pointers with “p” or a int *a_ptr = &a; “ptr” in the name 7 a_ptr y_ptr • yPtr • 7 name_ptr • Asterisk (*) in declaring variables doesn’t distribute to all names in a declaration: int *p, q; /* not the same as: */ • a_ptr int *p, *q; • 501341 600000 ... a 600000 7 3 4 Pointer Operations (cont.) Pointer “Deferencing” int a = 7; Asterisk (*) is the indirection or d ereferencing int *a_ptr = &a; operator printf( "The address of a is %p (%u)" "\nThe value of a_ptr is %p (%u)", &a, &a, a_ptr, a_ptr ); printf( "\n\nThe value of a is %d" int a = 7; "\nThe value of *a_ptr is %d", a, *a_ptr ); int *a_ptr = &a; printf( "\n\nShowing that * and & are complements of" "each other\n&*a_ptr = %p" "\n*&a_ptr = %p\n", &*a_ptr, *&a_ptr ); printf( “The value of a is %d", *a_ptr ); The address of a is 0xbffffc48 (3221224520) • Dereferencing a pointer that is not properly The value of a_ptr is 0xbffffc48 (3221224520) initialized/assigned a location in memory is error: The value of a is 7 • Fatal execution error The value of *a_ptr is 7 • Accidentally modify other (important) data and program Showing that * and & are complements ofeach other &*a_ptr = 0xbffffc48 continues running with incorrect results or crashes the whole *&a_ptr = 0xbffffc48 system later on 5 6 1
A swap Function Call-by-Reference void swap( int, int ); Function arguments in C are passed strictly int main(void) { using “call-by-value” mechanism int a = 5, b = 8; printf( "%d --- %d\n", a, b ); • Values of variables are copies into swap( a, b ); corresponding function parameters printf( "%d --- %d\n", a, b ); “Call-by-reference” can be simulated by return 0; } pointer parameters void swap( int a, int b ) { int t = a; a = b; b = t; } 7 8 A Working swap Function Void Pointers A pointer to void ( void * ) is a generic void swap( int *, int * ); pointer that represents any pointer type int main(void) { • Any pointer type can be assigned to a void int a = 5, b = 8; printf( "%d --- %d\n", a, b ); pointer and vice versa, without any need for a swap( &a, &b ); cast printf( "%d --- %d\n", a, b ); • Void pointers cannot be (directly) dereferenced return 0; (syntax error) } int a; void swap( int *p, int *q ) { void *p = &a; int t = *p; printf("a=%d\n", a); *p = *q; *(int*)p = 5; *q = t; printf("a=%d\n", a); } 9 10 The ________ of an identifier is #include <stdio.h> the part of the program in which int a = 10; Storage Classes the identifier is known or int *q = &a; accessible. A. “Scope” void foo( void ); Basic rule: identifiers are Section 8.6 (page 274-280) int main( void ) { accessible only within the block in int a = 5; Every variable and function in C has two which declared. int *p = &a; printf( "%d\n", a ); attributes: printf( "%d\n", *p ); printf( "%d\n", *q ); • Type { • Storage class int a = 7; printf( "%d\n", a ); Four possible storage classes : printf( "%d\n", *p ); } auto - default for variables declared in a block • printf( "%d\n", ++a ); extern - global variables with permanent storage • foo(); return 0; • “Look for it elsewhere, either in this file or in some other” } • All functions have external storage class register - store variable in high-speed memory void foo( void ) { • printf( "%d\n", a ); registers, if possible 11 12 } 2
External (Global) Variables Storage Class static /* file1.c */ Two different uses: int a = 100; • Allows local variable to retain previous value int addone( int b ) { when block is reentered return b + 1; } • In connection with external declarations /* file2.c */ void f( void ) { #include <stdio.h> static int cnt = 0; int zero = 0; int addone(int); printf( "zero is now %d," " count is now %d\n", ++zero, ++cnt ); int main( void ) { } extern int a; int main( void ) { printf( "%d dalmations\n", addone(a) ); f(); f(); f(); return 0; 13 return 0; 14 } } Static External Variables const Qualifier Second (more subtle) use of static Informs the compiler that the value of a particular variable should not be modified • Provides privacy mechanism for program modularity • Static external variables are scope restricted to the • (like final in Java) remainder of the source file in which they are declared With pointers, four possible situations: • (Example - pseudorandom number generator - pg. 279- • Non-constant pointer to non-constant data 280) • Data can be modified, pointer can be changed • Non-constant pointer to constant data • Data cannot be modified, pointer can be changed Note: Both external and static variables are • Constant pointer to non-constant data initialized to zero automatically by C compiler, • … but not auto or register variables • Constant pointer to constant data • … 15 16 int a = 5; Pointers and int cubeA( int c ) { return c * c * c; } Passing Data const int b = 10; int *p = &a; void cubeB( int *c ) { *c = *c * *c * *c; } const int * const q = &a; Between const int *r = &b; int c; const int * const s = &b; void cubeC( void ) { c = c * c * c; } Functions printf("\n====\n" "a=%d, b=%d, p=%p,\n" int main( void ) { "q=%p, r=%p, s=%p\n", int a = 5; Note : gcc compiler may ignore a, b, p, q, r, s); const qualifiers unless you compile a = cubeA( a ); with: a++; printf( "%d\n", a ); gcc -pedantic-errors … b++; /* error */ (*p)++; a = 5; p++; cubeB( &a ); (*q)++; printf( "%d\n", a ); q++; /* error */ (*r)++; /* error */ Note: Avoid global a = 5; r++; c = a; variables!!! (*s)++; /* error */ cubeC(); s++; /* error */ printf( "%d\n", c ); printf("\na=%d, b=%d, p=%p,\n" return 0; "q=%p, r=%p, s=%p\n", } 17 18 a, b, p, q, r, s); 3
Recommend
More recommend