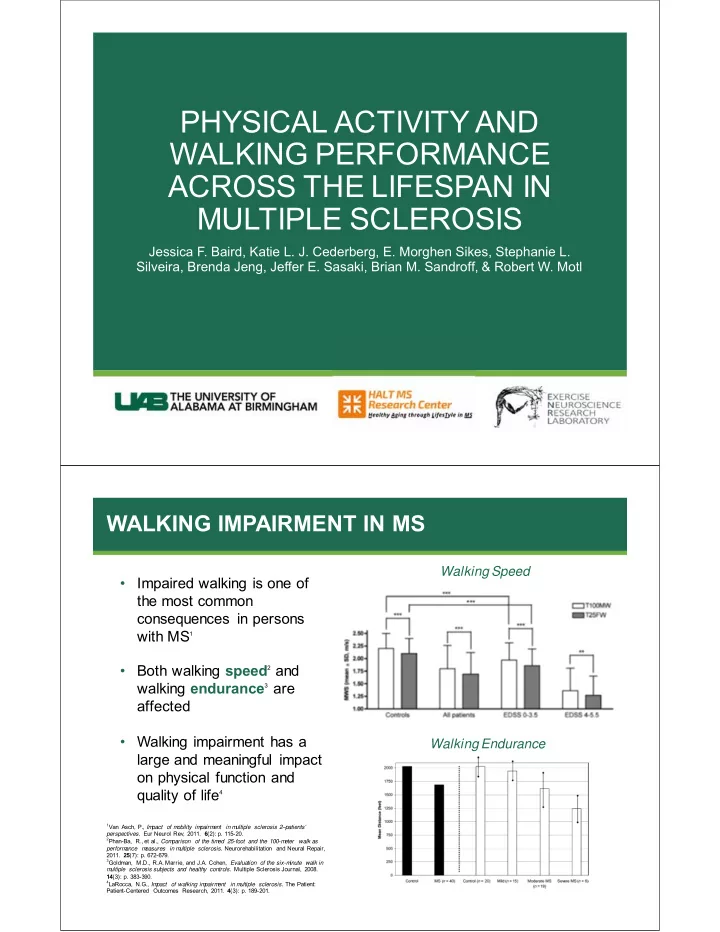

PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND WALKING PERFORMANCE ACROSS THE LIFESPAN IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Jessica F. Baird, Katie L. J. Cederberg, E. Morghen Sikes, Stephanie L. Silveira, Brenda Jeng, Jeffer E. Sasaki, Brian M. Sandroff, & Robert W. Motl WALKING IMPAIRMENT IN MS Walking Speed • Impaired walking is one of the most common consequences in persons with MS 1 2 and • Both walking speed 3 are walking endurance affected • Walking impairment has a Walking Endurance large and meaningful impact on physical function and quality of life 4 1 Van Asch, P., Im pact of m obility im pairm ent in m ultiple sclerosis 2–patients’ perspectives. Eur Neurol Rev, 2011. 6 (2): p. 115-20. 2 Phan-Ba, R., et al., Com parison of the tim ed 25-foot and the 100-m eter walk as ultiple sclerosis. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, perform ance m easures in m 2011. 25 (7): p. 672-679. 3 Goldman, M.D., R.A. Marrie, and J.A. Cohen, Evaluation of the six-m inute walk in m ultiple sclerosis subjects and healthy controls. Multiple Sclerosis Journal, 2008. 14 (3): p. 383-390. 4 LaRocca, N.G., Im ultiple sclerosis. The Patient: pact of walking im pairm ent in m Patient-Centered Outcomes Research, 2011. 4 (3): p. 189-201.
WALKING PERFORMANCE AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY 43.4 ± 7.7 0.40 * * * 0.47 VO 2peak MVPA 0.62 6MW (ml/kg/min) (min/day) (feet) 45.9 ± 9.6 49.5 ± 10.2 49.0 ± 11.6 THE PREVALENCE OF OLDER ADULTS WITH MS IS ON THE RISE Purpose: Examine the relationship between physical activity and walking performance across the lifespan among adults with MS
METHODS: PARTICIPANTS AND PROCEDURES • Participants • Walking Performance • 20 to 79 years of age • Walking speed = T25FW • Diagnosis of MS • Walking endurance = 6MW • Ambulatory with or without assistance • Physical Activity • Relapse free for at least 30 days • ActiGraph, model GT3X+ • 7 days; valid day = minimum 10 hours • Categorized into one of three wear time predetermined groups based on age: • Data processed into 60 second epochs • Young Adults = 20 – 39 years • Time spend engaged in Light Physical • Middle-age Adults = 40 – 59 years Activity ( LPA ) and Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity ( MVPA ) calculated with • Older Adults = 60 – 79 years MS specific cutpoints 5 5 Sandroff, B.M., R.W. Motl, and Y. Suh, Accelerom eter output and its association with energy expenditure in ultiple sclerosis. Journal of Rehabilitation Research & Development, 2012. 49 (3). persons with m HYPOTHESES • We expected walking performance and physical activity to decrease with increasing age • Trend analysis • We expected there to be a strong association between physical activity and walking performance, and this relationship would be strongest among older adults with MS • Spearman’s rank-order correlations • Examined initial group differences as potential confounders
RESULTS: PARTICIPANTS Table 1. Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants by age group Age Groups Young (n=39) Middle-aged (n=44) Older (n=41) Total (124) p -value Age; years 33.3 (5.0) 48.5 (5.8) 65.8 (4.5) 49.4 (14.1) 0.001** Sex; % female 79.5 72.7 73.2 75.0 0.74 Race; % Caucasian 43.6 65.9 82.9 64.5 0.01* Type of MS; % RRMS 87.2 88.6 82.9 89.9 0.82 PDDS; Median (IQR) 0.0 (3.0) 1.0 (2.0) 2.0 (3.5) 1.0 (3.0) 0.02* Disease Duration; years 6.7 (5.0) 12.4 (5.8) 19.9 (8.7) 13.1 (8.6). 0.001** Data presented as mean (SD) unless otherwise noted. MS = multiple sclerosis; RRMS = relapsing- remitting MS; PDDS = Patient Determined Disease Steps; * = p <0.05; ** = p <0.01; Young adults = 20-39 years; Middle-aged = 40-59 years; Older adults = 60-79 years RESULTS: WALKING PERFORMANCE AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY BY AGE GROUP Y oung Middle-aged Older F p LPA; min/day 307.0 (100.2) 309.1 (79.8) 296.1 (97.9) 0.24 0.62 MVPA; min/day 21.7 (14.4) 24.6 (17.4) 12.8 (13.1) 6.05 0.02* T25FW; sec 4.7 (1.7) 5.5 (3.5) 6.0 (3.1) 4.45 0.04 * 6MW; ft 1584.8 (359.3) 1551.4 (554.5) 1378.3 (404.9) 4.12 0.04* 330 7 * (min/day) T25FW (sec) 310 6 290 5 LPA 270 4 250 3 30 1700 * * (min/day) 25 1600 6MW (ft) 20 1500 15 1400 MVPA 10 1300 5 1200 Young Middle-aged Older Young Middle-aged Older
RESULTS: THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND WALKING PERFORMANCE LPA MVPA Young Middle-aged Older Overall Young Middle-aged Older Overall T25FW -0.27 0.08 -0.40* -0.17 -0.22 -0.51** -0.62** -0.54** 6MW 0.21 -0.08 0.34* 0.17 0.33 0.43** 0.62** 0.56** 700 700 600 600 (min/day) 500 500 400 400 300 300 LPA 200 200 100 100 0 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 140 140 120 120 (min/day) 100 100 80 80 60 60 MVPA 40 40 20 20 0 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 T25FW (sec) 6MW (ft) RESULTS: CONTROLLING FOR RACE, AMBULATORY DISABILITY, AND DISEASE DURATION LPA MVPA Young Middle-aged Older Overall Young Middle-aged Older Overall T25FW -0.15 0.15 -0.44* -0.10 -0.01 -0.16 -0.63** -0.33** 6MW 0.02 -0.13 0.31 0.08 0.10 0.08 0.70** 0.38** 250 250 (residuals; min) 150 150 50 50 -50 -50 LPA -150 -150 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 -600 -100 400 900 30 30 (residuals; min) 20 20 10 10 0 0 MVPA -10 -10 -20 -20 -4 -2 0 2 4 6 -600 -100 400 900 T25FW (residuals; sec) 6MW (residuals; ft)
CONCLUSIONS • MVPA, walking speed, and walking endurance progressively decreased with increasing age • Older adults with MS have a particular need for rehabilitation approaches aimed at improving walking performance • Aging + MS = ? • MVPA strongly correlated with walking performance in Older adults with MS • Behavior change interventions that target MVPA may be an approach for improving walking performance in older adults with MS • What about LPA? • What about young adults with MS? ACKNOWLEDGMENTS • UAB Center for Exercise Medicine NIH T32 postdoctoral training grant • Exercise Neuroscience Research Laboratory
QUESTIONS? EMAIL: JFBAIRD@UAB.EDU
Recommend
More recommend