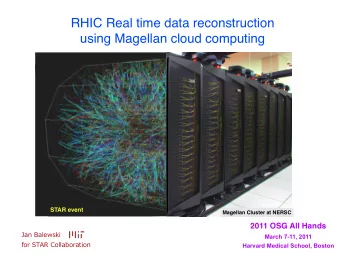
On unreasonable ineffectiveness Problem of security engineering: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Ineffectiveness of trust D. Pavlovic On unreasonable ineffectiveness Problem of security engineering: Background Analysis the case of adverse selection Method of trust certificates Conclusion Dusko Pavlovic Kestrel Institute and Oxford
Ineffectiveness of trust D. Pavlovic On unreasonable ineffectiveness Problem of security engineering: Background Analysis the case of adverse selection Method of trust certificates Conclusion Dusko Pavlovic Kestrel Institute and Oxford University Elva, Estonia June 2010
Ineffectiveness of Outline trust D. Pavlovic Problem Problem : All protocols are insecure Background Analysis Background : Notion of trust Method Conclusion Analysis : Trust dynamics Method : Learning trust concepts Conclusion : Security is an elephant
Ineffectiveness of Outline trust D. Pavlovic Problem Problem : All protocols are insecure The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust The life cycle of security Background Adverse selection Analysis Method Problem of trust Conclusion Background : Notion of trust Analysis : Trust dynamics Method : Learning trust concepts Conclusion : Security is an elephant
Ineffectiveness of The Unreasonable Effectiveness trust D. Pavlovic of Mathematics in Natural Sciences Problem E. Wigner (1960) The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background Analysis ◮ Why is nature made in the measure of our mind? Method Conclusion
Ineffectiveness of The Unreasonable In effectiveness trust D. Pavlovic of Engineering in Security Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background Analysis ◮ Why are we not becoming more secure Method from more security technologies? Conclusion
Ineffectiveness of The Unreasonable In effectiveness trust D. Pavlovic of Engineering in Security Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background Analysis Method Conclusion Why?
Ineffectiveness of Failures are first-class citizens trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background Analysis Method Conclusion
Ineffectiveness of Failures are first-class citizens trust D. Pavlovic Bull’s protocol Problem The life cycle of security ◮ Isabelle: secure for E ( k , m ; n ) Adverse selection Problem of trust ◮ Ryan & Schneider: not for E ( k , m ; n ) = n ⊕ H k ( m ) Background Analysis Method Conclusion
Ineffectiveness of Failures are first-class citizens trust D. Pavlovic Bull’s protocol Problem The life cycle of security ◮ Isabelle: secure for E ( k , m ; n ) Adverse selection Problem of trust ◮ Ryan & Schneider: not for E ( k , m ; n ) = n ⊕ H k ( m ) Background Analysis Method IPSec GDoI Conclusion ◮ IETF MSec WG: secure (7 drafts), verified (3 times) ◮ Cathy & Dusko: GDoI_PoP attack
Ineffectiveness of Failures are first-class citizens trust D. Pavlovic Bull’s protocol Problem The life cycle of security ◮ Isabelle: secure for E ( k , m ; n ) Adverse selection Problem of trust ◮ Ryan & Schneider: not for E ( k , m ; n ) = n ⊕ H k ( m ) Background Analysis Method IPSec GDoI Conclusion ◮ IETF MSec WG: secure (7 drafts), verified (3 times) ◮ Cathy & Dusko: GDoI_PoP attack MQV ◮ NSA: "MQV is critical for national security of US" ◮ Krawczyk: MQV insecure
Ineffectiveness of Failures are first-class citizens trust D. Pavlovic Bull’s protocol Problem The life cycle of security ◮ Isabelle: secure for E ( k , m ; n ) Adverse selection Problem of trust ◮ Ryan & Schneider: not for E ( k , m ; n ) = n ⊕ H k ( m ) Background Analysis Method IPSec GDoI Conclusion ◮ IETF MSec WG: secure (7 drafts), verified (3 times) ◮ Cathy & Dusko: GDoI_PoP attack MQV ◮ NSA: "MQV is critical for national security of US" ◮ Krawczyk: MQV insecure, HMQV proven secure
Ineffectiveness of Failures are first-class citizens trust D. Pavlovic Bull’s protocol Problem The life cycle of security ◮ Isabelle: secure for E ( k , m ; n ) Adverse selection Problem of trust ◮ Ryan & Schneider: not for E ( k , m ; n ) = n ⊕ H k ( m ) Background Analysis Method IPSec GDoI Conclusion ◮ IETF MSec WG: secure (7 drafts), verified (3 times) ◮ Cathy & Dusko: GDoI_PoP attack MQV ◮ NSA: "MQV is critical for national security of US" ◮ Krawczyk: MQV insecure, HMQV proven secure ◮ Menezes: HMQV insecure
Ineffectiveness of Security is an adversarial process trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background Protocol Analysis Method Conclusion Attack
Ineffectiveness of Security is an adversarial process trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background Protocol Analysis theory Method Conclusion counter-model Attack
Ineffectiveness of Adverse selection trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background T RUST E-certified uncertified Analysis honest 94.6% 97.5% Method Conclusion malicious 5.4% 2.5 % Table: Trustworthyness of T RUST E [Edelman 2007]
Ineffectiveness of Adverse selection trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Google Background sponsored organic Analysis top 4.44% 2.73% Method top 3 5.33% 2.93 % Conclusion top 10 5.89% 2.74 % top 50 5.93% 3.04 % Table: Malicious search engine placements [Edelman 2007]
Ineffectiveness of Adverse selection trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Yahoo! Background sponsored organic Analysis top 6.35% 0.00% Method top 3 5.72% 0.35 % Conclusion top 10 5.14% 1.47 % top 50 5.40% 1.55 % Table: Malicious search engine placements [Edelman 2007]
Ineffectiveness of Adverse selection trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Ask Background sponsored organic Analysis top 7.99% 3.23% Method top 3 7.99% 3.24 % Conclusion top 10 8.31% 2.94 % top 50 8.20% 3.12 % Table: Malicious search engine placements [Edelman 2007]
Ineffectiveness of Adverse selection trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background "Pillars of the society" phenomenon Analysis Method ◮ social hubs are more often corrupt Conclusion ◮ the rich are more often thieves ◮ . . .
Ineffectiveness of Problem of trust trust D. Pavlovic Problem The life cycle of security Adverse selection Problem of trust Background ◮ Why does adverse selection happen? Analysis Method ◮ Can it be eliminated? Limited? Conclusion ◮ Can we hedge against it? ◮ Is there a rational trust policy?
Ineffectiveness of Outline trust D. Pavlovic Problem Problem : All protocols are insecure Background Analysis Background : Notion of trust Method Conclusion Analysis : Trust dynamics Method : Learning trust concepts Conclusion : Security is an elephant
Ineffectiveness of What is trust? trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Alice trusts that Bob will act according to protocol Φ . Analysis Method Conclusion
Ineffectiveness of What is trust? trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Alice trusts that Bob will act according to protocol Φ . Analysis Method Conclusion Examples ◮ shopping: Bob will deliver goods ◮ marketing: Bob will pay for goods ◮ access control: Bob will not abuse resources ◮ key infrastructure: Bob’s keys are not compromised
Ineffectiveness of Modeling trust trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Analysis Φ Trust relation u −→ j Method r Conclusion ◮ u : trustor ◮ j : trustee ◮ Φ : entrusted concept (protocol, task, property) ◮ r : trust rating
Ineffectiveness of Views of Trust trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Analysis Method Local: trust logics Conclusion Φ u −→ j means that ◮ u requires Φ ◮ j guarantees Φ
Ineffectiveness of Views of Trust trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Global: trust networks Analysis d d b u v w k means that −→ −→ −→ Method r s t Conclusion ◮ u has a delegation certificate for v ◮ v has a delegation certificate for w ◮ w has a binding certificate for the key k
Ineffectiveness of Views of Trust trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Global: trust networks Analysis d d b u v w k means that −→ −→ −→ Method r s t Conclusion ◮ u has a delegation certificate for v ◮ v has a delegation certificate for w ◮ w has a binding certificate for the key k ◮ thus u can use the key k ◮ even compute its trust rating rst ◮ although they had no direct contact
Ineffectiveness of Network dynamics trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Analysis Networks are built upon networks: Method Conclusion ◮ session keys upon long term keys ◮ strong secrets upon weak secrets ◮ crypto channels upon physical or social channels
Ineffectiveness of Network dynamics trust D. Pavlovic Problem Background Analysis Networks are built upon networks: Method Conclusion ◮ session keys upon long term keys ◮ strong secrets upon weak secrets ◮ crypto channels upon physical or social channels ◮ secure interactions upon trust ◮ trust upon secure interactions
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.