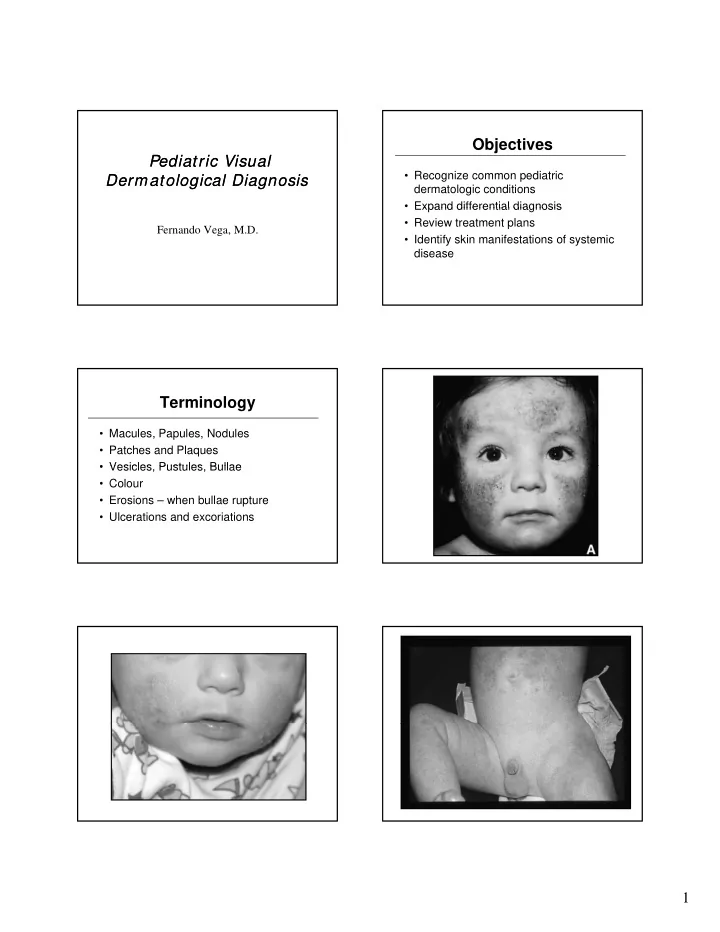

Objectives Pediatric Visual Pediatric Visual • Recognize common pediatric Dermatological Diagnosis Dermatological Diagnosis dermatologic conditions • Expand differential diagnosis Expand differential diagnosis • Review treatment plans Fernando Vega, M.D. • Identify skin manifestations of systemic disease Terminology • Macules, Papules, Nodules • Patches and Plaques • Vesicles Pustules Bullae • Vesicles, Pustules, Bullae • Colour • Erosions – when bullae rupture • Ulcerations and excoriations 1
Atopic Dermatitis • 3-5% of children 6 mo to 10 yr • Described in 1935 • Ill defined red pruritic papules/plaques • Ill-defined, red, pruritic, papules/plaques • Diaper area spared • Acute: erythema, scaly, vesicles, crusts • Chronic: scaly, lichenified, pigment changes Atopic Dermatitis Hints to diagnosis • Generalized dry skin • Accentuation of skin markings on palms • Accentuation of skin markings on palms and soles • Dennie-Morgan lines • Fissures at base of earlobe • Allergic history 2
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment • Moisturize • Baths only • Anti histamine • Anti-histamine • Topical steroids to red and rough areas – Prevex HC – Desacort • Immune modulators Superinfected Eczema • Red and crusty • Usually S. aureus • Cephalexin 40 mg/kg/day divided TID for 10 p g g y days • More potent topical steroid • Topical antibiotic – Fucidin • Anti-histamine • Refer to Dermatology 3
Scabies • Intense pruritus • Diffuse, papular rash – Between fingers, flexor aspects of wrists, g , p , anterior axillary folds, waist, navel • May be vesicular in children < 2 years – Head, neck, palms, soles – Hypersensitivity reaction to protein of parasite Scabies Treatment • 5% permethrin cream for infants, young children, pregnant and nursing mother – Kwellada-P or Nix Kwellada P or Nix – Cover entire body from neck down – Include head and neck for infants – Wash after 8-14 hours • Can use Lindane for older children 4
Tinea corporis Ringworm • Face, trunk or limbs • Pruritic, circular, slightly erythematous • Well-demarcated with scaly, vesicular or Well demarcated with scaly, vesicular or pustular border • Id reaction • Mistaken for atopic, seborrheic or contact dermatitis • Treament: Terbinafine (Lamisil) Pityriasis Rosea • Begins with herald patch – Large, isolated oval lesion with central clearing • More lesions 5-10 days later • Christmas tree distribution • Treatment: anti-histamines Eczema • Differential Diagnosis – Atopic dermatitis – Scabies – Tinea corporis Tinea corporis – Pityriasis rosea • If vesicular, check for HSV1, HSV2, VZV • Beware of superinfection • Think of immune deficiency if difficult to treat 5
Urticaria • Transient, well-demarcated wheels • Pruritic • Part of IgE mediated hypersensitivity • Part of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction • May leave central clearing • Triggers are numerous 6
Kawasaki Disease Kawasaki Disease Diagnostic Criteria Lab Features • ↑ WBC • Fever for 5 or more days • ↑ ESR, positive CRP • Presence of 4 of the following: 1. Bilateral conjunctival injection • Anemia • Anemia 2. Changes in the oropharyngeal mucous • Mild ↑ transaminases membranes 3. Changes of the peripheral extremities • ↓ albumin 4. Rash • Sterile pyuria, aseptic meningitis 5. Cervical adenopathy • ↑ platelets by day 10-14 • Illness can’t be explained by other disease Kawasaki Disease Kawasaki Disease Differential Diagnosis Difficulties with Diagnosis • Measles • Stevens-Johnson • Clinical diagnosis Syndrome • Scarlet fever • No single test • Systemic Onset • Drug reactions g • Diagnosis of exclusion • Diagnosis of exclusion Juvenile • Viral exanthems • Atypical KD Rheumatoid Arthritis • Toxic Shock • Staph scalded skin – Do not fulfill all criteria Syndrome syndrome – More common in < 1 year and > 8 years Kawasaki Disease Kawasaki Disease Treatment Treatment • IV Ig 2 g/kg as single dose – Expect rapid resolution of fever • Admit to monitor cardiac function – Decrease coronary artery aneurysms from 20% to < 5% < 5% • Complete cardiac evaluation • Complete cardiac evaluation – CXR, EKG, echo • ASA - low dose vs high dose • IV Ig – 80-100 mg/kg/day until day 14 – 3-5 mg/kg/day for 6 weeks • ASA • Repeat echocardiogram at 6 weeks 7
Coxsackie Virus Hand-Foot-and-Mouth • Painful, shallow, yellow ulcers surrounded by red halos • Found on buccal mucosa, tongue, soft palate, uvula and anterior tonsillar pillars uvula and anterior tonsillar pillars • Oral lesions without the exanthem = herpangina • Exanthem involves palmar, plantar and interdigital surfaces of the hands and feet +/- buttocks Erythema Infectiosum Fifth Disease • Parvovirus B19 • Mostly preschool age • Mostly preschool age • Recognized by exanthem • Contagious before rash • Resolution between 3 and 7 days 8
Roseola • 6 to 36 months • Human herpesvirus 6 • High fever without source and irritability • High fever without source and irritability for 3 days • Rash develops as fever decreases Impetigo • Mostly face, extremities, hands and neck • Localized unless underlying skin y g disease • Strep or Staph • Honey-coloured crust • Treatment: topical and systemic antibiotics 9
Herpes Simplex • Gingivostomatitis most common 1º infection in children – Fever, irritability, cervical nodes – Small yellow ulcerations with red halos on mucous membranes • Involvement more diffuse – easy to differentiate from herpangina and exudative tonsillitis • Treatment: supportive Herpetic Whitlow • Lesions on thumb usually 2 ° to autoinoculation • Group, thick-walled vesicles on p erythematous base • Painful • Tend to coalesce, ulcerate and then crust • May require topical or oral acyclovir 10
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura Clinical features • Palpable purpura of extremities • Arthralgia or non-migratory arthritis – No permanent deformities p – Mostly ankles and knees • Abdominal pain – May develop intussusception • Renal involvement – Hematuria, hypertension, renal failure HSP HSP Indications for admission Management • Supportive • R/O intussusception • NSAIDs may control the pain and do not • Severe GI bleed increase the risk of bleeding • Severe renal disease • Severe renal disease • Steroids – controversial • Need for renal biopsy – Efficacy not proven re: abdo pain – No effect on purpura, duration of the illness or the • Hypertension frequency of recurrences • Pulmonary hemorrhage – Unclear of protective effect on renal disease Acute Hemorrhagic Edema of Infancy • 4-24 months • Recent URI or antibiotics • Non toxic • Non-toxic • Resolves in 1-3 weeks • small- vessel, leukocytoclastic vasculitis • Annular or targetoid pupura and edema on face and extremities 11
Conclusions • Not all that itches is eczema • Treatment is often supportive for viral exanthems exanthems • Remember rashes as a sign of systemic illness • Careful history and physical essential for evaluation of bruises 12
Recommend
More recommend