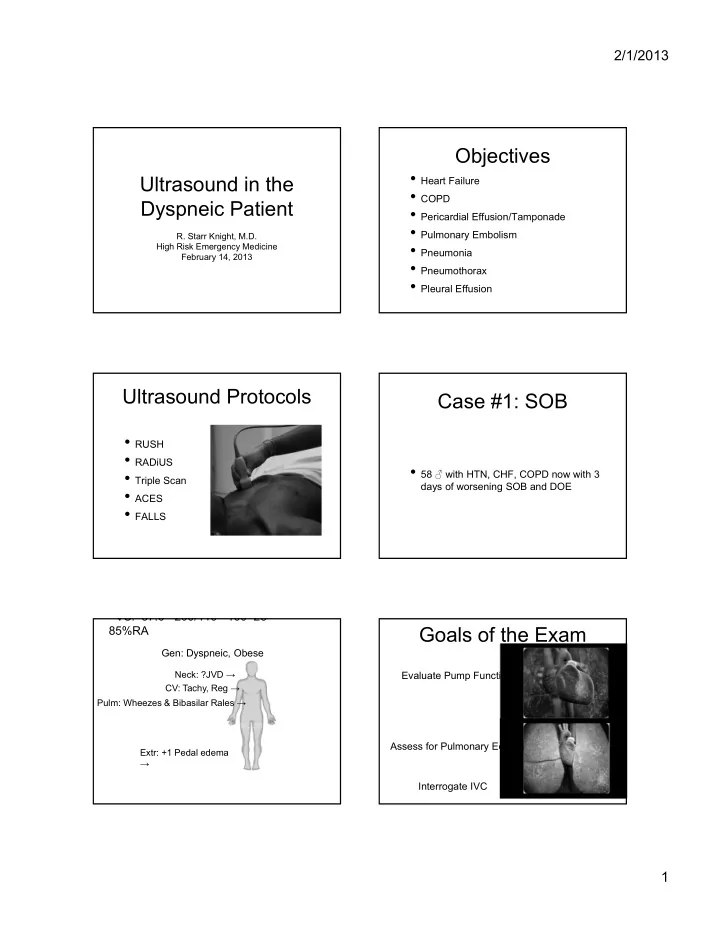

2/1/2013 Objectives • Heart Failure Ultrasound in the • COPD Dyspneic Patient • Pericardial Effusion/Tamponade • Pulmonary Embolism R. Starr Knight, M.D. • Pneumonia High Risk Emergency Medicine February 14, 2013 • Pneumothorax • Pleural Effusion Ultrasound Protocols Case #1: SOB • RUSH • RADiUS • 58 ♂ with HTN, CHF, COPD now with 3 • Triple Scan days of worsening SOB and DOE • ACES • FALLS VS: 37.0 200/110 100 28 Goals of the Exam 85%RA Gen: Dyspneic, Obese Neck: ?JVD → Evaluate Pump Function CV: Tachy, Reg → Pulm: Wheezes & Bibasilar Rales → Assess for Pulmonary Edema Extr: +1 Pedal edema → Interrogate IVC 1
2/1/2013 Parasternal Long Protocol 1. Cardiac Ultrasound 2. Lung Ultrasound 3. IVC Ultrasound Parasternal Long DTA Parasternal Short Parasternal Long 2
2/1/2013 Parasternal Short Subxiphoid / Subcostal Subxiphoid Protocol 1. Cardiac Ultrasound 2. Lung Ultrasound 3. IVC Ultrasound 3
2/1/2013 Normal Lung: Comet Tails Linear Probe Rib 10 11 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 2 Rib Rib Pulmonary Edema B Lines • Arise from the pleural line • Arise from the pleural line • Well-defined B lines B lines • Well-defined • Move with lung sliding • Move with lung sliding • Reach the edges of the • Reach the edges of the screen screen Acute pulmonary edema 4
2/1/2013 Normal Lung: Sliding Visceral Pleura B lines B lines • Highly sensitive Rib • Cardiogenic pulmonary edema • ARDS Alveoli • Pulmonary contusion • Pulmonary fibrosis Rib • Interstitial pneumonia Shadow Rib Rib Parietal Pleura Visceral Pleura Comet Tails (Artifact) B lines = increased fluid in the interstitium Location Location Location 5
2/1/2013 Hyperinflated Lungs Non-HF Non-HF HF HF Protocol 1. Cardiac Ultrasound RA 2. Lung Ultrasound Liver IVC 3. IVC Ultrasound 6
2/1/2013 COPD • Presence of A line • Lack of B lines • Clinical signs of COPD COPD COPD 7
2/1/2013 Pericardial Effusion Pericardial Effusion Cardiac Tamponade Cardiac Tamponade • Right Heart Collapse during diastole • RV or RA • Can be subtle • Diastole • Correlate with Mitral Valve Opening • IVC Plethora Cardiac Tamponade Pulmonary Embolism • RV Dilitation (RV:LV > 1:1) • RV Systolic Dysfunction • Free-Floating Thrombus 8
2/1/2013 Pulmonary Embolism • IVC Dilatation • Presence of DVT in LE • McConnell ’ s Sign Pneumonia Pneumonia • Air Bronchograms • static and dynamic • B Lines adjacent to consolidation • Associated pleural effusions Pneumonia Pneumothorax 9
2/1/2013 Air goes up Air goes up 10
2/1/2013 Abnormal Lung: Pneumothorax Rib Rib Parietal Pleura Parietal Pleura AIR Visceral Pleura Air (Scatter) Normal Pneumothorax 11
2/1/2013 References Thank You • Volpicelli G, Mussa A, Garofalo G, et al. Bedside lung ultrasound in the assessment of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Am J Emerg Med. Oct 2006;24(6):689-696. • Parlamento S, Copetti R, Di Bartolomeo S. Evaluation of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the ED. Am J Emerg Med. May 2009;27(4):379-384. • Cortellaro F, Colombo S, Coen D, et al. Lung ultrasound is an accurate diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. Oct 28 2010. • Lichtenstein D, Meziere G, Biderman P, et al. The comet-tail artifact: an ultrasound sign ruling out pneumothorax. Intensive Care Med. Apr 1999;25(4):383-388. • Lichtenstein D, Meziere G, Biderman P, et al. The comet-tail artifact. An ultrasound sign of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. Nov 1997;156(5):1640-1646. • Lichtenstein DA, Menu Y. A bedside ultrasound sign ruling out pneumothorax in the critically ill. Lung sliding. Chest. Nov 1995;108(5):1345-1348. • Alrajhi K, Woo M, Vaillancourt C. Test Characteristics of Ultrasonography for the Detection of Pneumothorax. CHEST.141(3) MARCH 2012 • Wu Ding W, Yuehong S ,Yang J. Diagnosis of Pneumothorax by Radiography and Ultrasonography.CHEST.140 (4) OCTOBER, 2011 Apical 4 chamber 4 Chamber 12
2/1/2013 4 Chamber 13
Recommend
More recommend