Object-Oriented Design Activity Diagrams Sharif University of - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Object-Oriented Design Activity Diagrams Sharif University of Technology 1 Department of Computer Engineering Analysis Workflow: Analyze a Use Case The analysis workflow consists of the following activities: Architectural analysis
Object-Oriented Design Activity Diagrams Sharif University of Technology 1 Department of Computer Engineering
Analysis Workflow: Analyze a Use Case • The analysis workflow consists of the following activities: • Architectural analysis • Analyze a use case • Outputs: • analysis classes • use case realizations • Analyze a class • Analyze a package 2 Sharif University of Technology
Activity Diagrams • Activity diagrams are OO flowcharts: • used for modeling all types of processes; • can be attached to any modeling element to capture its behavior; • a good activity diagram communicates one specific aspect of a system's behavior; • in UML 2, activity diagrams have Petri Net semantics. 3 Sharif University of Technology
Activities • Activities are networks of nodes connected by edges. • Categories of nodes: • action nodes - atomic units of work within the activity; • control nodes - control the flow through the activity; • object nodes - represent objects used in the activity. • Categories of edges: • control flows - represent the flow of control though the activity; • object flows - represent the flow of objects through the activity. • Activities can have preconditions and postconditions. 4 Sharif University of Technology
Activities: Example 5 Sharif University of Technology
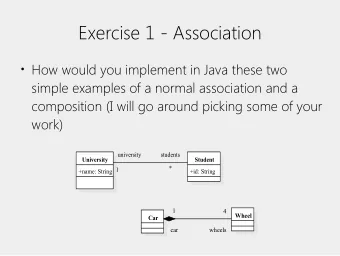
Activity Diagrams: Use Case Modeling 6 Sharif University of Technology
Activities: Tokens • Tokens flow around the network and can represent: • the flow of control; • an object; • some data. • Tokens move from a source node to a target node across an edge depending on: • source node postconditions; • edge guard conditions; • target preconditions. 7 Sharif University of Technology
Activity Partitions • Activity partitions - a high-level grouping of related actions. • Partitions form a hierarchy rooted in a dimension. 8 Sharif University of Technology
Action Nodes • Execute when there is a token simultaneously on each of their input edges AND their preconditions are satisfied. • After execution, action nodes offer tokens simultaneously on all output edges whose postconditions are satisfied: 9 Sharif University of Technology
Action Nodes: Types 10 Sharif University of Technology
Action Nodes: Call • Call action node: • call an activity - use the rake symbol; • call a behavior; • call an operation. 11 Sharif University of Technology
Action Nodes: Accept Time Event • Accept time event action node - executes when its time expression is true: • an event in time (e.g., end of business year); • a point in time (e.g., on 11/03/1960); • a duration (e.g., wait 10 seconds). 12 Sharif University of Technology
Control Nodes 13 Sharif University of Technology
Control Nodes: Decision and Merge 14 Sharif University of Technology
Control Nodes: Fork and Join 15 Sharif University of Technology
Object Nodes • Object nodes represent instances of a classifier. • Input and output edges are object flows - represent the movement of objects. • Object node output edges compete for each output token. 16 Sharif University of Technology
Object Nodes: Buffer Semantics • Object nodes act as buffers: • {upperBound= n}; • {ordering= FIFO} XOR {ordering= LIFO}; • {ordering= FIFO} is the default; • may have a «selection». • Object nodes can represent objects in a particular state. 17 Sharif University of Technology
Object Nodes: Activity Parameters • Activity parameters are object nodes input to or output from an activity: • drawn overlapping the activity frame; • input parameters have one or more output edges into the activity; • output parameters have one or more input edges out of the activity. 18 Sharif University of Technology
Pins • A Pin is an object node that represents one input to or output from an action or activity. 19 Sharif University of Technology
Connectors 20 Sharif University of Technology
Interruptible Activity Regions • interrupted when a token traverses an interrupting edge. • all flows in the region are aborted when it is interrupted. • interrupting edges are drawn as a zigzag arrow or as a normal arrow with a zigzag icon above it. 21 Sharif University of Technology
Exception Handling • Exception pins: • output an exception object from an action; • are indicated with an equilateral triangle. • Protected nodes: • have an interrupting edge leading to an exception handler; • abort when an exception of the right type is raised, and flow passes to the exception handler node. 22 Sharif University of Technology
Expansion Nodes • Represent a collection of objects flowing into or out of an expansion region. • The region is executed once per input element. • Constraints: • the type of the output collection must match the type of the input collection; • the type of object held in the input and output collections must be the same. • Modes: • Iterative - process each element of the input collection sequentially; • Parallel - process each element of the input collection in parallel; • Stream - process each element of the input collection as it arrives at the node; • there is no default mode. 23 Sharif University of Technology
Expansion Nodes: Example 24 Sharif University of Technology
Sending Signals and Accepting Events • Signals: • information that is passed asynchronously between objects; • class stereotyped «signal»; • the information is held in the attributes. 25 Sharif University of Technology
Sending Signals and Accepting Events: Action Nodes • Send Signal action node: • starts when there is a token on all input pins; • executes - a signal object is constructed and sent; • then ends and offers control tokens on its output edges. • Accept Event action node: • started by an incoming control edge or if no incoming edge, when its owning activity starts; • waits for an event of the specified type: • outputs a token that describes the event; • continues to accept events while the owning activity executes; • for a signal event, the output token is a signal. 26 Sharif University of Technology
Sending Signals and Accepting Events: Examples 27 Sharif University of Technology
Streaming 28 Sharif University of Technology
Advanced Object Flows • input and output effects show the effects an action has on its input and output objects: • write the effect in braces close to the pin; • selection - a condition on an object flow that causes it to accept only those objects that satisfy the condition: • put the selection condition in a note stereotyped «selection» attached to the object flow; • transformation - transforms objects in an object flow to a different type: • put the transformation expression in a note stereotyped «transformation» attached to the object flow. 29 Sharif University of Technology
Input and Output Effects 30 Sharif University of Technology
Multicast and Multireceive • Multicast sends an object to many receivers: • stereotype the object flow «multicast». • Multireceive receives objects from many senders: • stereotype the object flow «multireceive». 31 Sharif University of Technology
Parameter Sets • Parameter sets allow an action to have alternative sets of input and output pins: • input parameter sets contain input pins; • output parameter sets contain output pins; • only one input parameter set and one output parameter set may be used per execution of the action. 32 Sharif University of Technology
Central Buffer Nodes • Central buffer node - object nodes that are used specifically as buffers: • stereotype the object node «centralBuffer». 33 Sharif University of Technology
Interaction Overview Diagrams • Interaction overview diagrams show flow between interactions and interaction occurrences 34 Sharif University of Technology
Reference • Arlow, J., Neustadt, I., UML 2 and the Unified Process: Practical Object- Oriented Analysis and Design , 2 nd Ed. Addison-Wesley, 2005. 35 Sharif University of Technology
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.