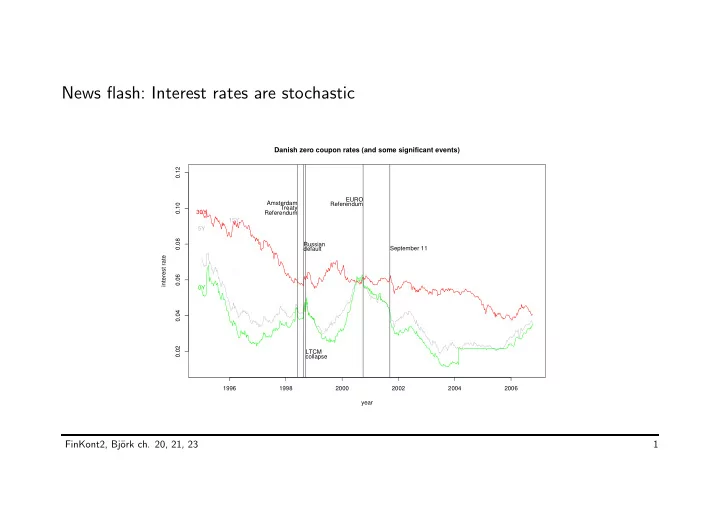

News flash: Interest rates are stochastic Danish zero coupon rates (and some significant events) 0.12 EURO Amsterdam Referendum 0.10 Treaty 30Y Referendum 15Y 5Y 0.08 Russian September 11 default interest rate 0.06 0Y 0.04 0.02 LTCM collapse 1996 1998 2000 2002 2004 2006 year FinKont2, Bj¨ ork ch. 20, 21, 23 1
Weeks 1 & 2: Bj¨ ork’s Chapters 20-23 with some detours. • Abstract nonsense , general theory, HJM-formalism. Ch. 20, 23, and 21. • Concrete 1-dimensional models; Ch. 22. Tons of stuff, we can calculate. – The (mean-reverting) affine short rate models: Vasicek, Cox-Ingersoll-Ross. – Calibration and/or estimation. FinKont2, Bj¨ ork ch. 20, 21, 23 2
Week 3: Bj¨ ork’s Chapters 24-25. • Change of numeraire. Needed for option-pricing. Ch. 24, but I won’t do it like that. • Options on bonds – Zero coupon bonds; Ch. 24. – Coupon bonds and swaptions; trick & Ch. 25. FinKont2, Bj¨ ork ch. 20, 21, 23 3
What determines interest rates? And what moves them around? • Agents’ preferences for consuming now vs. saving for later. • Supply and demand. Not to be forgotten. • “Usual macroeconomic suspects”: – Growth rates. – Expected inflation. – Fiscal policy (in the hand of politicians). – Monetary policy (largely central banks nowadays). – International effects, exchange rates. • Institutional structure (labor and housing market, legal and political system, . . . ) FinKont2, Bj¨ ork ch. 20, 21, 23 4
Overload: Too much to model! Randomness is a very large component. Let’s just accept that and build empirically plausible stochastic models. Worked well for stocks. Wilmott and Rasmussen quote FinKont2, Bj¨ ork ch. 20, 21, 23 5
Complication: Many assets (bonds) are different (because they pay at different times) but not too different. That is what interest rate (or term structure or fixed income ) modelling is about. Fixed income markets are huge. DK government bonds at CSX: Around 1,200 billion (1.2 × 10 12 ) DKK. About the same in mortgage-backed bonds. And thats only the securitized stuff. Add bank loans, credit cards, devivatives. Nice: The martingale formalism, our fundamental theorems of asset pricing (absence of arbitrage, completeness, . . . ) carry over. We will be looking only at non-trivial special cases . (And the more special, the more non-trivial.) FinKont2, Bj¨ ork ch. 20, 21, 23 6
Recommend
More recommend