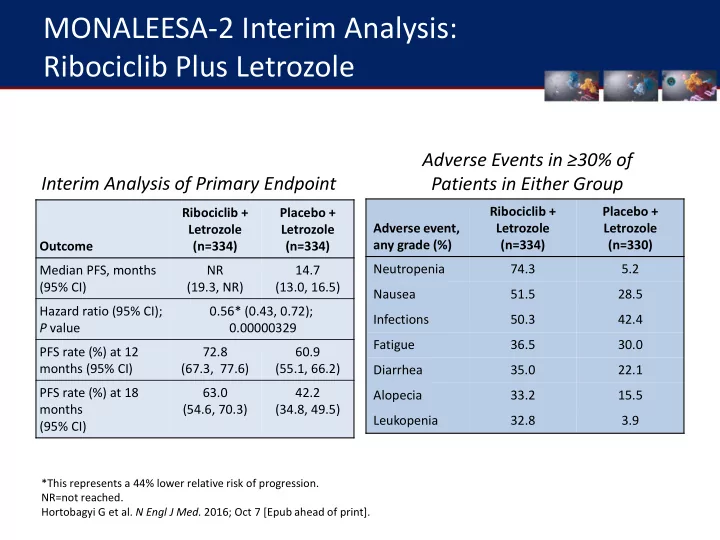

MONALEESA-2 Interim Analysis: Ribociclib Plus Letrozole Adverse Events in ≥30% of Interim Analysis of Primary Endpoint Patients in Either Group Ribociclib + Placebo + Ribociclib + Placebo + Adverse event, Letrozole Letrozole Letrozole Letrozole any grade (%) (n=334) (n=330) Outcome (n=334) (n=334) Neutropenia 74.3 5.2 Median PFS, months NR 14.7 (95% CI) (19.3, NR) (13.0, 16.5) Nausea 51.5 28.5 Hazard ratio (95% CI); 0.56* (0.43, 0.72); Infections 50.3 42.4 P value 0.00000329 Fatigue 36.5 30.0 PFS rate (%) at 12 72.8 60.9 months (95% CI) (67.3, 77.6) (55.1, 66.2) Diarrhea 35.0 22.1 PFS rate (%) at 18 63.0 42.2 Alopecia 33.2 15.5 months (54.6, 70.3) (34.8, 49.5) Leukopenia 32.8 3.9 (95% CI) *This represents a 44% lower relative risk of progression. NR=not reached. Hortobagyi G et al. N Engl J Med. 2016; Oct 7 [Epub ahead of print].
Neoadjuvant Studies of CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Combination with ET Abemaciclib* (Abem) Palbociclib (Palbo) Ribociclib (Ribo) (N=173) 1 (N=50) 2 (N=14) 3 ET Anastrozole (ANZ) ANZ Letrozole (LET) Phase 2; randomized; Phase 2; randomized for first 2 Phase 2; single arm Arm 1: LET 2.5 mg (n=4) Study weeks (abem, n=58; ANZ, 28-day cycle 0: ANZ alone Arm 2: LET + ribo 400 mg (n=6) design n=59; combo, n=56), then 28-day cycles 1-4 ANZ + palbo Arm 3: LET + ribo 600 mg open label combo for 14 weeks (n=4) % with complete cell cycle Primary Ki67 change from baseline to Ki67 change from baseline to arrest (CCCA; Ki67 ≤2.7%) after endpoint week 2 (geometric mean) day 14 (±3 days) 15 days of ANZ + palbo Arm 1: – 69% (range 38% – 100%; n=2) Abem + ANZ: – 93.5%; n=23† 87% (n=45); Arm 2: – 96% Result Abem: –93.1%; n=19† 90% CI: 75% to 94% (range 78% – 100%; n=6) ANZ: – 71.0%; n=22 Arm 3: – 92% (range 75% – 100%; n=3) Pts with Ki67 <2.7: Levels of phosphorylated Rb Additional Abem + ANZ: 69.6% decreased in 5 of 8 evaluable ANZ alone (n=43): 26% findings Abem: 68.4% patients in Arms 2 and 3 (mean ANZ: 22.7% 59% decrease) *150 mg bid; †One -sided P <0.001 vs ANZ 1. Hurvitz S et al . Presented at the European Society of Medical Oncology Annual Congress; October 7 – 11, 2016; Copenhagen, Denmark: LBA13; 2. Ma C et al. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Eighth Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium: 2015 Dec 8-12; San Antonio, TX. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res . 2016;76(4 Suppl):Abstract S6-05; 3. Curigliano G et al. Breast . 2016;28:191-198.
Common AEs in Neoadjuvant Studies of CDK4/6 Inhibitor + ET Drug Combination Key Findings 3 most common investigator-assessed Diarrhea* (46%) treatment-emergent AEs (any grade) in Constipation (36%) all groups combined (N=173) Nausea (34%) Abemaciclib + anastrozole 1 3 most common laboratory Creatinine increased (93%) abnormalities (any grade) in all groups Neutrophil count decreased (65%) combined (N=173) WBC decreased (61%) Neutropenia (56%) Palbociclib + 3 most common AEs (any grade) with Leukopenia (46%) anastrozole 2 combination therapy (n=50) Fatigue (40%) Nausea (20%) Most common treatment-related AEs Ribociclib + Asthenia (20%) (n > 1; any grade) with combination letrozole 3 QTcF prolongation (20%) therapy (arms 2 and 3 combined; n=10) Decreased appetite (20%) *Loperamide was administered as primary prophylaxis with each abemaciclib dose 1. Hurvitz S et al . Presented at the European Society of Medical Oncology Annual Congress; October 7 – 11, 2016; Copenhagen, Denmark: LBA13; 2. Ma C et al. In: Proceedings of the Thirty-Eighth Annual CTRC-AACR San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium: 2015 Dec 8-12; San Antonio, TX. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res . 2016;76(4 Suppl):Abstract S6-05; 3. Curigliano G et al. Breast . 2016;28:191-198.
Recommend
More recommend