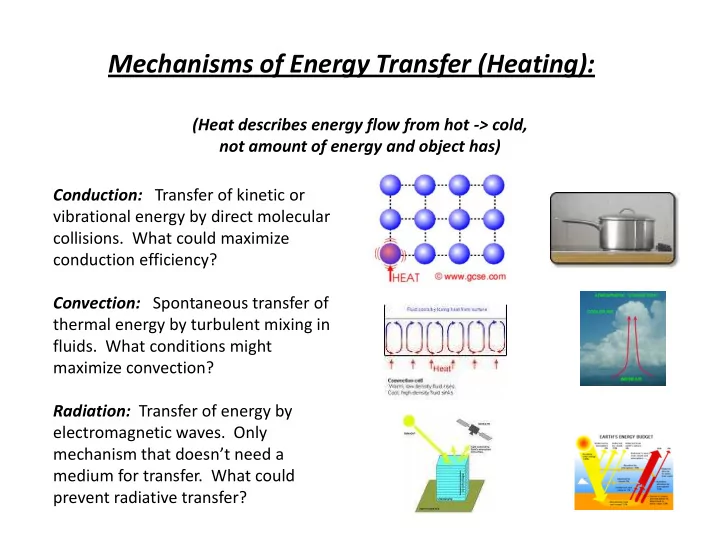

Mechanisms of Energy Transfer (Heating): (Heat describes energy flow from hot -> cold, not amount of energy and object has) Conduction: Transfer of kinetic or vibrational energy by direct molecular collisions. What could maximize conduction efficiency? Convection: Spontaneous transfer of thermal energy by turbulent mixing in fluids. What conditions might maximize convection? Radiation: Transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves. Only mechanism that doesn’t need a medium for transfer. What could prevent radiative transfer?
How does direct radiation from the sun warm a cup of water (PS 2) ? ?
Simple Thermodynamic Relationships P( in W) = Power = Energy / time Q(in J)=Total Energy= Power x time x area P W incoming solar radiation density (power/are a) 2 A m P Q t A 1 A Q mc T P t A 1 A T m c
Assumptions in calculating Temp. warming: • No significant net heat lost by conduction, convection, or radiation (this is BS except for rare special circumstances) • All incident solar radiation is absorbed (or reduced by known albedo) • Uniform temperature of object c p Substance Phase J g −1 K −1 Air (Sea level, dry, 0 °C) gas 1.0035 Air (typical room conditions A ) gas 1.012 Aluminium solid 0.897 Ammonia liquid 4.700 Copper solid 0.385 Diamond solid 0.5091 Gasoline liquid 2.22 Gold solid 0.1291 Graphite solid 0.710 Typical Heat Capacities: Iron solid 0.450 Lead solid 0.127 Lithium solid 3.58 Magnesium solid 1.02 Mercury liquid 0.1395 Nitrogen gas 1.040 Oxygen gas 0.918 Paraffin wax solid 2.5 Silica (fused) solid 0.703 Uranium solid 0.116 gas (100 °C) 2.080 Water liquid (25 °C) 4.1813 solid (0 °C) 2.114
Average Emitted infrared radiation
Incoming solar radiation for August
Solar radiation absorbed yesterday
August solar radiation absorbed by surface
Sea Surface Temperatures
Sea Surface Temperature Anomaly
Recommend
More recommend