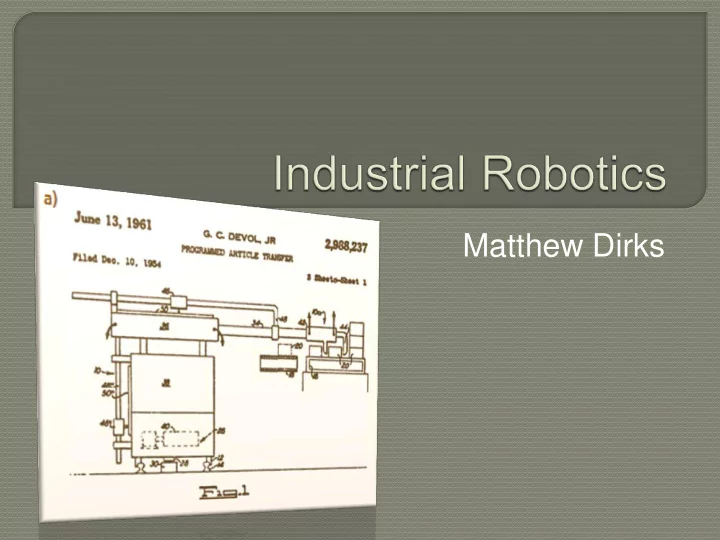

Matthew Dirks
Klas Nilsson Martin Hägele J. Norberto Pires Of book chapter “Industrial Robotics”, Springer, 2008
IR Visual and visual tracking CCD Cameras • Laser triangulation principle Force-torque sensors • Wrist force sensor • Force feedback in the robot fingers Potentiometers Tachometers
Link to video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uQu1vEkssz4
Usually programmed offline before hand Often have connection to a PC Link to video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=POx_UElOmMY
Synchronize timing with other work cells Pre-programmed means less decision making
Accuracy within ±0.1mm Carrying weight: 1 – 1500kg Often 6 DOF Parallel kinematic machines, or Delta About 1/3 the cost of high-performance robots Link to video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Du2f-EUDqio
Often an assembly line, where a robot at each station does a few actions before moving on. Connecting to other work-cells: 1/2 the cost
Teachable robots (by guiding) Tactile command via handle Tele-commands
Link to video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3WcIu4JBsPY
Link to video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W_gxLKSsSIE
Recommend
More recommend