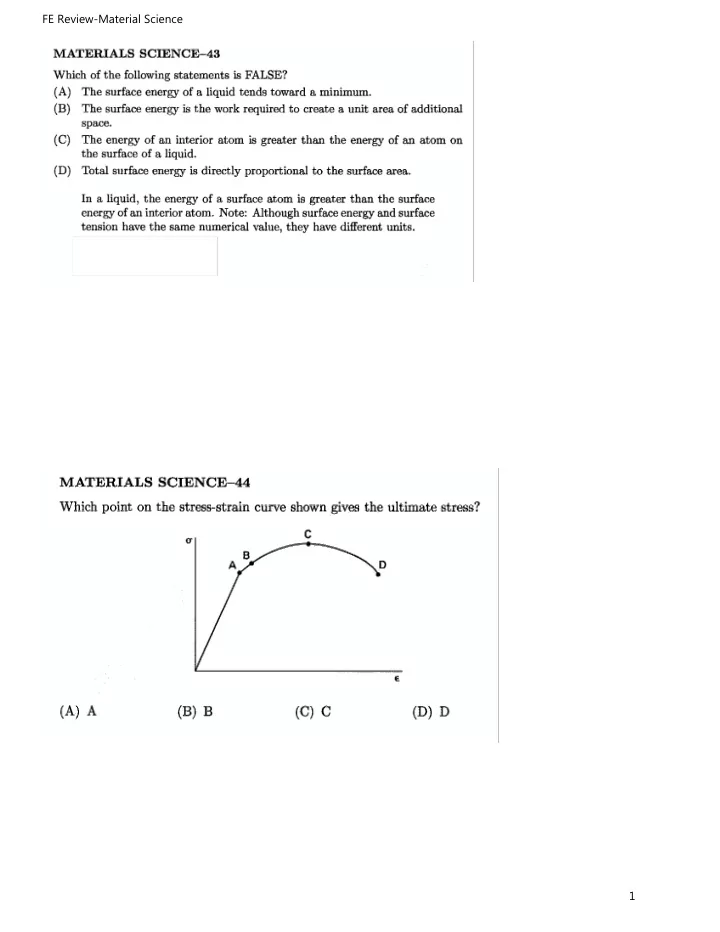

FE Review-Material Science MATERIALS SCIENCE 43 Which of the following statements is FALSE? (A) The surface energy of a liquid tends toward a minimum. (B) The surface energy is the work required to create a unit area of additional space. (C) The energy of an interior atom is greater than the energy of an atom on the surface of a liquid. (D) Total surface energy is directly proportional to the surface area. In a liquid, the energy of a surface atom is greater than the surface energy of an interior atom. Note: Although surface energy and surface tension have the same numerical value, they have different units. The answer is (C). MATERIALS SCIENCE-44 Which point on the stress-strain curve shown gives the ultimate stress? G D € (A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D 1
FE Review-Material Science MATERIALS SCIENCE-45 A 8tres8-straia diagram for a polymer is shown. Identify items A, B, and C. B a -» C G (A) A = lower yield point; B — plastic deformation; C = upper yield point (B) A — iower yield point; B = proportional limit; C — upper yield point (C) A = yield point; B — elastic deformation; C = elastic limit (D) A = yield point; B = elongation at fracture; C = fracture point MATERIALS SCIENCE-46 Which statement is true for the stress-strain relationship for the metal shown? it 0 E (A) Point A is the lower yield point, (B) Point D is the fracture stress point, (C) Point B is the upper yield point. (D) The range from point C to point D is known as the elastic range. 2
FE Review-Material Science MATERIALS SCIENCE-47 Identify the properties of the materials whose stress-strain diagrams arc shown. n. m. (A) I: soft and weak; II: soft and tough; III: hard and brittle (B) I: hard and brittle; II: soft and weak; III: hard and tough (C) I: soft and tough; II: hard and brittle; III: hard and strong (D) I: hard and strong; II: soft and brittle; III: soft and tough MATERIALS SCIENCE-48 Which statement is most accurate regarding the two materials represented in the given stress-strain diagrams? material B matorial A (A) Material B is more ductile and has a lower modulus of elasticity than material A. (B) Material B would require more total energy to fracture than material A. (C) Material A will withstand more stress before plastically deforming than material B. (D) Material B will withstand a higher load than material A but is more likely to fracture suddenly. 3
FE Review-Material Science MATERIALS SCIENCE -50 Which of the following best describes the 0.2% offset yield stress? (A) It is the elastic limit after which a measurable plastic strain has occurred. (B) It is the stress at which the material plastically strains 0.2%. (C) It is the stress at which the material elastically strains 0,2%. (D) It is 0,2% below the fracture point of the material. MATERIALS SCIENCE-53 Under conditions of very slow deformation and high temperature, it is possible to have plastic how in a crystal at shear stresses lower than the critical shear stress. What is this phenomenon called? (C) creep (D) bending (A) slip (B) twinning 4
FE Review-Material Science MATERIALS SCIENCE-69 In general, what are the effects of cold working a metal? (A) increased strength and ductility (B) increased strength, decreased ductility (C) decreased strength and ductility (D) decreased strength, increased ductility MATERIALS SCIENCE-70 Which of the following does cold working a metal cause? (A) elongation of grains in the flow direction, an increase in dislocation density, and an overall increase in energy of the metal (B) elongation of grains in the flow direction, a decrease in dislocation density, and an overall decrease in energy of the metal (C) elongation of grains in the flow direction, a decrease in dislocation density, and an overall increase in energy of the metal (D) shortening of grains in the flow direction, a decrease in dislocation density, and an overall decrease in the energy of the metal MATERIALS SCIENCE-71 Which of the following statements is FALSE? (A) The amount or percentage of cold work cannot be obtained from informs tion about change in the area or thickness of a metal, (B) The process of applying force to a metal at temperatures below the tem perature of crystallization in order to plastically deform the metal is called cold working, (C) Annealing eliminates most of the defects caused by the cold working of a metal. (D) Annealing reduces the hardness of the metal. 5
FE Review-Material Science MATERIALS SCIENCE—72 Which of the following statements is FALSE? (A) There is a considerable increase in the hardness and the strength of a cold- worked metal. (B) Cold working a metal significantly reduces its ductility. (C) Cold working causes a slight decrease in the density and electrical conduc tivity of a metal. (D) Cold work decreases the yield point of metal. MATERIALS SCIENCE-73 Which of the following statements is FALSE? (A) Hot working can be regarded as the simultaneous combination of cold work ing and annealing. (B) Hot working increases the density of the metal. (C) One of the primary goals of hot working is to produce a fine-grained prod uct. (D) Hot working causes much strain hardening of the metal. 6
MATERJALS SCIENCE.90 0 Contider the Ag-Cu phate diagram givfn. Calculate the equilibrium amount of 70 80 90 100 Ag Cu Cu (wu%) (A) 0.0% (B) 22% (D) 52% MATERJALS SCIEN�91 Using the given phasf diagram 1 what ase the relative weight.b of phasfs 01 and a 2 fpr an alloy of 70% B at temperature T1? 10 40 A B(wu%) B C) 50% 01 , 50% 02 ( (B) 30% a.1, 70% a.2 (A) 10% n1, 90% a2 90 100 20 80 70 60 60 40 30 50 60 30 I /4 in an alloy of 30% Ag, 70% Cu at 850 ° 0. 1100 1000 2 900 13 � 800 � 600 20 :4:% I 500. - I I 10 0 ..../ .....` __` 400��-��--.--......`__.-_....` 1083 ° I I I I FE Review-Material Science TO > + 0 0 ! , 7 (C) 49% (D) 70% 0;1 1 30% a;2 7
FE Review-Material Science 1. A stress-strain diagram is shown. cr e What test is represented by the illustration? (A) resilience test (B) rotating beam test (C) ductility test (D) tensile test 2. A 0.4 m long steel rod has a diameter of 0.05 m and a modulus of elasticity of 20 x 10 4 MPa. The rod supports a 10 000 N compressive load. What is most nearly the decrease in the steel rod's length? (A) 1.3 x 10~ 6 m (B) 2.5 x 10" 6 m (C) 5.1 x 10~ 6 m (D) 1.0 x 10~ 5 m 8
FE Review-Material Science 3. What is the term for the ratio of stress to strain Gbelow the proportional limit? (A) modulus of rigidity (B) Hooke's constant (C) Poisson's ratio (D) Young's modulus 4. What do impact tests determine? (A) hardness (B) yield strength (C) toughness (D) creep strength 5yThe density of a particular metal is 2750 kg/m 3 . The modulus of elasticity for this metal is 210 GPa. A cir cular bar of this metal 3.5 m long and 160 cm 2 in cross- sectional area is suspended vertically from one end. What is most nearly the elongation of the bar due to its own mass? (A) 0.00055 mm (B) 0.00079 mm (C) 0.0016 mm (D) 0.0024 mm 9
FE Review-Material Science 6. A stress-strain diagram is shown. <T (MPa) 500 400 250 150 0.00075 | 0.02 0.2 0.25 0.28 e 0.0013 What is most nearly the percent elongation at failure? (A) 14% (B) 19% (C) 25% (D) 28% Which of the following statements regarding the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature is true? I. It is important for structures used in cold environments. II. It is the point at which the size of the shear lip or tearing rim goes to zero. III. It is the temperature at which 20 J of energy causes failure in a Charpy V-notch specimen of standard dimensions. (A) I only (B) I and II (C) I and III (D) II and III 10
FE Review-Material Science What does the value of 40 MPa in the illustration ^nown represent? stress (MPa) 5 6 log N I. fatigue limit II. endurance limit III proportional limit IV yield stress (A) I only (B) I and II (C) II and IV (D) I, II, and IV 8. If 8 is deformation, and L is the original length of the specimen, what is the definition of normal strain, el (A) £ ~ L + 8 L (B) £ = L + 8 8 8 (C) £ = L + 8 (D) £ = 8 L 11
F E R e v i e w - M a t e r i a l S c i e n c e •*'. (MPa) 500 400 250 150 0.2 0.25 0.28 e 0.00075 | 0.02 0.0013 What is most nearly the modulus of elasticity of the material? (A) 20 GPa (B) 80 GPa (C) 100 GPa (D) 200 GPa 1. Refer to the phase diagram shown. The region enclosed by points DEF can be described as a (A) mixture of solid [3 component and liquid a component (B) mixture of solid f3 and liquid (3 component (C) peritectic composition (D) mixture of solid (3 component and a molten mix ture of a and (3 components 1 2
FE Review-Material Science 2. Which of the following figures is a cooling curve of a pure metal? (A) liquid liquid and solid solid time (B) a) 3 03 P <D 1 Q. 1 E +-* liquid 1 liquid^ 1 and 1 1 solid 1 solid 1 1 time (C) liquid liquid I and j \ solid i solid time (D) 1 1 \ 1 \ 1 x liquid | ijquid K i \ and i i \ \ I \ 1 solid I solid _l time 13
F E R e v i e w - M a t e r i a l S c i e n c e 3. A composite material consists of 20 kg of material A, AO kg of material B, and 5 kg of material C. The den sities of materials A, B, and C are 2 g/cm 3 , 3 g/cm 3 , and 4 g/cm 3 , respectively. What is most nearly the density of the composite material? (A) 2.1 g/cm 3 (B) 2.4 g/cm 3 (C) 2.7 g/cm 3 (D) 3.3 g/cm 3 1 4
Recommend
More recommend