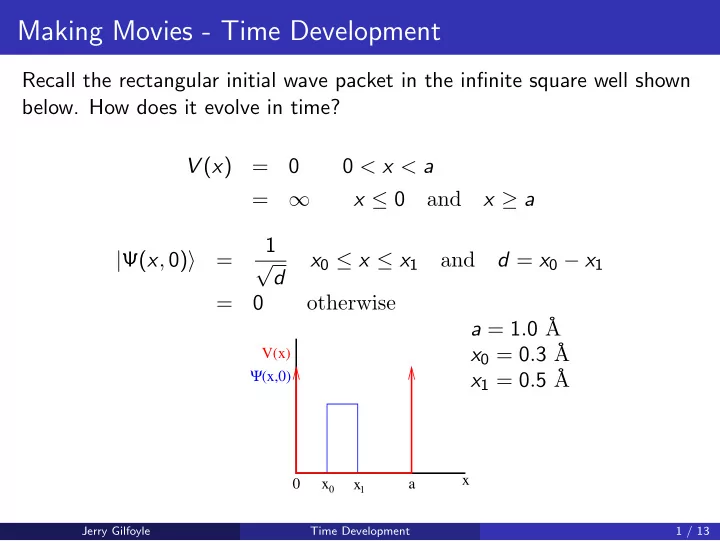

Making Movies - Time Development Recall the rectangular initial wave packet in the infinite square well shown below. How does it evolve in time? V ( x ) = 0 0 < x < a = ∞ x ≤ 0 and x ≥ a 1 √ | Ψ( x , 0) � = x 0 ≤ x ≤ x 1 and d = x 0 − x 1 d = 0 otherwise a = 1 . 0 ˚ A x 0 = 0 . 3 ˚ A V(x) x 1 = 0 . 5 ˚ Ψ (x,0) A x 0 x 0 a x 1 Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 1 / 13
Probabilities of Different States Rectangular Wave in a Square Well 0.4 a = 1.0 Å x 0 = 0.3 Å 0.3 x 1 = 0.5 Å Probability 0.2 0.1 0.0 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 Energy ( eV ) Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 2 / 13
Time Development of a Square Wave time = 0.0000 ⨯ 10 - 16 s. time = 0.0040 ⨯ 10 - 16 s. 8 8 Probability Density Probability Density 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 x x time = 0.0080 ⨯ 10 - 16 s. time = 0.0120 ⨯ 10 - 16 s. 8 8 Probability Density Probability Density 6 6 4 4 2 2 0 0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 x x Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 3 / 13
Comparison of Bound and Free Particles Particle in a Box Free Particle The potential The potential V =0 0 < x < a V = 0 = ∞ otherwise Eigenfunctions and eigenvalues Eigenfunctions and eigenvalues E = � 2 k 2 1 e ± ikx | φ ( k ) � = √ � E n = n 2 � 2 π 2 2 2 m � n π x 2 π � | φ n � = a sin 2 ma 2 a Superposition Superposition � ∞ | ψ � = b ( k ) φ ( k ) dk ∞ � −∞ | ψ � = b n | φ n � � φ m | φ n � = δ m , n � φ ( k ′ ) | φ ( k ) � = δ ( k − k ′ ) n =1 Getting the coefficients Getting the coefficients P n = | b n | 2 b n = � φ n | ψ � P n = | b ( k ) | 2 b ( k ) = � φ ( k ) | ψ � Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 4 / 13
ψ Time Development of the Initial Gaussian Recall the Gaussian initial wave packet for the free particle shown below. How does it evolve in time? 1 (2 πσ 2 ) 1 / 4 e − x 2 / 4 σ 2 V ( x ) = 0 | Ψ( x , 0) � = 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 - 4 - 2 0 2 4 x Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 5 / 13
Time Development of the Initial Gaussian t = 0 t = 1.5 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 | ψ 2 | ψ 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 x x t = 3. t = 4.5 5 5 4 4 3 3 2 2 | ψ 2 | ψ 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 x x Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 6 / 13
Time Development of Nuclear Fusion Consider a case of one dimensional nuclear ‘fusion’. A neutron is in the potential well of a nucleus that we will approximate with an infinite square well with walls at x = 0 and x = L . The eigenfunctions and eigenvalues are E n = n 2 � 2 π 2 � 2 � n π x � φ n = a sin 0 ≤ x ≤ a 2 ma 2 a = 0 x < 0 and x > a . The neutron is in the n = 4 state when it fuses with another nucleus that is the same size, instantly putting the neutron in a new infinite square well with walls at x = 0 and x = 2 a . 1 What are the new eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of the fused system? 2 How will the initial wave packet evolve in time? Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 7 / 13
Time Development of Nuclear Fusion t = 0 × 10 - 21 s t = 0.3 × 10 - 21 s 0.20 0.20 0.15 0.15 2 2 0.10 0.10 | ψ | ψ 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.00 0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20 x ( fm ) x ( fm ) t = 0.6 × 10 - 21 s t = 0.9 × 10 - 21 s 0.20 0.20 0.15 0.15 2 2 0.10 0.10 | ψ | ψ 0.05 0.05 0.00 0.00 0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20 x ( fm ) x ( fm ) Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 8 / 13
Comparison of Bound and Free Particles Particle in a Box Free Particle The potential The potential V =0 0 < x < a V = 0 = ∞ otherwise Eigenfunctions and eigenvalues Eigenfunctions and eigenvalues E = � 2 k 2 1 � n π x e ± ikx � E n = n 2 � 2 π 2 2 | φ ( k ) � = √ � | φ n � = a sin 2 m 2 π 2 ma 2 a Superposition Superposition � ∞ ∞ | ψ � = b ( k ) φ ( k ) dk � | ψ � = b n | φ n � � φ m | φ n � = δ m , n −∞ � φ ( k ′ ) | φ ( k ) � = δ ( k − k ′ ) n =1 Getting the coefficients Getting the coefficients P n = | b n | 2 b n = � φ n | ψ � P n = | b ( k ) | 2 b ( k ) = � φ ( k ) | ψ � Time Dependence Time Dependence ∞ � ∞ � b n | φ n ( x ) � e − i ω n t Ψ( x , t ) = b ( k ) φ k ( x ) e − i ω ( k ) t dk Ψ( x , t ) = n =1 −∞ Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 9 / 13
Liboff 6.4 - 1 Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 10 / 13
Liboff 6.4 - 2 Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 11 / 13
Liboff 6.4 - 3 Mathematica result Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 12 / 13
Liboff 6.4 - 4 Mathematica result Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 13 / 13
Liboff 6.4 - 5 Square Wave Time Development 12 10 Black Curve - Initial Probability 8 Density. 2 ( m - 1 ) Red Curve - Probability 6 Density at t = 10 s. | ψ 4 Chance of being in the original box: 0.993 2 0 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.06 0.07 x ( m ) Jerry Gilfoyle Time Development 14 / 13
Recommend
More recommend