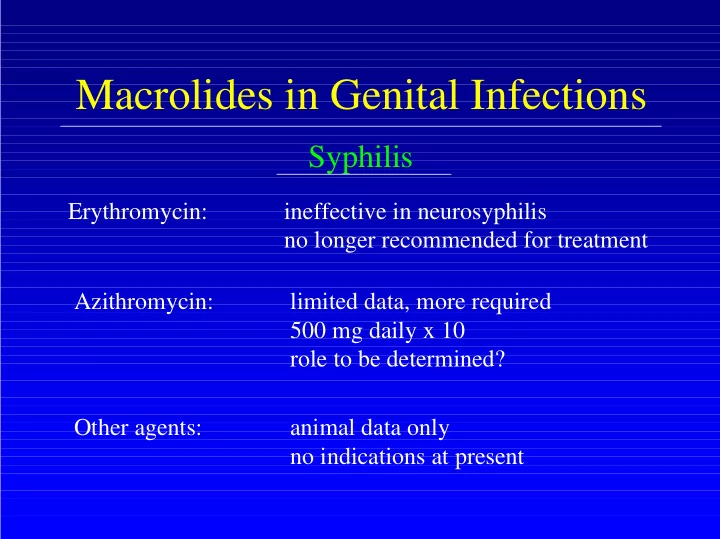

Macrolides in Genital Infections Syphilis Erythromycin: ineffective in neurosyphilis no longer recommended for treatment Azithromycin: limited data, more required 500 mg daily x 10 role to be determined? Other agents: animal data only no indications at present
Macrolides in Genital Infections Chancroid Erythromycin: 500 mg 6 hourly for 7 days effective, but ? compliance Azithromycin: 500 mg orally x 1 effective, both for culture positive and negative ulcers Donovanosis (Granuloma inguinale) Erythromycin: 500 mg 6 hourly for 2 to 3 weeks established therapy Azithromycin: 500 mg orally x 7 days, or 1 gram weekly for 4 weeks effective, both for histological and clinical cases
Macrolides in Genital Infections Gonorrhoea Erythromycin: active in vivo. not effective in single dose unless combined with rifampicin Spiramycin: single doses of 2.5 g, or 4 - 12g x 2 days 80 - 85% effective in single dose Azithromycin: 1 g x 1 is 85 - >95% effective 2 g x1 >99% effective, but SE problem? ?cost
Macrolides in Genital Infections Activity of various macrolides against C. trachomatis Antimicrobial MIC (mg/l Clarithromycin 0.007 Josamycin 0.03 Roxithromycin 0.03 Midecamycin 0.06 acetate Erythromycin 0.06 Azithromycin 0.125 Spiramycin 0.5
Macrolides in Genital Infections Activity of various macrolides against M. hominis &U. urealyticum Antimicrobial M. hominis U. urealyticum MIC (mg/l) MIC (mg/l) Midecamycin 0.008 - 0.12 0.03 - 0.25 acetate Clarithromycin 8 - 64 0.025 - 1.0 Josamycin not available 0.02 - 0.5 Roxithromycin 8 - >64 0.06 - 1.0 Azithromycin 2 - 16 0.12 - 1.0 Erythromycin >32 0.12 - 2.0
Macrolides in Genital Infections Chlamydial and non-specific genital infection Erythromycin: 500 mg 6- 12 hourly for 7 - 14 days effective, but ?compliance? Spiramycin: 1g 12 hourly for 14 days Roxithromycin 300 - 450 mg daily for 7 - 14 days Josamycin 500 mg 12 hourly for 12 days (? Pregnancy) 500 mg 8 hourly for 8 days Clarithromycin 250 mg 12 hourly for 7 No indication to use any of above except erythromycin (cheap)
Macrolides in Genital Infections Chlamydial and non-specific genital infection Azithromycin • single oral dose of 1 g • microbiological cure rates approach 100% • clinical cure rates for chlamydia positive or negative non-gonococcal in fection range between 80% and 95% • clinical cure rates same as conventional doxycycline • pharmacoeconomics may favour first line use • role in PID requires further study
Macrolides in Genital Infections C ompliance C omeback C ounselling C ondom C ontact tracing C ost
Recommend
More recommend