Lars Groth Master in Dr. oecon., NHH organizational Norwegian - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
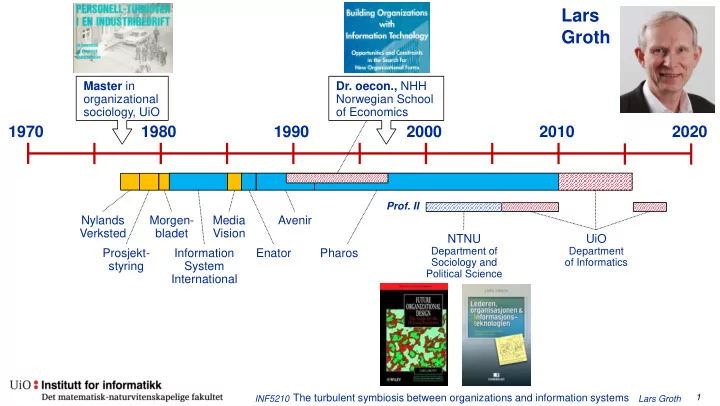
Lars Groth Master in Dr. oecon., NHH organizational Norwegian School sociology, UiO of Economics 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 Prof. II Nylands Morgen- Media Avenir Verksted bladet Vision NTNU UiO Department of Department
Lars Groth Master in Dr. oecon., NHH organizational Norwegian School sociology, UiO of Economics 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 2020 Prof. II Nylands Morgen- Media Avenir Verksted bladet Vision NTNU UiO Department of Department Prosjekt- Information Enator Pharos Sociology and of Informatics styring System Political Science International INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 1 Lars Groth
INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems Lars Groth INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 2 Lars Groth
The fundamental cause behind any organization – and its main challenge Tasks too big for one person must be divided into smaller tasks suitable for one individual Since a number of people now need to cooperate, we need coordination to make the work of each one fit into the larger picture Here you will find the root of most organizational challenges! INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 3 Lars Groth
What is an organization? The essence - 1 “ Every organized human activity - from the making of pots to the placing of a man on the moon - gives rise to two fundamental and opposing requirements: the division of labor into various tasks to be performed and the coordination of these tasks to accomplish the activity. The structure of an organization can be defined simply as the sum total of the ways in which it divides its labor into distinct tasks and then achieves coordination among them. " Henry Mintzberg Henry Mintzberg in "The Structuring of Organizations” INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 4 Lars Groth
What is an organization? The essence - 2 “ Organization is what distiguishes Rosenborg’s first team from 11 unaquainted young men on Elgeseter bridge.” Jay R. Galbraith in ”Organization Design”, page 2 (adapted to a Norwegian context) Jay R. Galbraith , ”Organization Design”, p. 2: ”As a beginning, it can be said that organization is that ” something ” which distinguishes any collection of 50 individuals in Kennedy International Airport from the 50 individuals comprising av football team in the National Football League. ” INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 5 Lars Groth
INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 6 Lars Groth
INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 7 Lars Groth
Organisation and systems are intervowen – indeed, they are one and the same! INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 8 Lars Groth
But why do we really need organizations? Asset specificity Transaction uncertainty Transaction frequency Oliver Williamson INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 9 Lars Groth
Modern car manufacturing Extended value chain INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 10 Lars Groth
1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990 2000 2010 Herbert A. Joan Woodward Henry Mintzberg Back Max Weber Elton Mayo Simon ”Management and ” The Structuring of Theory of Bureaucracy to Human Relations Bounded Technology” Organizations” Rationality Basics Frederick Taylor John W. Meyer and Burns and Stalker Jaques Derrida Scientific Management Luther Gulick Brian Rowan ”The Management of Epistemological and Lyndall Urwick ” Formal Structure as Innovation ” postmodernism “Papers on the Science of Myth and Ceremony” Wanda Administration” Orlikowski and Henri Fayol Philip Selznick Paul R. Lawrence Jeffrey Pfeffer and Susan Scott Administrative theory The organization and Jay W. Lorsch Gerald D.Salancik Sociomateriality Chester Barnard as social arena Resource-based theory ”Organization and “The Functions of the Jean-François Environment” Executive” Lyotard Michael T. Hannan Tor Hernes Eric Trist, Kenneth Epistemological Organization theory – and John H. Freeman The organisation Daniel Katz and Bramforth, Fred Emery Ronald Coase postmodernism Population ecology as process Robert L. Kahn Sosiotechnics Transaction cost The enterprise as a timeline Oliver E. Williamson an open system Transaction cost Jean Baudrillard Ludwig von Herbert A. Simon Poststructuralism, Bertalanffy Charles D. Perrow Paul J. DiMaggio and and James March Classical theory ”A Framework for epistemological General systems Walter W. Powell ”Organizations” Comparative Analysis postmodernism theory Institutional of Organizations” isomorphism Neoclassical and institutional theory W. Ross Ashby Systems theory: Self- Harry Braverman Stewart R. Clegg Systems theory regulation and law of Marxist organisation Ontological requisite variety theory postmodernism Contingency theory James D. Karl E. Weick Erving Goffman Thompson Interactionism Organisation Symbolic ” Organizations culture interactionsm in Action” Postmodern approaches David Silverman William G. Ouchi Other theories Action perspective Culture and team (theory Z) INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 11 Lars Groth
Sosiotechnics Eric Trist, British social psychologist (1909-93) – published in 1951 together with Kenneth Bamforth, a former coal miner, ”Some Social and Psychological Consequences of the Longwall Method of Coal Getting“ in Human Relations – Director of The Tavistock Institute of Human Relations in London for more than 20 years – Designed a theory about the interaction between people and technology in work places, basedon a study of technology change in British coal mines during the transition from the “ shortwall ” to the “ longwall ” method for coal mining. INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 12 Lars Groth
Contingency theory Joan Woodward (1916-1971 – ”Management and Technology”, 1958, ”Industrial Organization”, 1965 – Studied a large number of firms (100) in the South Essex area of England in the 1950s – Found that organizational form varied, and correlated with production technology – Concluded that there was not ” one best way ” to organize – the nature of the production process would determine which form that would be most suitable Tom Burns (1913-2001) and G. M. Stalker – ”The Management of Innovation ” (1961) – Studied the introduction of electronics in Scottish industry – Described two ideal types of organization on each side of a continuum – the mechanistic and the organismic (organic) organization – Viewed the organization as a result of the simultaneous working of (at least) three different social systems: • Formal authority: aims, technology, relations with the environment • Cooperative systems of people with different aspirations • The political system – the competition and cooperation for power INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 13 Lars Groth
Contingency theory Henry Mintzberg – ”The Structuring of Organizations” (1979) – Synthesized large parts of the organizational research up to ca. 1975 – Proposed five basic organizational configurations (forms), each based on one main coordinating mechanism and one key part of the organization: • The Simple Structure (Entrepreneurial Form) – based on Direct supervision, Strategic Apex key • The Machine Bureaucracy – based on Standardization of work, Technostructure key • Professional Bureaucracy – based on Standardization of skills, Operating core key • The Adhocracy (Innovative Organization) – based on Mutual adjustment, Support staff (R&D) key • The Divisionalized Form (Diversified Organization) – based on Standardization of output, Middle line key – Has later suggested two new configurations: • The Missionary Organization – based on Standardization of norms, Ideology key • The Political Organization – no prime coordinating mechanism, no key part Professional Bureaucracy Standardization of skills Simple Structure Adhocracy Divisionalized Form Direct supervision Mutual coordination Standardization of output Machine Bureaucracy Standardization of work INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 14 Lars Groth
Interactionism Karl E. Weick – ”The Social Psychology of Organizing” (1969) – Enactment : Organizations are enacted, they are created by being talked about – Sensemaking : Organizations are primarely “ sensemaking systems”, incessantly create and recreate conceptions about themselves – Loose coupling : The lack of firmness in the coupling among some of the parts of the organization – changes can take place locally with little consequence elswhere INF5210 The turbulent symbiosis between organizations and information systems 15 Lars Groth
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.











![A New Approach to Treat the RANS-LES interface in PANS [1] Lars Davidson Lars Davidson,](https://c.sambuz.com/896511/a-new-approach-to-treat-the-rans-les-interface-in-pans-1-s.webp)


![Inlet boundary conditions for two-equation hybrid LES-RANS models [2] Lars Davidson Lars](https://c.sambuz.com/952287/inlet-boundary-conditions-for-two-equation-hybrid-les-s.webp)